Abstract
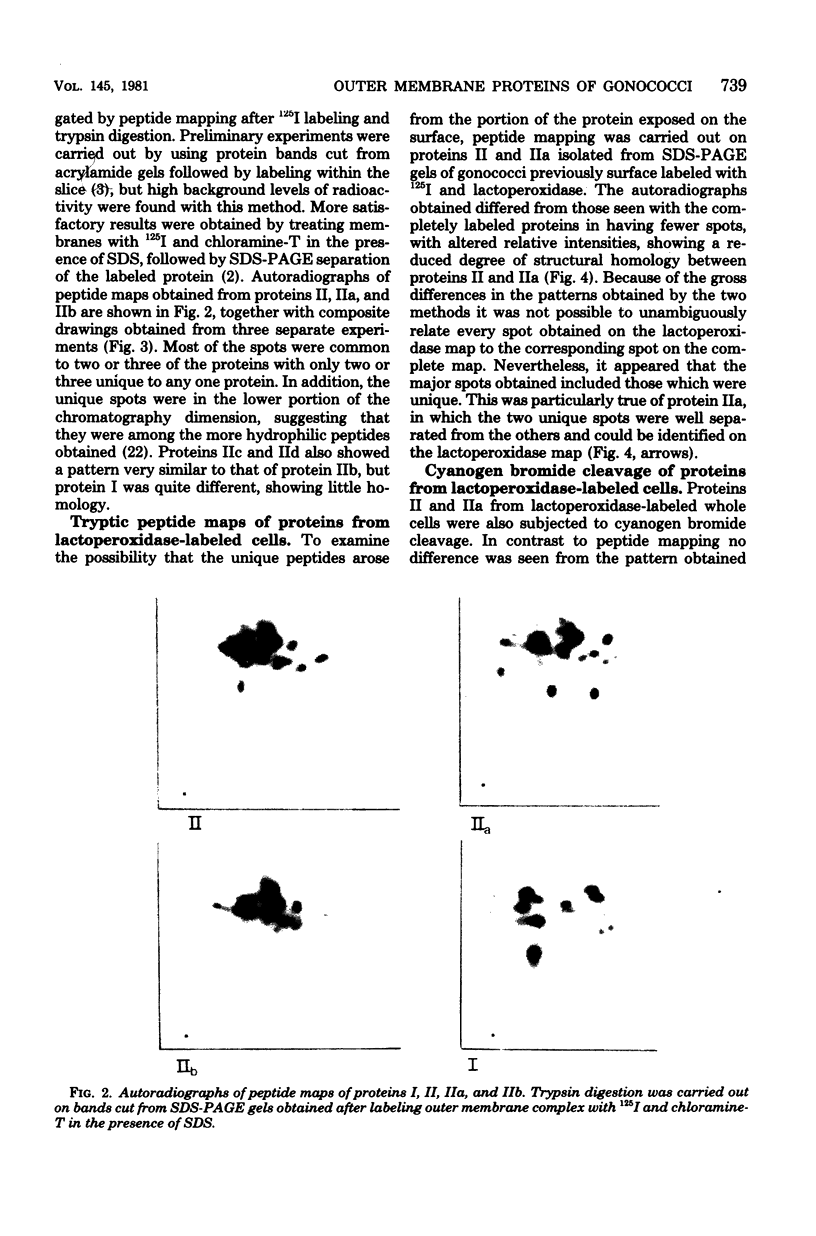
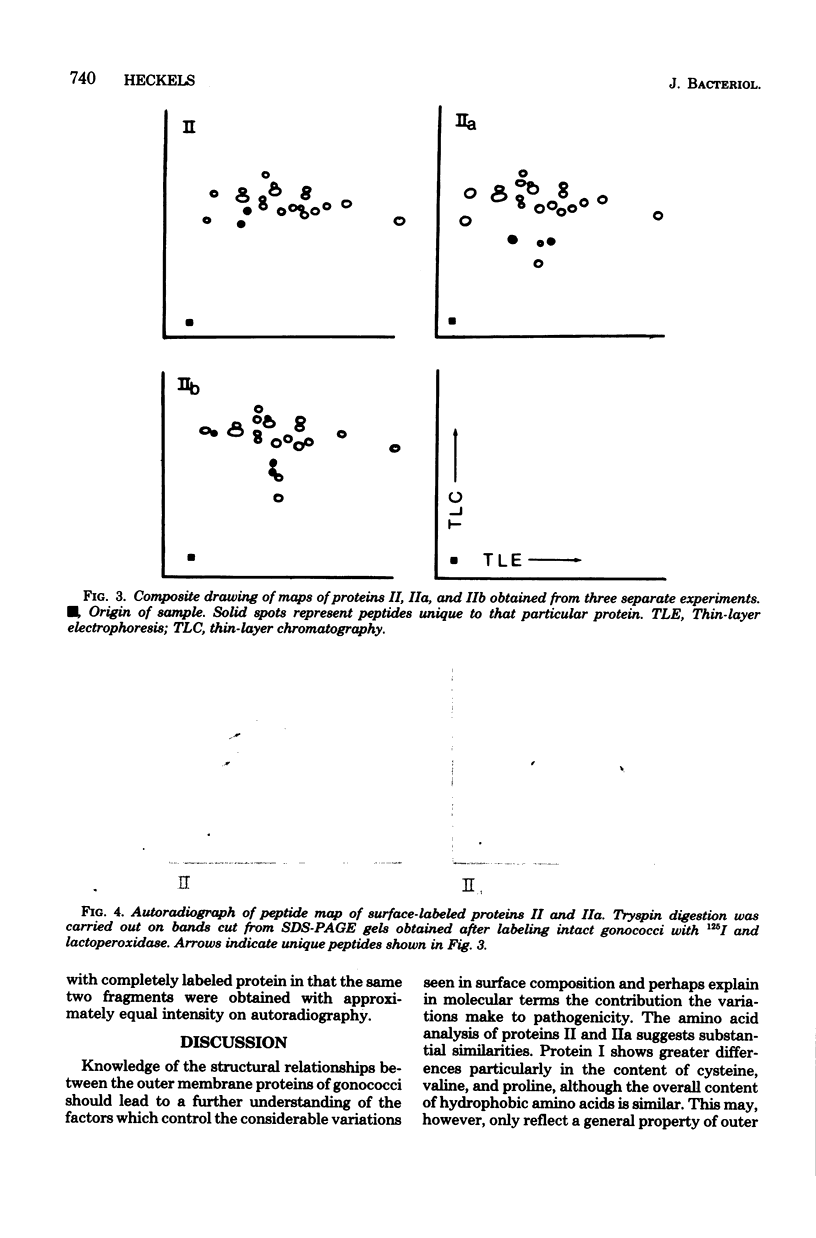
Outer membranes from opaque colonia variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9 contain a major outer membrane protein (protein I) together with one or more of a series of heat-modifiable proteins (proteins II). Proteins I. II, and IIa have been isolated by detergent extraction of outer membranes. Amino acid analysis showed proteins II and IIa to have a very similar composition. Cyanogen bromide cleavage of proteins II and IIa produced a pair of fragments with identical molecular weight and a pari which differed by an amount (0.5K) equivalent to the difference between the intact proteins. Tryptic peptide maps of 125I-labeled proteins II, IIa, and IIb showed many similarities, with only a few peptides unique to any one protein. Peptide maps of protein IIa from cells which had been surface labeled showed that the unique peptides were exposed on the surface. The heat-modifiable proteins thus appear to form a family of proteins with closely related structure probably differing in that part which is exposed on the bacterial surface.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates D. L., Perham R. N., Coggins J. R. Methods for obtaining peptide maps of proteins on a subnanomole scale. Anal Biochem. 1975 Sep;68(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90692-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel T. R., Brown F. Tryptic peptide analysis of the structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):351–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Henning U. Cell envelope and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the major ghost-membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):343–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E., Everson J. S. The isolation of a new outer membrane protein from the parent strain of Neisseria gonorrhoeae P9. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 May;106(1):179–182. doi: 10.1099/00221287-106-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: isolation of the major components of the outer membrane. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):333–341. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James J. F., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIII. Occurrence of color/opacity colonial variants in clinical cultures. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):332–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.332-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. J., Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XV. Identification of surface proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae correlated with leukocyte association. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):575–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.575-584.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambden P. R., Heckels J. E., James L. T., Watt P. J. Variations in surface protein composition associated with virulence properties in opacity types of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):305–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Crombie I. K., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Control of protein synthesis in herpesvirus-infected cells: analysis of the polypeptides induced by wild type and sixteen temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV strain 17. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):347–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movva N. R., Nakamura K., Inouye M. Amino acid sequence of the signal peptide of ompA protein, a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):27–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. N., Vincent P., Ward M. E. The preparation and properties of gonococcal pili. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Sep;102(1):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. J., Neuberger M. R., Liu T. Y. Complete amino acid analysis of proteins from a single hydrolysate. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1936–1940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. Chemical analysis of major outer membrane proteins of Neisseria meningitidis: comparison of serotypes 2 and 11. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):169–176. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.169-176.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]