Abstract
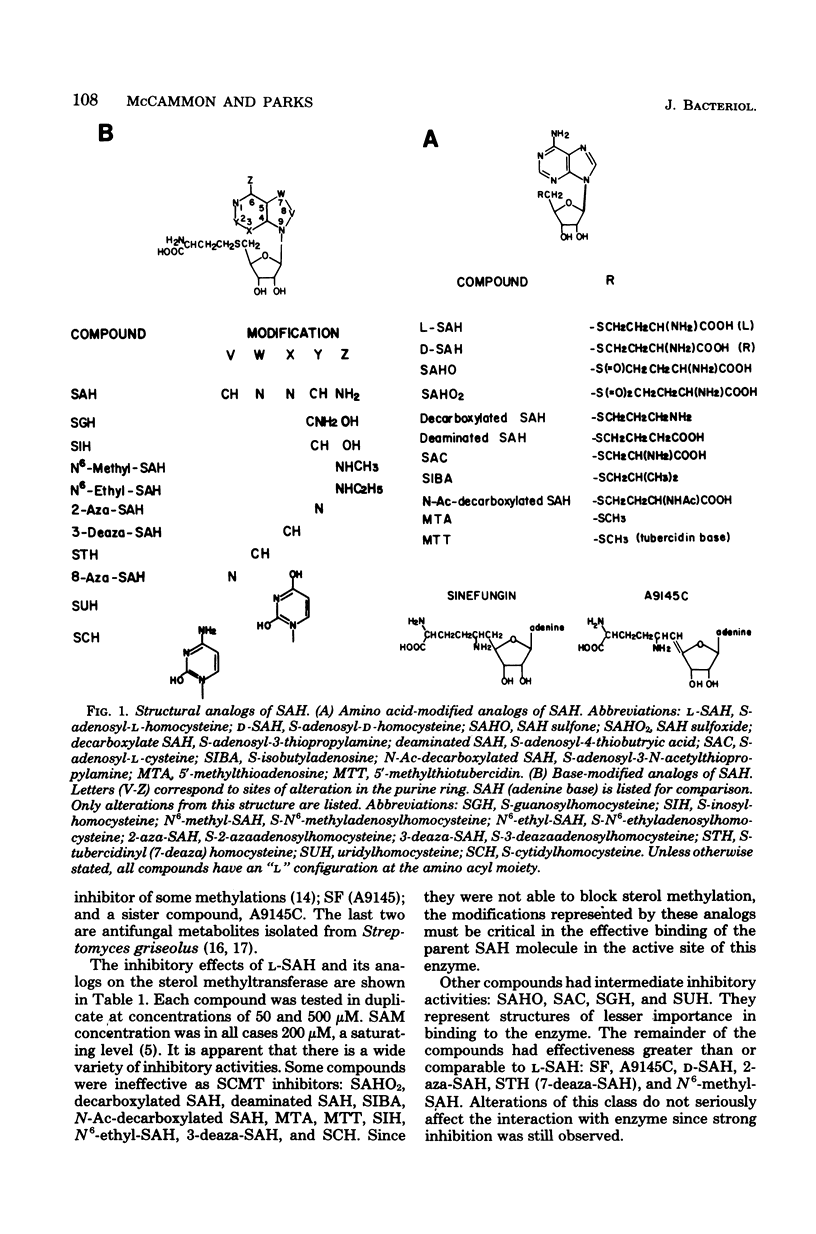
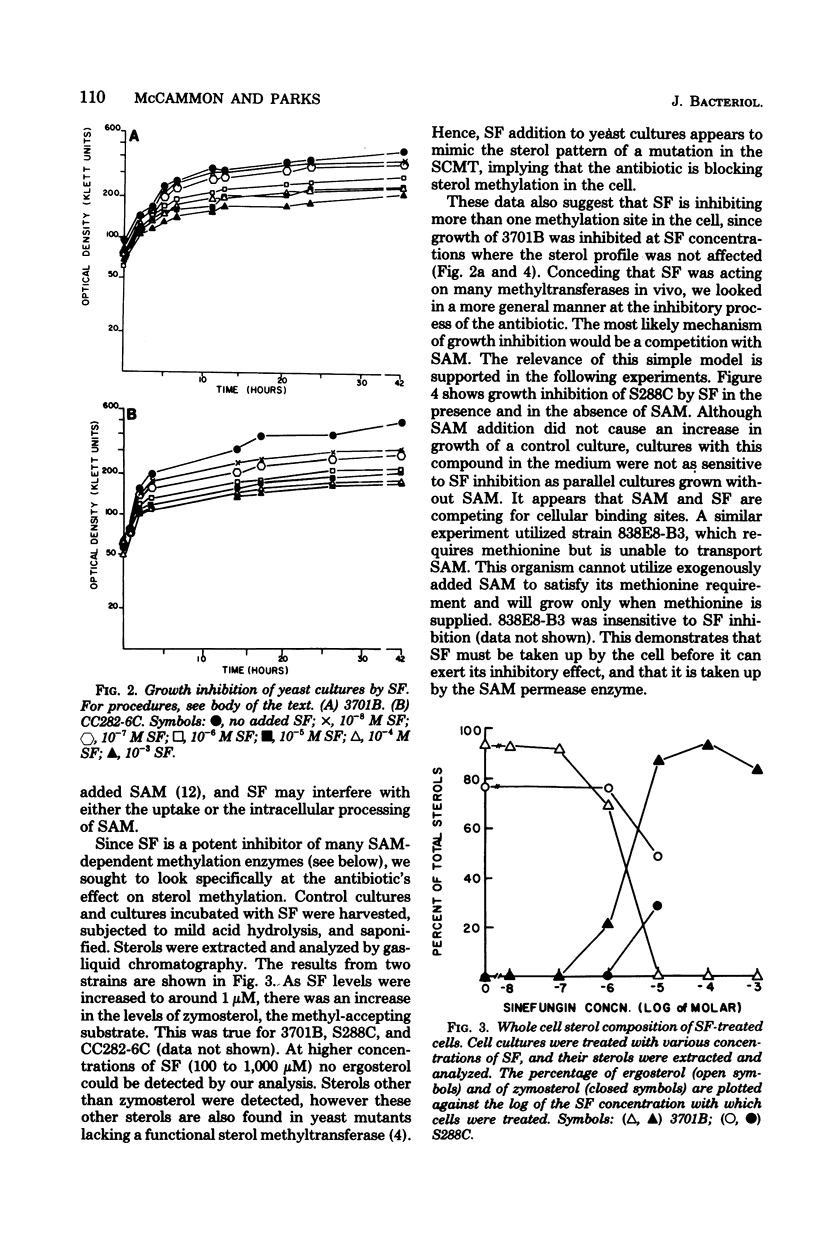
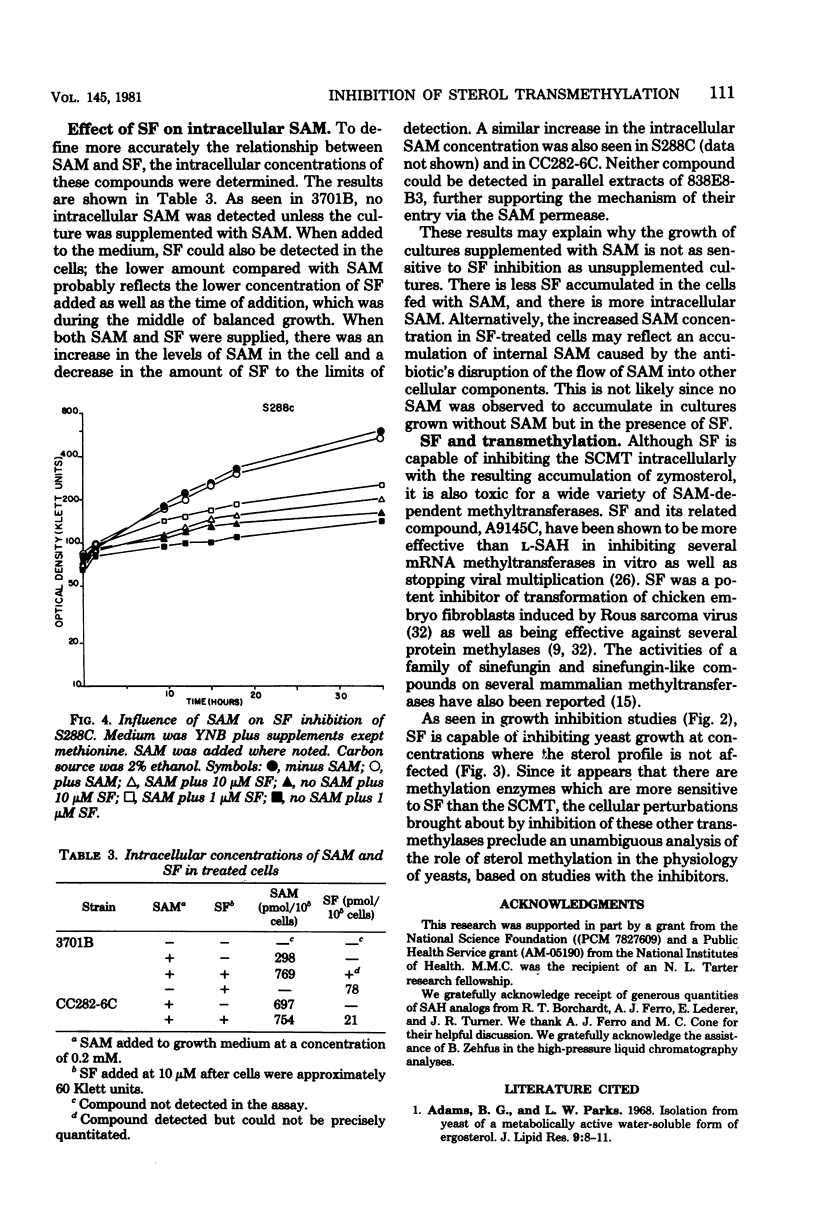
Structural analogs of S-adenosylhomocysteine were tested in vitro for inhibition of the yeast S-adenosylmethionine:delta 24-sterol-C-methyltransferase enzyme. A wide inhibitory range by these compounds was observed, suggesting which structural features of the parent compound are important for binding to the enzyme. No analog tested had inhibitory activity specific only for this enzyme. The most active compound was sinefungin, a metabolite of Streptomyces griseolus, which was also able to inhibit growth of yeast cultures. Sterol extracts of cells grown in the presence of sinefungin revealed a dramatic increase in the levels of zymosterol, the sterol substrate in the transmethylation under study, and a concomitant decrease in the levels of ergosterol. Evidence is presented that sinefungin is transported inside the cell by the same permease as S-adenosylmethionine. We conclude that sinefungin is blocking the in vivo methylation of sterols in yeast. The implications of this finding are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B. G., Parks L. W. Isolation from yeast of a metabolically active water-soluble form of ergosterol. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):8–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Hays P. R., Parks L. W. Homoazasterol-mediated inhibition of yeast sterol biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):730–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.730-734.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Miller L., Parks L. W. Enzymatic analysis of C27 sterol-accumulating yeast strains. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):1012–1013. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.1012-1013.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Parks L. W. Yeast sterol esters and their relationship to the growth of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):606–612. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.606-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. R., Abbott B. J. Incorporation of 14C-labeled compounds into sinefungin (A9145), a nucleoside antifungal antibiotic. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Mar;31(3):185–191. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. T., Eiden L. E., Wu B., Rutledge C. O. Sinefungin, a potent inhibitor or S-adenosylmethionine: protein O-methyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):919–924. