Abstract
We identified primary cilia and centrosomes in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) by antibodies to acetyl-α-tubulin and capillary morphogenesis gene-1 product (CMG-1), a human homologue of the intraflagellar transport (IFT) protein IFT-71 in Chlamydomonas. CMG-1 was present in particles along primary cilia of HUVEC at interphase and around the oldest basal body/centriole at interphase and mitosis. To study the response of primary cilia and centrosomes to mechanical stimuli, we exposed cultured HUVEC to laminar shear stress (LSS). Under LSS, all primary cilia disassembled, and centrosomes were deprived of CMG-1. We conclude that the exposure to LSS ends the IFT in cultured endothelial cells.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas; IFT; HUVEC; CMG-1; PKD-1
Introduction
We identified capillary morphogenesis gene-1 product (CMG-1) as the human homologue of IFT-71, a complex B protein supporting intraflagellar transport (IFT) in Chlamydomonas (Iomini et al., 2001). The antibodies against CMG-1 allowed us to detect primary cilia in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and find conditions eliciting the disassembly of these cilia.
Factors determining assembly and disassembly of primary cilia are unknown. Primary cilia respond to chemical and physical stimuli (Pazour and Witman, 2003) and regulate tissue morphogenesis in vertebrates (Nonaka et al., 1998; Nauli et al., 2003). They are composed of 3–30-μm-long, 9+0 axonemes stemming from the oldest centrioles of interphase cells from all tissues listed in http://members.global2000.net/bowser/cilialist.html. They disassemble at mitosis (Wheatley et al., 1996).
The IFT is required for assembly and maintenance of Chlamydomonas flagella and occurs in cilia and flagella regardless of their motility or differentiation (Rosenbaum and Witman, 2002). The IFT machinery is composed of kinesin II (Kozminski et al., 1995; Piperno et al., 1996), cytoplasmic dynein (Pazour et al., 1999a), and protein complexes (Piperno and Mead, 1997), referred to as IFT complex A and IFT complex B (Cole et al., 1998).
CMG-1 could be induced in HUVEC during vasculogenesis but was not located in any cellular compartment or identified as an IFT component. CMG-1 was previously cloned from a differential display cDNA library generated from HUVEC at different stages of capillary morphogenesis in vitro (Bell et al., 2001).
Primary cilia were not detected in endothelial cells in culture (Wheatley et al., 1996) but could be expressed in these cells for the following reasons. Primary cilia were observed in human aorta by electron microscopy (Bystrevskaya et al., 1992). Furthermore, polycystin-1 (PKD-1), a membrane protein mutated in polycystic kidney disease, is concentrated in primary cilia of various cells (Barr et al., 2001) (Yoder et al., 2002), including kidney cells. Finally, mutations in PKD-1 affect the formation of capillaries in pkd-1 mice (Kim et al., 2000).
Results and discussion
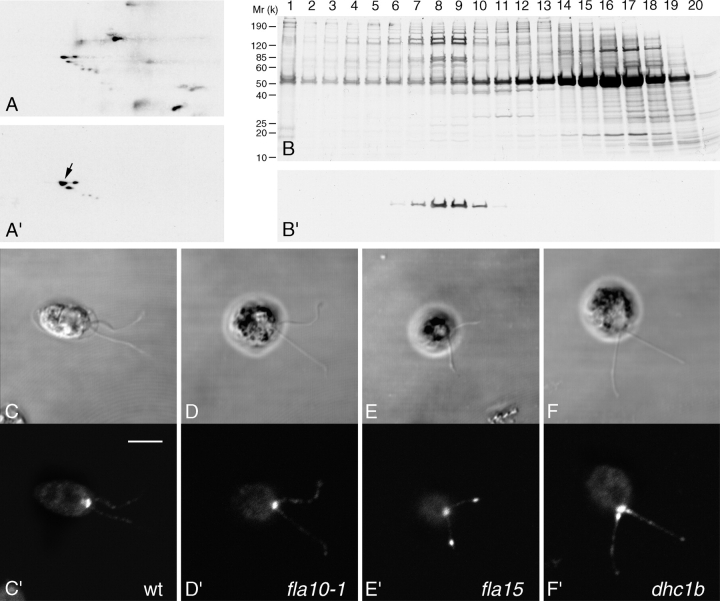
To identify a component of the IFT machinery in human, we initially analyzed the gene encoding Chlamydomonas IFT-71. We used amino acid sequences of seven peptides (sequences surrounded by lines in Fig. 1 A) from the most abundant isoform of IFT-71 (see arrow in Fig. 2 A') for the identification of a full-length cDNA clone. The IFT-71 cDNA encodes a protein with molecular weight 71,540 D and isoelectric point 8.98 in agreement with the migration of IFT-71 in two-dimensional PAGE (Piperno et al., 1998). The nucleotide sequence of IFT-71 is single copy, contains nine introns (Fig. 1 B), and likely expresses only one IFT-71 RNA, as assessed by Northern blot (not depicted). Therefore, the six isoforms of IFT-71 that were identified by a monoclonal antibody to IFT-71 (IFT-71ab) (Iomini et al., 2001; Fig. 2 A') are likely products of posttranslational modification.
