Abstract
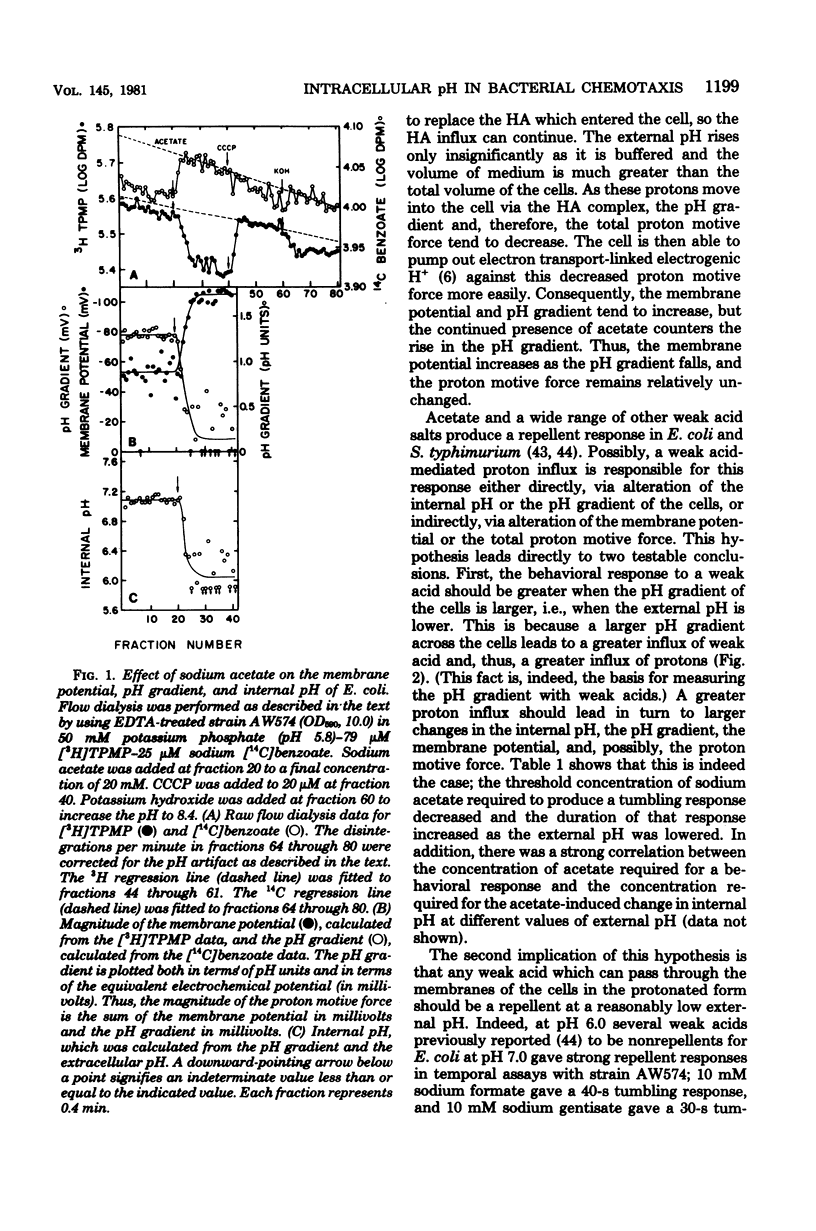
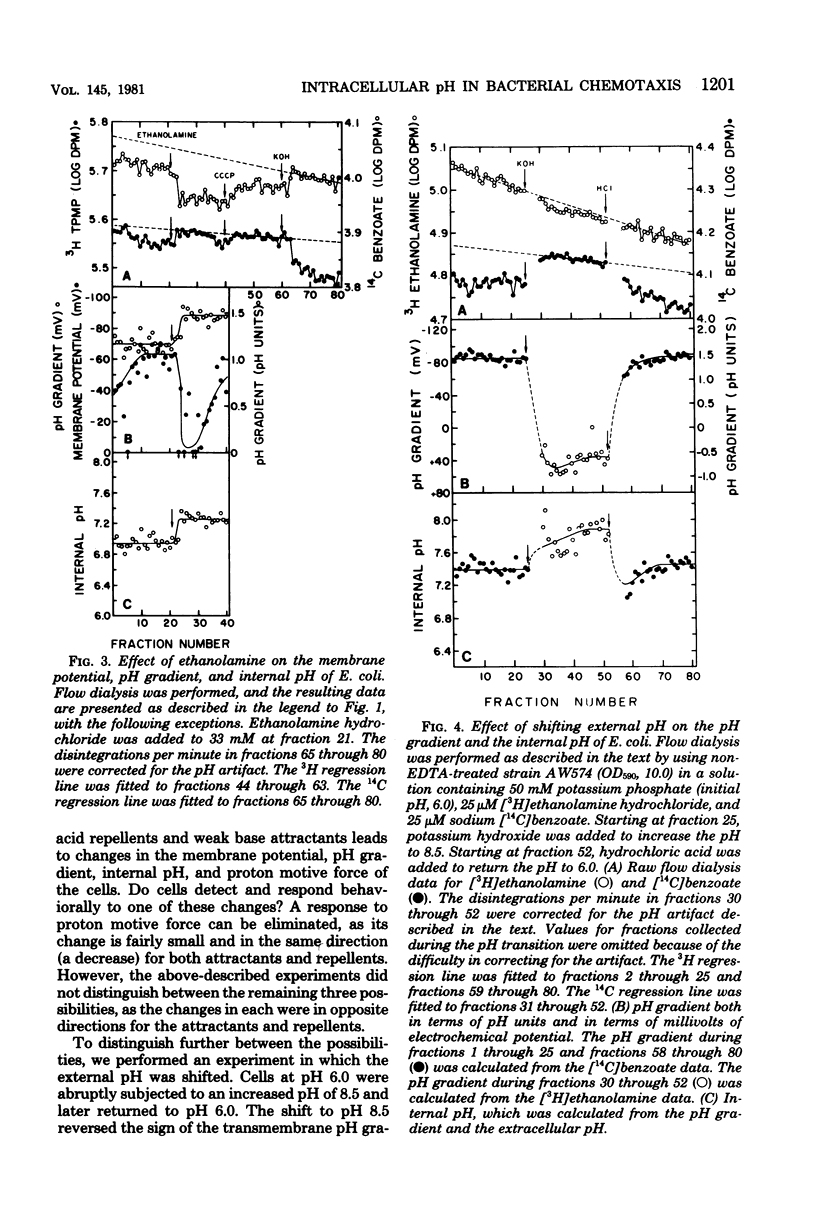
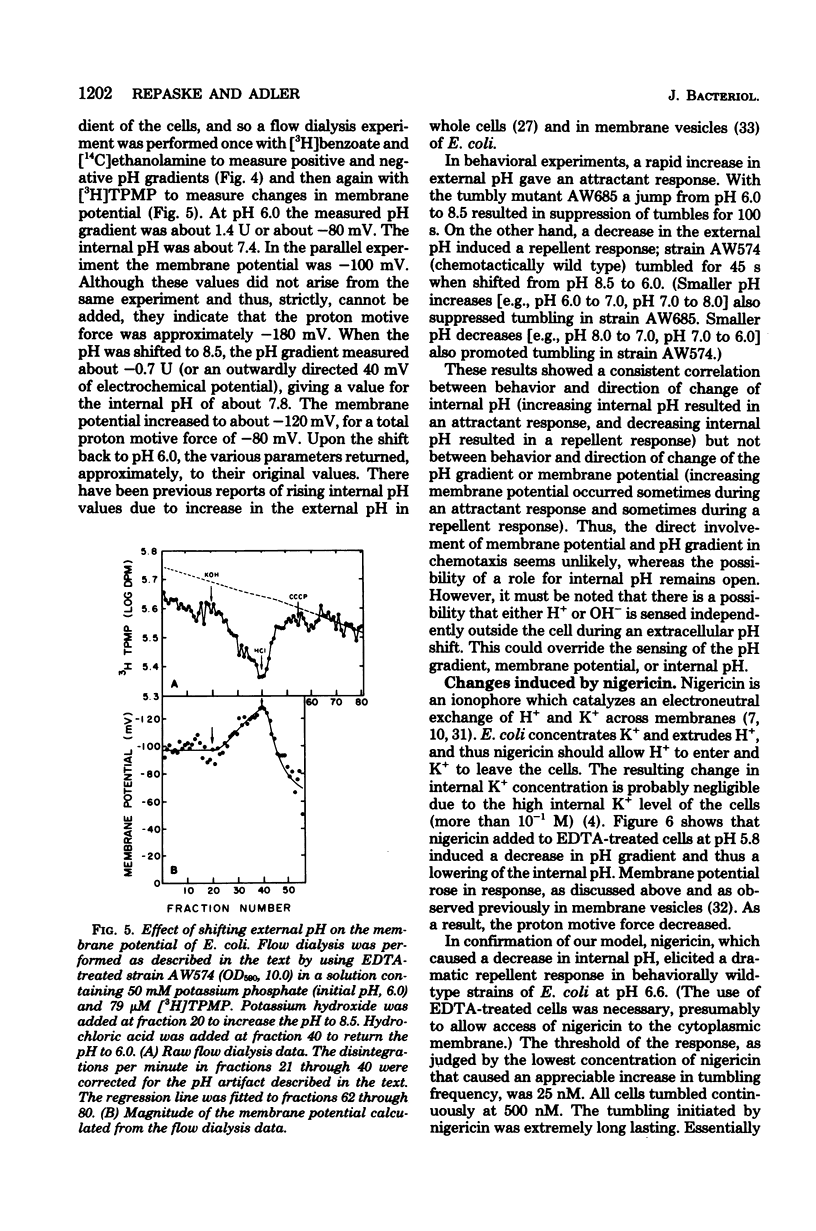
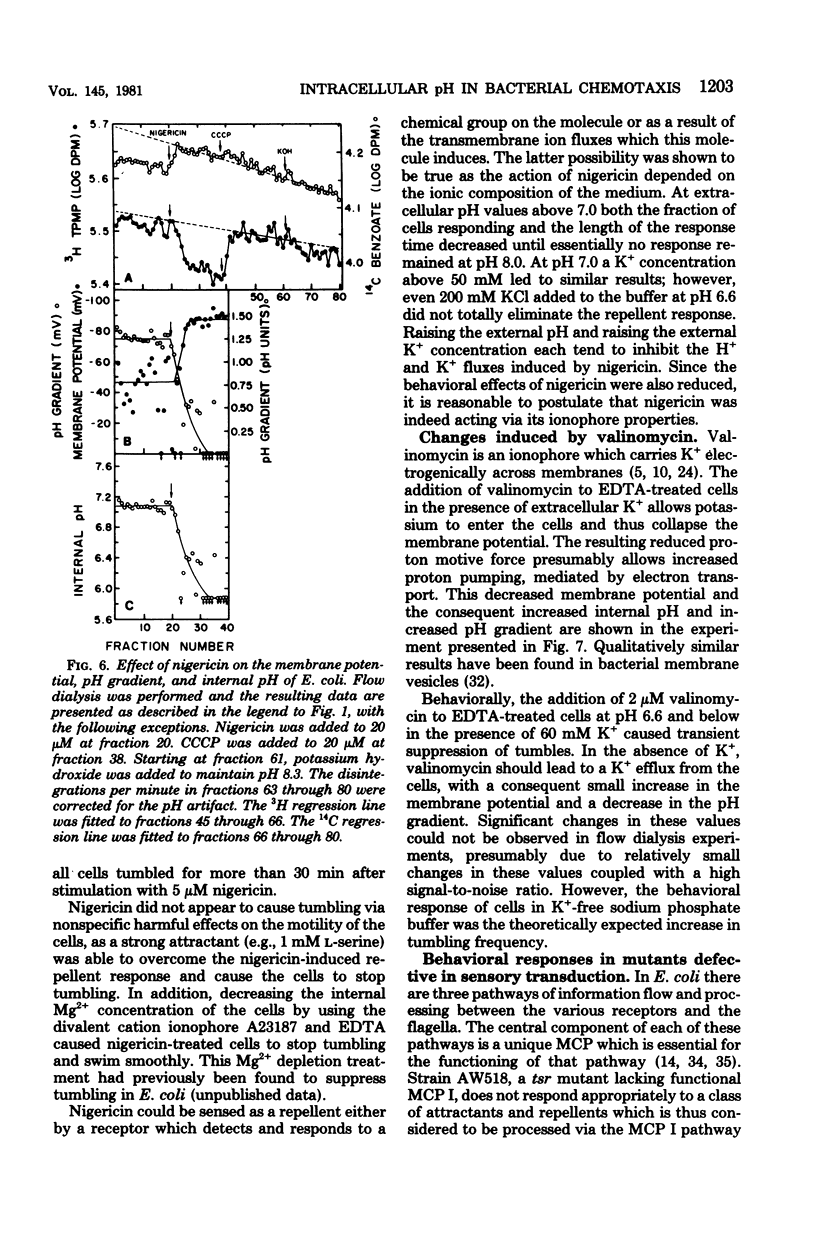
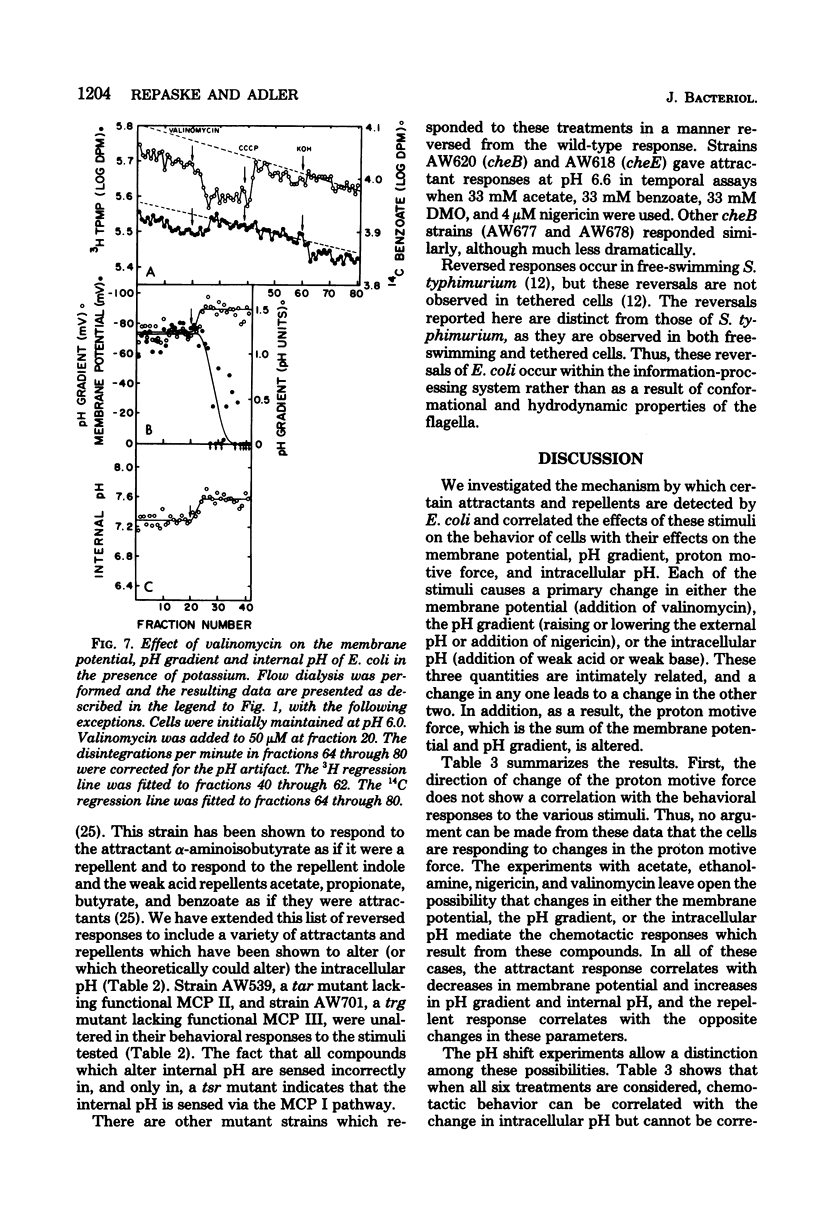
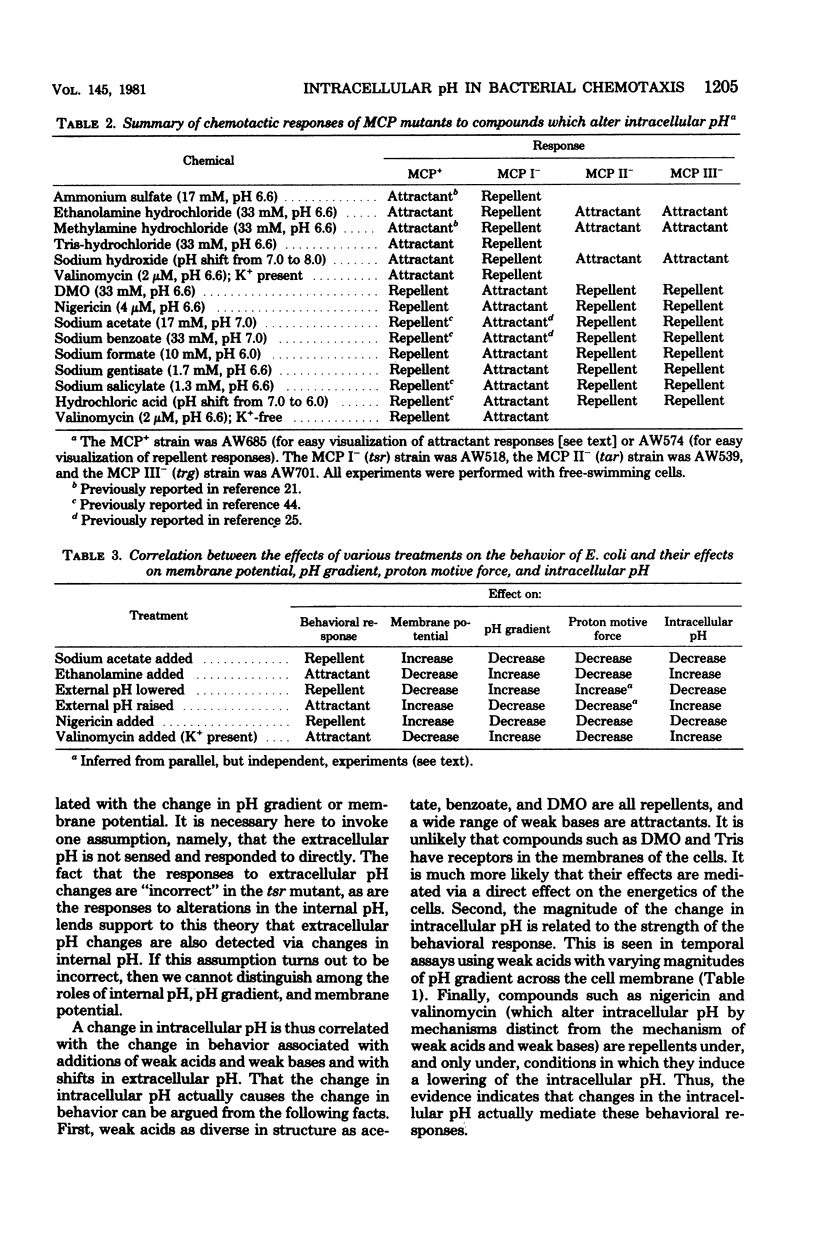
Changes in the membrane potential, pH gradient, proton motive force, and intracellular pH of Escherichia coli were followed during the chemotactic responses to a variety of potentially membrane-active compounds. Lipophilic weak acids, decreases in extracellular pH, and nigericin each caused a repellent response. Lipophilic weak bases, increases in extracellular pH, and valinomycin in the presence of K+ each caused an attractant response. Changes in membrane potential, pH gradient, and proton motive force did not correlate with the behavioral responses to these treatments, but changes in intracellular pH did correlate. Furthermore, the strength of the response to a weak acid was correlated with the magnitude of the change of the intracellular pH, and many compounds which could alter the intracellular pH were found to be chemotactically active. Apparently these attractants and repellents are not detected by specific chemoreceptors but rather are detected via the ability of cells to sense and respond to changes in intracellular pH. The pathway of sensory transduction which proceeds through methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein I was found to be involved in the response to a change in intracellular pH.