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91866-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. T. S-Adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent macromolecule methyltransferases: potential targets for the design of chemotherapeutic agents. J Med Chem. 1980 Apr;23(4):347–357. doi: 10.1021/jm00178a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottema C. K., Parks L. W. Delta14-sterol reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 22;531(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherest H., Surdin-Kerjan Y. S-adenosyl methionine requiring mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidences for the existence of two methionine adenosyl transferases. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 11;163(2):153–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00267406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Barchas J. Inhibition of transmethylations of biogenic amines by S-adenosylhomocysteine. Enhancement of transmethylation by adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3175–3181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Nagarajan R. Inhibition of methyltransferases by some new analogs of S-adenosylhomocysteine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(15):1981–1983. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordee R. S., Butler T. F. A9145, a new adenine-containing antifungal antibiotic. II. Biological activity. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Aug;26(8):466–470. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil R. L., Hoehn M. M. A9145, a new adenine-containing antifungal antibiotic. I. Discovery and isolation. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1973 Aug;26(8):463–465. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.26.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildesheim J., Hildesheim R., Blanchard P., Farrugia G., Michelot R. Studies on synthetic inhibitors of t-RNA methyl transferases: analogs of S-adenosyl homocysteine. Biochimie. 1973 May;55(5):541–546. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80414-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal W. D., Parks L. W. Sterol 24(28) methylene reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1375–1378. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1375-1378.