Figure 1.

Chlamydomonas IFT-71 has amino acid sequence similarity with predicted proteins in other organisms. (A) IFT-71 (GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession no. AY505143) was aligned with other predicted proteins using ClustalX. Dark shading indicates amino acid sequences identical to those of IFT-71 and lighter shading indicates conserved amino acid residues. Line boxes indicate the seven peptides sequenced by mass spectrometry and used for the identification of IFT-71. Thick underlines denote long homology region-1 (LHR-1) and LHR-2. Accession nos. are AAK77221.1 for Hs-CMG1, BAC35365.1 and NP_080595.1 for Mm-CMG1, and C18H9.8 for Ce-IFT-71. (B) IFT-71 has 10 exons, thick lines, and nine introns, thin lines, covering a total of 4,602 nt of genomic DNA.
Figure 2.
IFT-71 is a subunit of a 17S protein complex found around the basal bodies and along Chlamydomonas flagella. (A) Autoradiogram of a partial two-dimensional polyacrylamide map resolving a subset of 35S-labeled polypeptides of IFT complex A and complex B. (A') Western blot of the map shown in A developed by the IFT-71ab. An arrow indicates the prominent spot of IFT-71 that was analyzed by mass spectrometry. (B and B') IFT complex A and complex B in fractions 8 and 9 were resolved from the remaining proteins of a flagellar extract. (B) Autoradiogram of 35S-labeled polypeptides contained in sucrose gradient fractions 1–20 and resolved by PAGE. Migration of molecular weight standards is indicated on the left side. Direction of sedimentation is from right to left. (B') Western blot of the electrophoretogram shown in B developed by hisIFT-71Ab. (C–F) Phase contrast micrographs. (C'–F') Immunofluorescence signals from hisIFT-71Ab applied to cells grown at 21°C. (C') Wild type. (D') fla10-1, temperature-sensitive mutant of anterograde IFT. (E' and F') Temperature-sensitive mutants of retrograde IFT. (E') fla15. (F') dhc1b. Bar, 5 μm.
To confirm the identification of IFT-71 as an IFT protein in Chlamydomonas, we prepared a polyclonal antibody to his-tagged IFT-71 (hisIFT-71Ab) and used the antibody to analyze flagellar extracts and whole cells. The sedimentation profile of IFT-71 from a 35S-labeled flagellar extract, as revealed by Western blot (Fig. 2 B'), coincided with the sedimentation peak of IFT complex A and complex B (Fig. 2 B). Immunofluorescence by hisIFT-71Ab in cells exposed at the permissive temperature of 21°C was barely detectable along flagella of wild type and fla10-1, a thermosensitive mutant of anterograde IFT (Iomini et al., 2001; Fig. 2, C' and D', respectively). In contrast, hisIFT-71Ab was concentrated in bulges along flagella of fla15 and dhc1b, temperature-sensitive mutants of retrograde IFT (Piperno et al., 1998; Pazour et al., 1999b; Fig. 2, E' and F'). In addition, hisIFT-71Ab was concentrated around the basal bodies of each of the four strains, wild type, fla10-1, fla15, and dhc1b (Fig. 2 C', D', E', and F'). Similar phenotypes of wild type, fla10-1, and fla15 were observed previously with antibodies to other subunits of the IFT machinery (Iomini et al., 2001).
IFT-71 is similar (NCBI, BLAST: 22% identical and 43% positive, E = 1e−16) to a Caenorhabditis elegans predicted protein C18H9.8, henceforth referred to as Ce-IFT-71. It is also similar (24% identical and 49% positive, E = 2e−36) to a human protein referred to as CMG-1 (Bell et al., 2001). Finally, CMG-1 is nearly identical (87.8% identical and 94.0% positive) to the mouse protein Mm-CMG-1, which we assembled from two predicted proteins, BAC35365.1 and NP_080595.1 (Fig. 1 A). These similarities extend throughout the full length of CMG-1, Ce-IFT-71, and Mm-CMG-1 proteins, and include long homology regions LHR-1 and LHR-2 (Fig. 1 A). These proteins have similar molecular weights and include several coiled-coil structures in similar positions, as predicted by SMART (not depicted).
