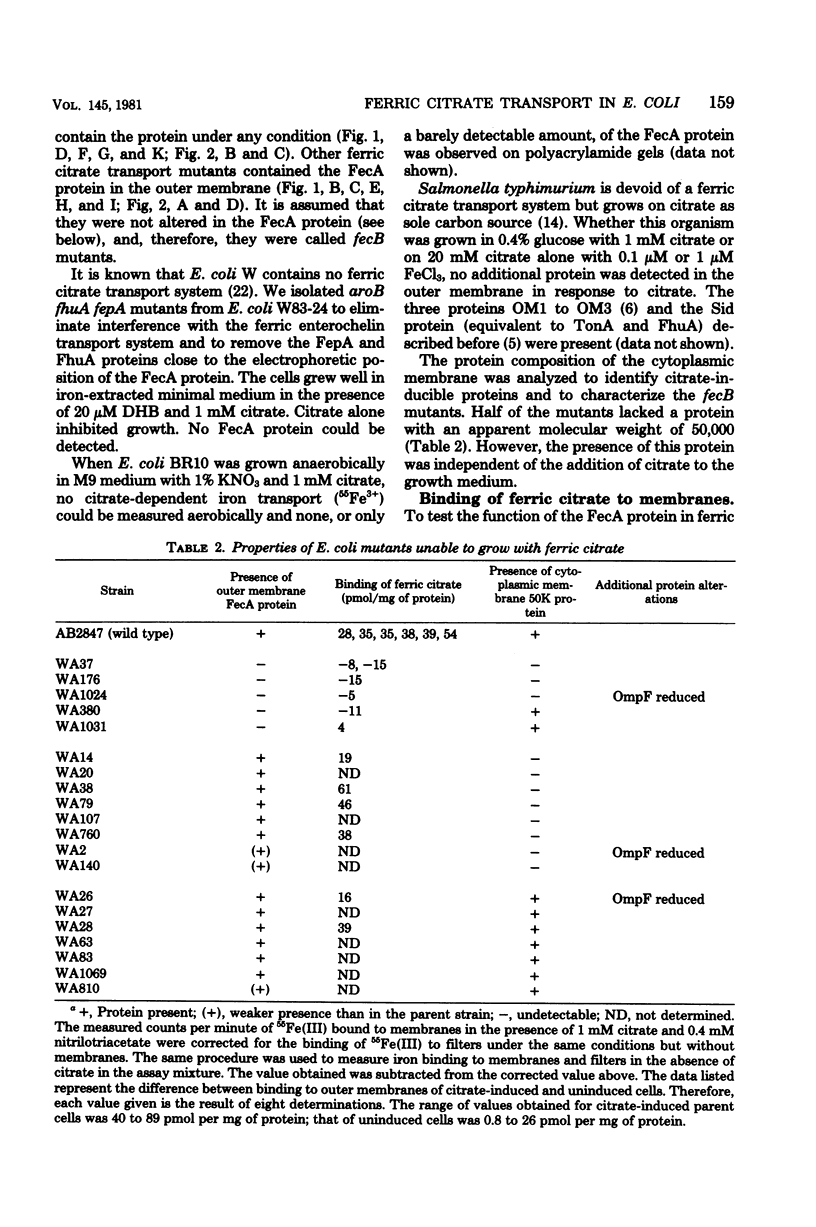
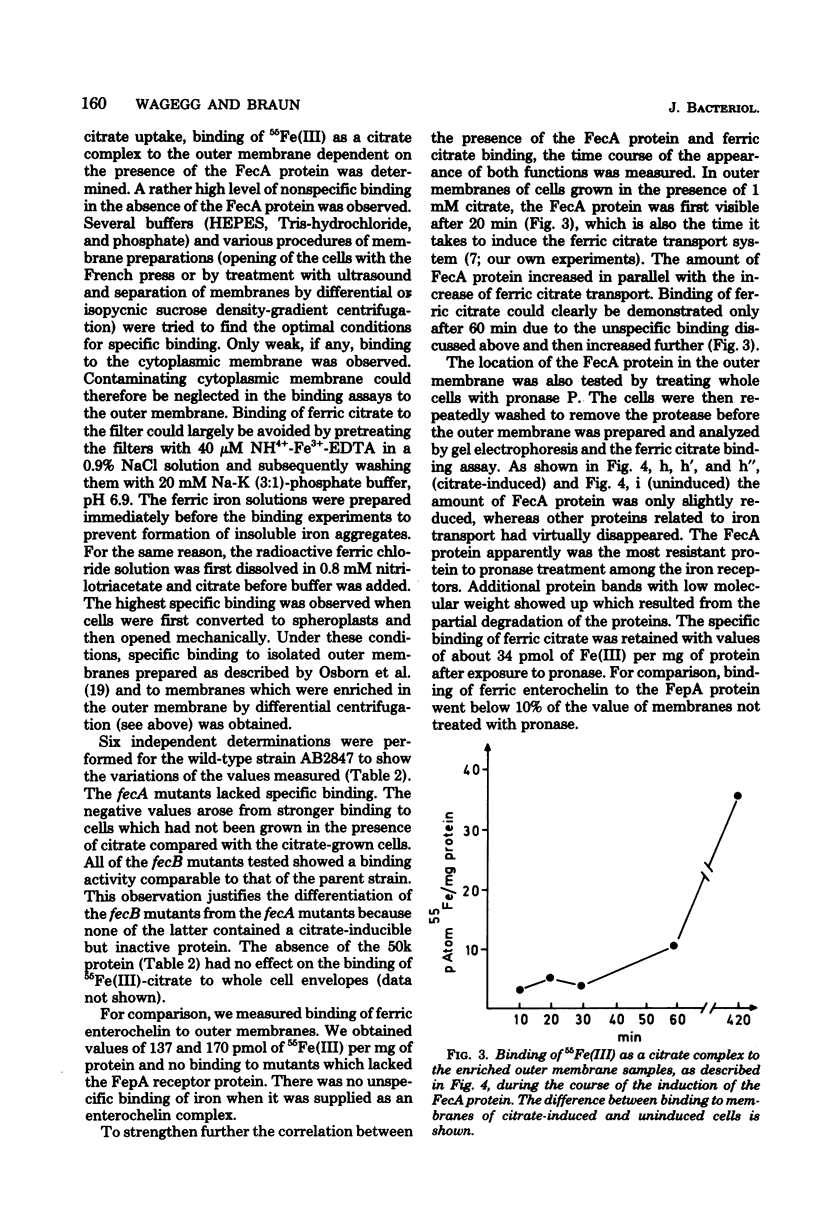
Abstract
Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 AB2847 and of E. coli K-12 AN92 were isolated which were unable to grow on ferric citrate as the sole iron source. Of 22 mutants, 6 lacked an outer membrane protein, designated FecA protein, which was expressed by growing cells in the presence of 1 mM citrate. Outer membranes showed an enhanced binding of radioactive iron, supplied as a citrate complex, depending on the amount of FecA protein. The FecA protein was the most resistant of the proteins involved in ferric irion iron translocation across the outer membrane (FhuA = TonA, FepA, Cir, or 83K proteins) to the action of pronase P. It is also shown that previously isolated fec mutants (G. C. Woodrow et al., J. Bacteriol. 133:1524-1526, 1978) which are cotransducible with argF all lack the FecA protein. They were termed fecA to distinguish them from the other ferric citrate transport mutants, now designated fecB, which mapped in the same gene region at 7 min but were not cotransducible with ArgF. E. coli W83-24 and Salmonella typhimurium, which are devoid of a citrate-dependent iron transport system, lacked the FecA protein. It is proposed that the FecA protein participates in the transport of ferric citrate.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Hartmann A. Functional organization of the outer membrane of escherichia coli: phage and colicin receptors as components of iron uptake systems. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(1):37–58. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Hantke K., Stauder W. Identification of the sid outer membrane receptor protein in Salmonella typhimurium SL1027. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Oct 20;155(2):227–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00393164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst J. F., Bennett R. L., Rothfield L. I. Constitutive expression of the iron-enterochelin and ferrichrome uptake systems in a mutant strain of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):928–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.928-934.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. Relationship between the tonB locus and iron transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.704-712.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. The inducible citrate-dependent iron transport system in Escherichia coli K12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 30;330(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Braun V. Iron transport in Escherichia coli K-12. 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate-promoted iron uptake. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Sep 28;114(3):231–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00446867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Hantke K., Braun V. Iron transport of Escherichia coli K-12: involvement of the colicin B receptor and of a citrate-inducible protein. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1370–1375. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1370-1375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K., Braun V. Membrane receptor dependent iron transport in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 1;49(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Heller K., Coulton J. W., Braun V. Genetic control of hydroxamate-mediated iron uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.256-264.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Cameron M. Citrate transport in Salmonella typhimurium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):270–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Nakae T. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;20:163–250. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyer J. L., McCay P. B. Reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide oxidase-catalyzed alterations of membrane phospholipids. IV. Dependence on Fe3+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):263–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow G. C., Langman L., Young I. G., Gibson F. Mutations affecting the citrate-dependent iron uptake system in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1524–1526. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1524-1526.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]