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks L. W., Anding C., Ourisson G. Sterol transmethylation during aerobic adaptation of yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):451–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks L. W. Metabolism of sterols in yeast. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1978;6(4):301–341. doi: 10.3109/10408417809090625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce A. M., Unrau A. M., Oehlschlager A. C., Woods R. A. Azasterol inhibitors in yeast. Inhibition of the delta 24-sterol methyltransferase and the 24-methylene sterol delta 24(28)-reductase in sterol mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Biochem. 1979 Mar;57(3):201–208. doi: 10.1139/o79-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh C. S., Borchardt R. T., Stone H. O. Inhibition of Newcastle disease virion messenger RNA (guanine-7-)-methyltransferase by analogues of S-adenosylhomocysteine. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3928–3932. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Géro M., Lawrence F., Farrugia G., Berneman A., Blanchard P., Vigier P., Lederer E. Inhibition of virus-induced cell transformation by synthetic analogues of S-adenosyl homocysteine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1242–1249. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence K. D. Mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae preventing uptake of S-adenosylmethionine. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.325-330.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. D., Parks L. W. The effect of altered sterol composition on cytochrome oxidase and S-adenosylmethionine: delta 24 sterol methyltransferase enzymes of yeast mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1207–1213. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90825-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vedel M., Lawrence F., Robert-Gero M., Lederer E. The antifungal antibiotic sinefungin as a very active inhibitor of methyltransferases and of the transformation of chick embryo fibroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):371–376. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappia V., Zydek-Cwick R., Schlenk F. The specificity of S-adenosylmethionine derivatives in methyl transfer reactions. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4499–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