Ce-IFT-71 is most likely a component of the IFT machinery. A regulatory element of IFT complex B genes in C. elegans (Swoboda et al., 2000) is present in a predicted intron of Ce-IFT-71 (Haycraft, C.J., personal communication). In contrast, the function and intracellular location of CMG-1 are unknown. Expression of a CMG-1–GFP chimera in HUVEC under control of an exogenous promoter failed to identify the intracellular location of CMG-1 (Bell et al., 2001).
To test the hypothesis that CMG-1 is a component of the IFT machinery, we tested whether CMG-1 is located in primary cilia. In turn, to identify primary cilia in HUVEC, we used a monoclonal antibody specific for acetyl-α-tubulin (AcTubab). Acetyl-α-tubulin is a major component of both primary cilia and centrioles (Piperno et al., 1987). Every HUVEC at interphase contained acetylated microtubules located mainly around the centrosomal region (Fig. 3 A). In addition, 5–35% of HUVEC expressed a primary cilium that was distinguished as a 4–5-μm rod containing the highest concentration of acetyl-α-tubulin (Fig. 3, A and B). HUVEC primary cilia occasionally were detectable by phase contrast (Fig. 4 B”). HUVEC expressed the highest percentage of primary cilia at passages 2–6. In contrast, they lacked cilia at passages higher than 12.
Figure 3.
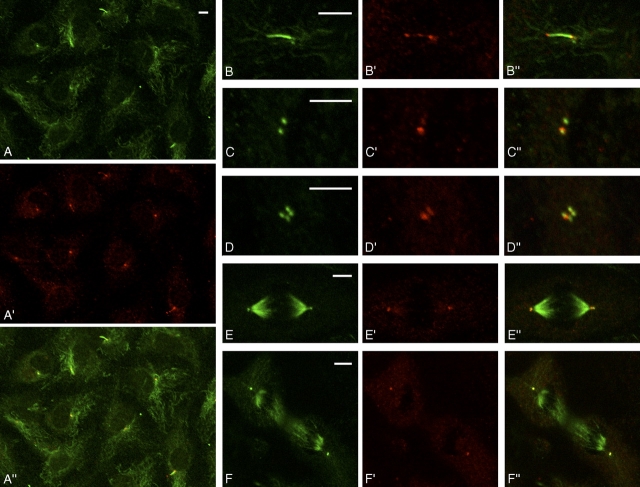
CMG-1 is concentrated around centrioles of HUVEC at interphase and mitosis and in particles located along primary cilia at interphase. (A–F) Immunofluorescence signals from AcTubab following the application to HUVEC. (A'–F') Immunofluorescence signals from hisCMG-1Ab. (A”–F”) Combined immunofluorescence signals from AcTubab and hisCMG-1Ab. Bars, 5 μm.
Figure 4.
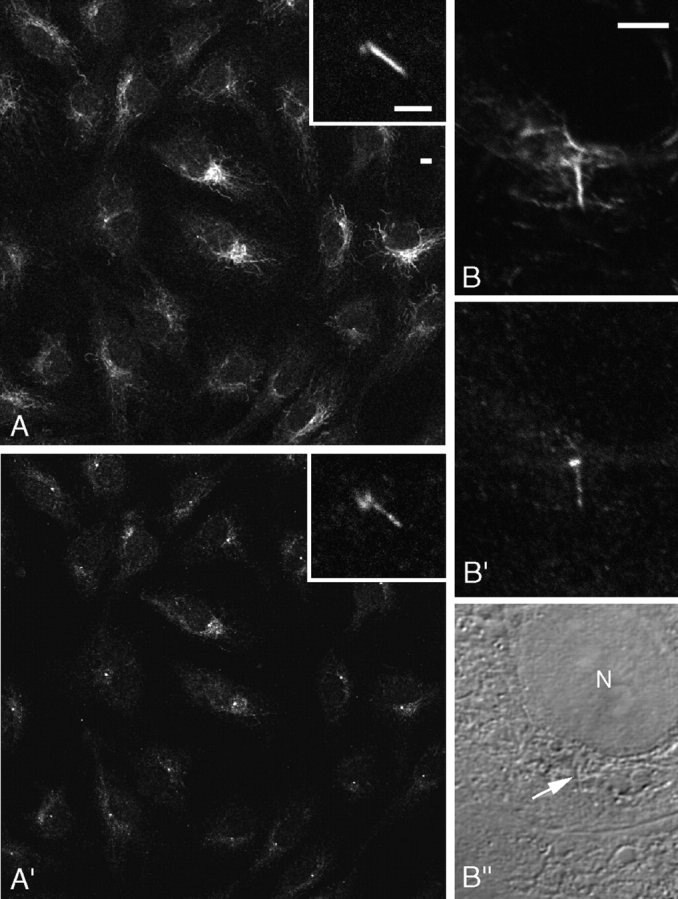
PKD-1 is concentrated around centrioles and in particles along primary cilia of HUVEC at the interphase. (A, B, and inset in A) Immunofluorescence signals from AcTubab. (A', B', and inset in A') Immunofluorescence signals from an antibody specific for the COOH terminus of PKD-1. (B”) Phase contrast micrograph corresponding to B and B'. An arrow indicates the primary cilium, and N marks the nucleus. Bars, 5 μm.