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke S., Koshland D. E., Jr Membrane receptors for aspartate and serine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9695–9702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong M. H., van der Drift C., Vogels G. D. Proton-motive force and the motile behavior of Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Dec 1;111(1-2):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00446543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Altendorf K. H., Hirata H. Probing membrane transport mechanisms with inophores. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):149–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Mesibov R. E., Adler J. Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis toward specific chemicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1300–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Genetic and biochemical properties of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in serine chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1048–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1048-1060.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Crofts A. R., von Stedingk L. V. Ion transport induced by light and antibiotics IN CHROMATOPHORES FROM Rhodospirillum rubrum. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Oct 17;6(1):41–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M., DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Inversion of a behavioral response in bacterial chemotaxis: explanation at the molecular level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4150–4154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H. Tumbling chemotaxis mutants of Escherichia coli: possible gene-dependent effect of methionine starvation. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):527–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.527-534.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hinkle P. C. Studies of the beta-galactoside transporter in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. I. Symmetrical facilitated diffusion and proton gradient-coupled transport. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7657–7661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Adler J., Gargus J. J., Hogg R. W. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M. Bacterial motility and chemotaxis: the molecular biology of a behavioral system. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1978;5(4):291–341. doi: 10.3109/10409237809177145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Adler J. Chemotaxis toward amino acids in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):315–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.315-326.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Protonmotive force and bacterial sensing. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.26-32.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. B., Koshland D. E., Jr Sensory electrophysiology of bacteria: relationship of the membrane potential to motility and chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4752–4756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Development of K+-Na+ discrimination in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes by macrocyclic antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90559-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muskavitch M. A., Kort E. N., Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Attraction by repellents: an error in sensory information processing by bacterial mutants. Science. 