Abstract
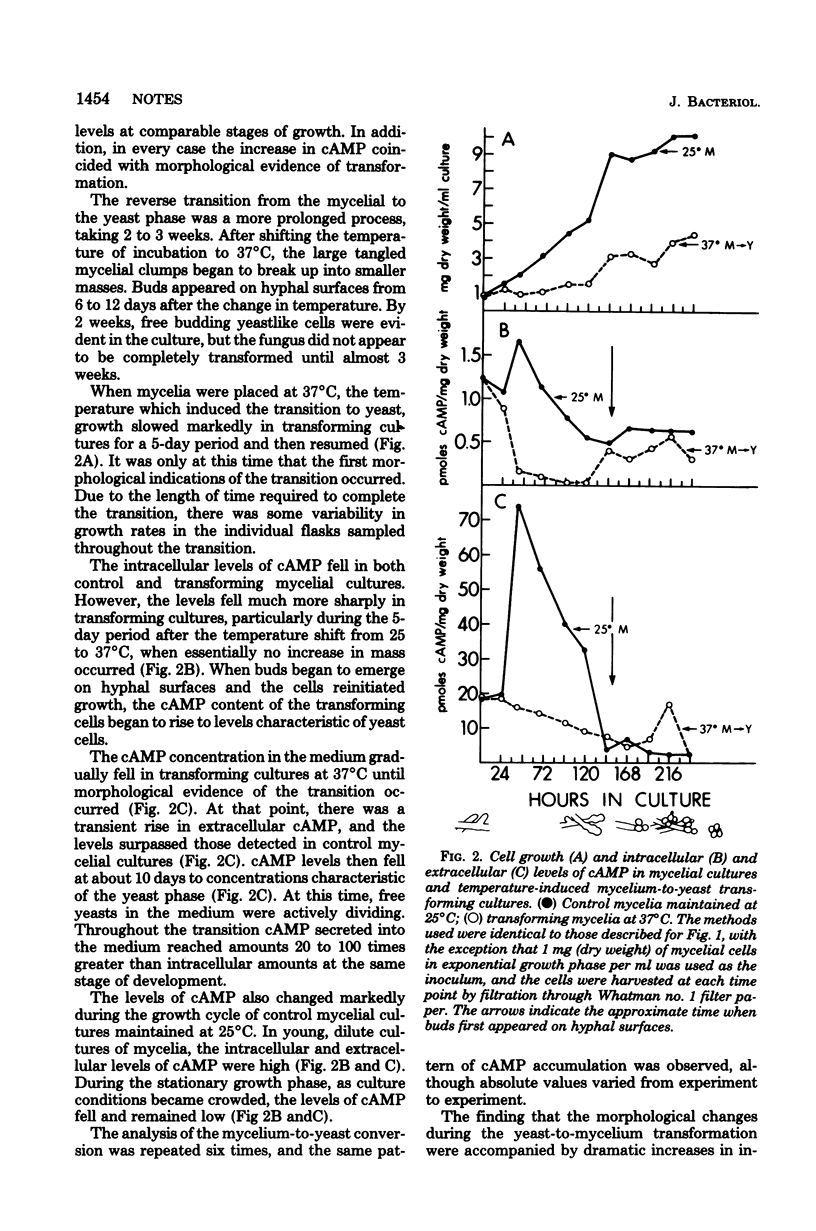
During temperature-induced transition of the dimorphic pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum from the single yeast cell form to the multicellular mycelial form, there was an increase in intracellular cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cAMP) levels as well as a striking accumulation of cAMP in the medium. cAMP levels also changed during the reverse mycelium-to-yeast transition.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheung S. S., Kobayashi G. S., Schlessinger D., Medoff G. RNA metabolism during morphogenesis in Histoplasma capsulatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):301–307. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Fromm H., Huesgen A., Wick U. Control of cell-contact sites by cyclic AMP pulses in differentiating Dictyostelium cells. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):547–549. doi: 10.1038/255547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Wick U. Intracellular oscillations and release of cyclic AMP from Dictyostelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):364–370. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP as a first messenger. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A. D., Sypherd P. S. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and morphogenesis in Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.432-438.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F. Biochemistry of Aggregation in Dictyostelium. A review. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maresca B., Jacobson E., Medoff G., Kobayashi G. Cystine reductase in the dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):987–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.987-992.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maresca B., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S. Regulation of dimorphism in the pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Nature. 1977 Mar 31;266(5601):447–448. doi: 10.1038/266447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niimi M., Niimi K., Tokunaga J., Nakayama H. Changes in cyclic nucleotide levels and dimorphic transition in Candida albicans. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):1010–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.1010-1014.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paznokas J. L., Sypherd P. S. Respiratory capacity, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and morphogenesis of Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.134-139.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERR G. H. Studies on the dimorphism of Histoplasma capsulatum. I. The roles of -SH groups and incubation temperature. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Feb;12(1):92–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90296-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