To identify the intracellular location of CMG-1, we prepared an affinity-purified polyclonal antibody against his-tagged CMG-1 (hisCMG-1Ab). hisCMG-1Ab was present along all primary cilia of interphase HUVEC (Fig. 3 A, A', and A”) and generated a dotted staining (Fig. 3, B' and B”) similarly to the IFT components along Chlamydomonas flagella (Cole et al., 1998). hisCMG-1Ab was detected around one centriole in HUVEC presumably at G1 phase (Fig. 3, B' and B”) and around two centrioles in HUVEC at S phase, when the distance between centrioles increases (Fig. 3, C' and C”) and centrioles duplicate (Fig. 3 D' and D”). hisCMG-1Ab was concentrated around both spindle poles at mitosis (Fig. 3, E', E”, F', and F”).
CMG-1, similar to IFT-71, was resolved in multiple isoforms in Western blots of proteins from HUVEC and mouse testes (unpublished data). Also it was part of 15–19S complexes from extracts of mouse testes (unpublished data).
The evidence described above confirms the presence of primary cilia in endothelial cells and supports the hypothesis that CMG-1 is a component of the IFT. The structures stained by hisCMG-1Ab matched both location and morphology of the IFT machinery components in Chlamydomonas at interphase and mitosis (Deane et al., 2001). IFT components at mitosis remain associated with the basal bodies/centrioles independently from the activity of IFT.
To support the hypothesis that primary cilia of HUVEC respond to mechanical stimuli, we identified the location of PKD-1, a protein mediating mechanosensation in primary cilia of kidney cells (Nauli et al., 2003; Praetorius et al., 2003). We found PKD-1 concentrated in the centrosomal region of all HUVEC (Fig. 4, A and A') and around both centrioles (Fig. 4, A and A', insets) by an antibody specific for the COOH terminus of the protein (Wilson et al., 1999). PKD-1 also was located in primary cilia of <10% of ciliated HUVEC, where it was found in particles along the cilia that resembled those stained by hisCMG-1Ab (Fig. 4, A and A', insets; Fig. 4, B and B'). Therefore, PKD-1 elicits a response to mechanical stimuli only in a subset of the HUVEC expressing primary cilia if it functions as mechanosensor.
To test the effects of mechanical stress on primary cilia, confluent HUVEC monolayers were subjected to laminar shear stress (LSS) in a flow chamber receiving a constant flow of medium for various times. Subsequently, HUVEC were scored for number of cilia and intracellular location of CMG-1. To ensure physiological relevance, a level of LSS of 15 dyn/cm2, similar to that generated in arterial circulation, was chosen.