1978 Jul 7;201(4350):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.351803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Goldman D. J. Chemotactic repellents of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 5;100(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Rottenberg H. The proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 1;63(2):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Bitensky M. W. Light-regulated enzymes of vertebrate retinal rods. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:265–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C., Harris E. J., Jagger W. S., Johnson J. H. Antibiotic-mediated transport of alkali ions across lipid barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1949–1956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Kaback H. R. The relationship between the electrochemical proton gradient and active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):854–859. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: methylation of che gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmelcman S., Adler J. Change in membrane potential during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4387–4391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Adler J. Methanol formation in vivo from methylated chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1761–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Attractants and repellents control demethylation of methylated chemotaxis proteins in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5544–5548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Mode of action of colicin Ia: effect of colicin on the Escherichia coli proton electrochemical gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2579–2583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang N., Macnab R., Koshland D. E., Jr Common mechanism for repellents and attractants in bacterial chemotaxis. Science. 1973 Jul 6;181(4094):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4094.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turin L., Warner A. Carbon dioxide reversibly abolishes ionic communication between cells of early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):56–57. doi: 10.1038/270056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Luria S. E. Reduction of membrane potential, an immediate effect of colicin K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong M. H., van der Drift C. Control of the chemotactic behavior of Bacillus subtilis cells. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jan 23;116(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00408727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