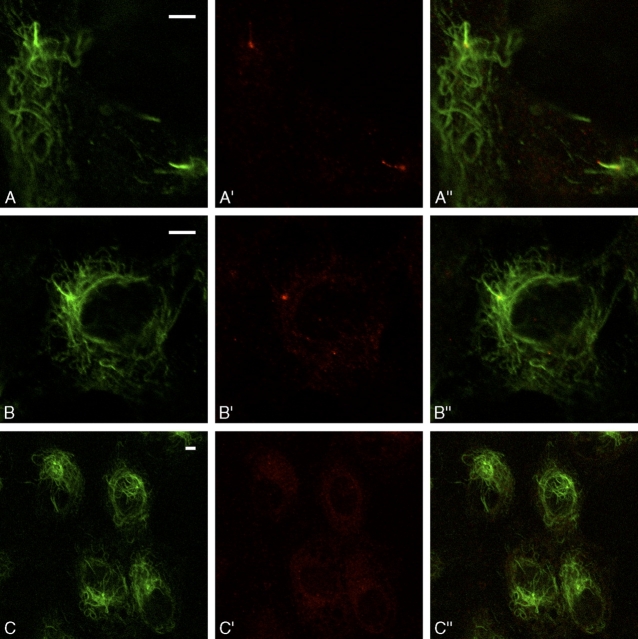
In a typical experiment, primary cilia of HUVEC under LSS were maintained for 1 h but totally disassembled in the following hour. On the other hand, CMG-1 became undetectable in the majority of primary cilia within 1 h and in the centrosomal region in the following hour (Table I). After 30-min and 1-h intervals, we detected CMG-1 along one primary cilium but not along a second cilium in HUVEC that were in the same microscopic fields (Fig. 5 A, A', and A”). After 1 h, we often observed CMG-1 located only in the centrosomal region, although the primary cilium was still present (Fig. 5 B, B', and B”). After 2 h of LSS, primary cilia were disassembled and CMG-1 was undetectable in the centrosomal region (Fig. 5 C, C', and C”). During this interval, the number and length of acetylated microtubules increased, and HUVEC oriented themselves in the direction of LSS with the centrosomal region often trailing from the leading edge of the cell (Fig. 5 C, C', and C”).
Table I. Primary cilia of HUVEC disassemble under LSS.
| Exposure time to LSS | Primary cilia identified by AcTubab | Primary cilia identified by hisCMG-1Ab | Centrosomes identified by hisCMG-1Ab |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8.0 | 7.6 | 100 |
| 0.5 h | 9.0 | 7.0 | 100 |
| 1 h | 7.3 | 2.6 | 100 |
| 2 h | 0 | 0 | 0 |
300 HUVEC were analyzed. Numbers are percentages.
Figure 5.
Under LSS, primary cilia disassemble, CMG-1 become undetectable in the centrosomal region, and HUVEC orient toward the direction of LSS. (A–C) Immunofluorescence signals from AcTubab. (A'–C') Immunofluorescence signals from hisCMG-1Ab. (A”–C”) Combined immunofluorescence signals from AcTubab and hisCMG-1Ab. (A and B) HUVEC after 1 h of LSS. (C) HUVEC after 2 h of LSS. Bars, 5 μm.
These observations suggest that HUVEC respond to LSS with the termination of IFT and the disassembly of primary cilia. They also suggest that ciliary PKD-1 in HUVEC either was undetected in the majority of primary cilia or is not required for the disassembly of primary cilia.
The disassembly of HUVEC primary cilia under LSS was similar in two aspects to the disassembly of flagella exposed at the restrictive temperature in fla, temperature-sensitive mutants of flagellar assembly in Chlamydomonas. First, components of the IFT machinery became undetectable along the axoneme within 1 h of exposure. Second, the axonemes disassembled in the following hour (Piperno and Mead, 1997; Iomini et al., 2001). On the other hand, components of the IFT machinery remained associated with the basal bodies/centrioles of the fla at the restrictive temperature, whereas CMG-1, the putative IFT component of HUVEC primary cilia, became undetectable under LSS. Therefore, HUVEC oldest centrioles did not maintain or initiate the assembly of primary cilia under LSS.
The disassembly of primary cilia of HUVEC under LSS was part of a major rearrangement of the cytoskeleton. It coincided with changes in the acetylation of microtubules and in the organization of microfilaments (Wojciak-Stothard and Ridley, 2003). It was complete and not partial, as observed for primary cilia subjected to low temperature or trypsinization (Wheatley et al., 1996) or flagella under condition of chemical or mechanical stimulation (Lefebvre and Rosenbaum, 1986).
Membrane domains in direct contact with primary cilia or centrosomes may be sites for induction of specific signals that reorganize the cytoskeleton and cause a new orientation of HUVEC. If the expression of CMG-1 is increased during capillary morphogenesis in vitro (Bell et al., 2001), primary cilia may also have an important role in vasculogenesis.
Materials and methods
Chlamydomonas strains and cell lines
Chlamydomonas strains 137 +, fla10-1, and fla15 were from our collection. dhc1b was provided by G. Pazour and G. Witman (University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA). HUVEC were from Cambrex Bio Science Walkersville, Inc. They were cultured in medium M199 (GIBCO BRL), 20% fetal calf serum, 4% human serum, 10 ng/ml human VEGF (PeproTech), 10 ng/ml human FGFb (PeproTech), 90 μg/ml heparin, 1% penicillin/streptomycin and used in passages 3–6. HUVEC were seeded at 6,000 cells/cm2 and grown for 5 d on gelatin-coated plastic slides or human fibronectin-coated glass slides.
Mass spectrometry
Coomassie-stained two-dimensional SDS-PAGE spots of IFT-71 were processed and analyzed as previously described (Nadal et al., 2003).
Cloning of IFT-71 and CMG-1
We cloned a 1,266-bp fragment of IFT-71 cDNA from Chlamydomonas by RT-PCR and used the fragment for the identification of full-length cDNA clones. We identified the partial-length cDNA clone by nucleotide sequences corresponding to six peptide sequences of the most abundant isoform of IFT-71. Peptide sequences of IFT-71 were obtained by mass spectrometry.
Total RNA was extracted from wild-type cells 30 min after deflagellation. Poly(A) RNA was purified with Oligo-kit (QIAGEN). Double-stranded cDNA was generated using Superscript Choice System Kit (Invitrogen). Degenerated primers 5′-CAGGAGGCICTSGCIGACTACAACACIGTSCTSGACAAG-3′ and 5′-CTTSAGGAACTCGTCCATCTCGAASACICCIGCISW-3′, where Y = C + T, R = A + G, W = A + T, S = G + C, and I = inosine, were designed from peptides QEALADYNTVLDK and SAGVFEMDEFL/IK, respectively, which were identified by mass spectrometry.
The cDNA fragment was used to screen a deflagellation cDNA library (Chlamydomonas genetic center, project ID 1030). Out of the nine positives clones identified by Southern blot, two were sequenced. The open reading frames in these clones encoded a protein of 641 amino acids (Fig. 1 A). The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ submission number of the cDNA sequence of IFT-71 is AY505143. The open reading frames of IFT-71 cDNA exactly matched the sequences corresponding to 10 predicted exons of IFT-71, as reported in the database of the Chlamydomonas genome available at ftp://ftp.jgi-psf.org/pub/JGI_data/Chlamy, see scaffold 246.
Following the identification of IFT-71, a BLAST search of the GenBank/DMBL/DDBJ database showed that IFT-71 cDNA is almost identical to the entry AY245434 (intraflagellar transport protein component IFT74/72) submitted by others (Qin et al., 2004). However, the sequence reported in AY245434 diverged by 10 nucleotides in the coding region from the predicted exons of IFT-71. As a consequence, the translated protein differed by 10 amino acids from the sequence that we predicted.
For Northern blot analysis, 3 μg of poly(A)+ RNA was run on an agarose gel and transferred to Gene screen Plus hybridization membrane (NEN Life Science Products) following standard methods. Probes were labeled with 32P using the random Prime-It Kit (Stratagene).
CMG-1 clone CS0DF006YJ09 was obtained from Invitrogen. The cDNA coding regions of both IFT-71 and CMG-1 were cloned into a pQE-30 bacterial expression vector using the KpnI and HindIII restriction sites at the 5′ and 3′ ends, respectively, created by PCR.
LSS
LSS was applied to HUVEC for times ranging from 30 min to 15 h using a parallel plate flow chamber set in a incubator with 5% CO2 at 37°C. A peristaltic pump and a depulsator (Nonaka et al., 2002) delivered a constant flow of medium to the chamber to obtain 15 dyn/cm2. The cross section of the flow chamber was 0.5 × 0.034 cm. Wall shear stress Tw was calculated using the equation 3yQ/2a2b (Houston et al., 1999), where y is viscosity (poise) of the medium at 37°C, Q is the volumetric flow rate (ml/s), a is the half channel height (cm), and b is the channel width (cm).
Preparation and use of antibodies
Preparation and specificity of the monoclonal antibody IFT-71ab were previously described (Iomini et al., 2001). Binding of this antibody provided a signal in Western blot but not in immunofluorescence of Chlamydomonas cells.
The two bacterial proteins hisIFT-71 and hisCMG-1 were affinity purified over an Ni-NTA agarose bead column (QIAGEN) and injected in rabbits by Covance Research Products Inc. The hisCMG-1Ab was affinity purified over hisCMG-1 (Olmsted, 1986).
Other procedures
Microscopy of Chlamydomonas and HUVEC was performed with a Leica TCS-SP (UV) confocal laser scanning microscope in an inverted configuration as previously described (Iomini et al., 2001). Images were processed by Adobe Photoshop 5.5®.
We isolated IFT complex A and complex B from the remaining proteins of the flagellar matrix and resolved all subunits of the IFT complexes as previously described (Piperno et al., 1998). Chlamydomonas culture, 35S labeling of proteins, gel electrophoresis, and Western blots were performed as previously described (Piperno et al., 1998).
Mouse testes were isolated, washed in PBS, frozen, and thin sliced. Extraction of the slices was performed with 0.3 ml/testes of 0.05 M NaCl, 4 mM MgCl, 0.001 M Hepes, pH 7.2, containing proteolysis inhibitors “Complete Mini” (Roche Diagnostics) one tablet/10 ml. The suspension was exposed to ultrasound, spun at 14,000 rpm for 10 min in a minifuge Eppendorf 5415 C at 4°C. 200 μl of the supernatant was resolved as Chlamydomonas flagellar extracts (Piperno et al., 1998).
Acknowledgments
This report is in memory of our colleague Massimo Sassaroli who died on July 6, 2003.
We thank Dr. Patricia Wilson (Mount Sinai School of Medicine) for the antibody specific for human PKD-1 and for calling our attention to the different phenotypes of pkd-1 mice. We also thank Dr. Ornella Flore (New York University School of Medicine) for her guidance in the culture of HUVEC. We are grateful to Dr. Igor Karpichev (City College of the City of New York, New York, NY) for his guidance in the cloning of the first IFT-71 cDNA fragment. We also are grateful to Dr. Jong-sun Kang (Mount Sinai School of Medicine) for her advice in every aspect of this study.
This work was supported by grant GM-44467 from the National Institutes of Health.
W. Mo's present address is Analytical Biochemistry, Drug Discovery, Biogen Idec, Inc., 12 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142.
Abbreviations used in this paper: CMG-1, capillary morphogenesis gene-1 product; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; IFT, intraflagellar transport; LSS, laminar shear stress.
References
- Barr, M.M., J. DeModena, D. Braun, C.Q. Nguyen, D.H. Hall, and P.W. Sternberg. 2001. The Caenorhabditis elegans autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene homologs lov-1 and pkd-2 act in the same pathway. Curr. Biol. 11:1341–1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell, S.E., A. Mavila, R. Salazar, K.J. Bayless, S. Kanagala, S.A. Maxwell, and G.E. Davis. 2001. Differential gene expression during capillary morphogenesis in 3D collagen matrices: regulated expression of genes involved in basement membrane matrix assembly, cell cycle progression, cellular differentiation and G-protein signaling. J. Cell Sci. 114:2755–2773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystrevskaya, V.B., V.V. Lichkun, A.V. Krushinsky, and V.N. Smirnov. 1992. Centriole modification in human aortic endothelial cells. J. Struct. Biol. 109:1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole, D.G., D.R. Diener, A.L. Himelblau, P.L. Beech, J.C. Fuster, and J.L. Rosenbaum. 1998. Chlamydomonas kinesin II–dependent intraflagellar transport (IFT): IFT particles contain proteins required for ciliary assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans sensory neurons. J. Cell Biol. 141:993–1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane, J.A., D.G. Cole, E.S. Seeley, D.R. Diener, and J.L. Rosenbaum. 2001. Localization of intraflagellar transport protein IFT52 identifies basal body transitional fibers as the docking site for IFT particles. Curr. Biol. 11:1586–1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston, P., M.C. Dickson, V. Ludbrook, B. White, J.L. Schwachtgen, J.H. McVey, N. Mackman, J.M. Reese, D.G. Gorman, C. Campbell, and M. Braddock. 1999. Fluid shear stress induction of the tissue factor promoter in vitro and in vivo is mediated by Egr-1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19:281–289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iomini, C., V. Babaev-Khaimov, M. Sassaroli, and G. Piperno. 2001. Protein particles in Chlamydomonas flagella undergo a transport cycle consisting of four phases. J. Cell Biol. 153:13–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K., I. Drummond, O. Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya, K. Klinger, and M.A. Arnaout. 2000. Polycystin 1 is required for the structural integrity of blood vessels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 97:1731–1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozminski, G.K., P.L. Beech, and J.L. Rosenbaum. 1995. The Chlamydomonas kinesin-like protein Fla10 is involved in motility associated with the flagellar membrane. J. Cell Biol. 131:1517–1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, P.A., and J.L. Rosenbaum. 1986. Regulation of the synthesis and assembly of ciliary and flagellar proteins during regeneration. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 2:517–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal, M.S., A. Ozaita, Y. Amarillo, E. Vega-Saenz de Miera, Y. Ma, W. Mo, E.M. Goldberg, Y. Misumi, Y. Ikehara, T.A. Neubert, and B. Rudy. 2003. The CD26-related dipeptidyl aminopeptidase-like protein DPPX is a critical component of neuronal A-type K+ channels. Neuron. 37:449–461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauli, S.M., F.J. Alenghat, Y. Luo, E. Williams, P. Vassilev, X. Li, A.E. Elia, W. Lu, E.M. Brown, S.J. Quinn, et al. 2003. Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nat. Genet. 33:129–137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, S., Y. Tanaka, Y. Okada, S. Takeda, A. Harada, Y. Kanai, M. Kido, and N. Hirokawa. 1998. Randomization of left-right asymmetry due to loss of nodal cilia generating leftward flow of extraembryonic fluid in mice lacking KIF3B motor protein. Cell. 95:829–837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, S., H. Shiratori, Y. Saijoh, and H. Hamada. 2002. Determination of left-right patterning of the mouse embryo by artificial nodal flow. Nature. 418:96–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted, J.B. 1986. Analysis of cytoskeletal structures using blot-purified monospecific antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 134:467–472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour, G.J., and G.B. Witman. 2003. The vertebrate primary cilium is a sensory organelle. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15:105–110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour, G.J., B.L. Dickert, and G.B. Witman. 1999. a. The DHC1b (DHC2) isoform of cytoplasmic dynein is required for flagellar assembly. J. Cell Biol. 144:473–481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazour, G.J., B.L. Dickert, and G.B. Witman. 1999. b. The DHC1B (DHC2) isoform of cytoplasmic dynein is necessary for flagellar maintenance as well as flagellar assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell. 10:369a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, G., and K. Mead. 1997. Transport of a novel complex in the cytoplasmic matrix of Chlamydomonas flagella. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:4457–4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, G., M. LeDizet, and X.J. Chang. 1987. Microtubules containing acetylated α-tubulin in mammalian cells in culture. J. Cell Biol. 104:289–302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, G., K. Mead, and S. Henderson. 1996. Inner dynein arms but not outer dynein arms require the activity of kinesin homologue protein KHP1FLA 10 to reach the distal part of flagella in Chlamydomonas. J. Cell Biol. 133:371–379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, G., E. Siuda, S. Henderson, M. Segil, H. Vaananen, and M. Sassaroli. 1998. Distinct mutants of retrograde intraflagellar transport (IFT) share similar morphological and molecular defects. J. Cell Biol. 143:1591–1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praetorius, H.A., J. Frokiaer, S. Nielsen, and K.R. Spring. 2003. Bending the primary cilium opens Ca2+-sensitive intermediate-conductance K+ channels in MDCK cells. J. Membr. Biol. 191:193–200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H., D.R. Diener, S. Geimer, D.G. Cole, and J.L. Rosenbaum. 2004. Intraflagellar transport (IFT) cargo: IFT transports flagellar precursors to the tip and turnover products to the cell body. J. Cell Biol. 164:255–266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum, J.L., and G.B. Witman. 2002. Intraflagellar transport. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:813–825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swoboda, P., H.T. Adler, and J.H. Thomas. 2000. The RFX-type transcription factor DAF-19 regulates sensory neuron cilium formation in C. elegans. Mol. Cell. 5:411–421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley, D.N., A.M. Wang, and G.E. Strugnell. 1996. Expression of primary cilia in mammalian cells. Cell Biol. Int. 20:73–81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, P.D., L. Geng, X. Li, and C.R. Burrow. 1999. The PKD1 gene product, “polycystin-1,” is a tyrosine-phosphorylated protein that colocalizes with alpha2beta1-integrin in focal clusters in adherent renal epithelia. Lab. Invest. 79:1311–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojciak-Stothard, B., and A.J. Ridley. 2003. Shear stress–induced endothelial cell polarization is mediated by Rho and Rac but not Cdc42 or PI 3-kinases. J. Cell Biol. 161:429–439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder, B.K., X. Hou, and L.M. Guay-Woodford. 2002. The polycystic kidney disease proteins, polycystin-1, polycystin-2, polaris, and cystin, are co-localized in renal cilia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 13:2508–2516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]