Abstract
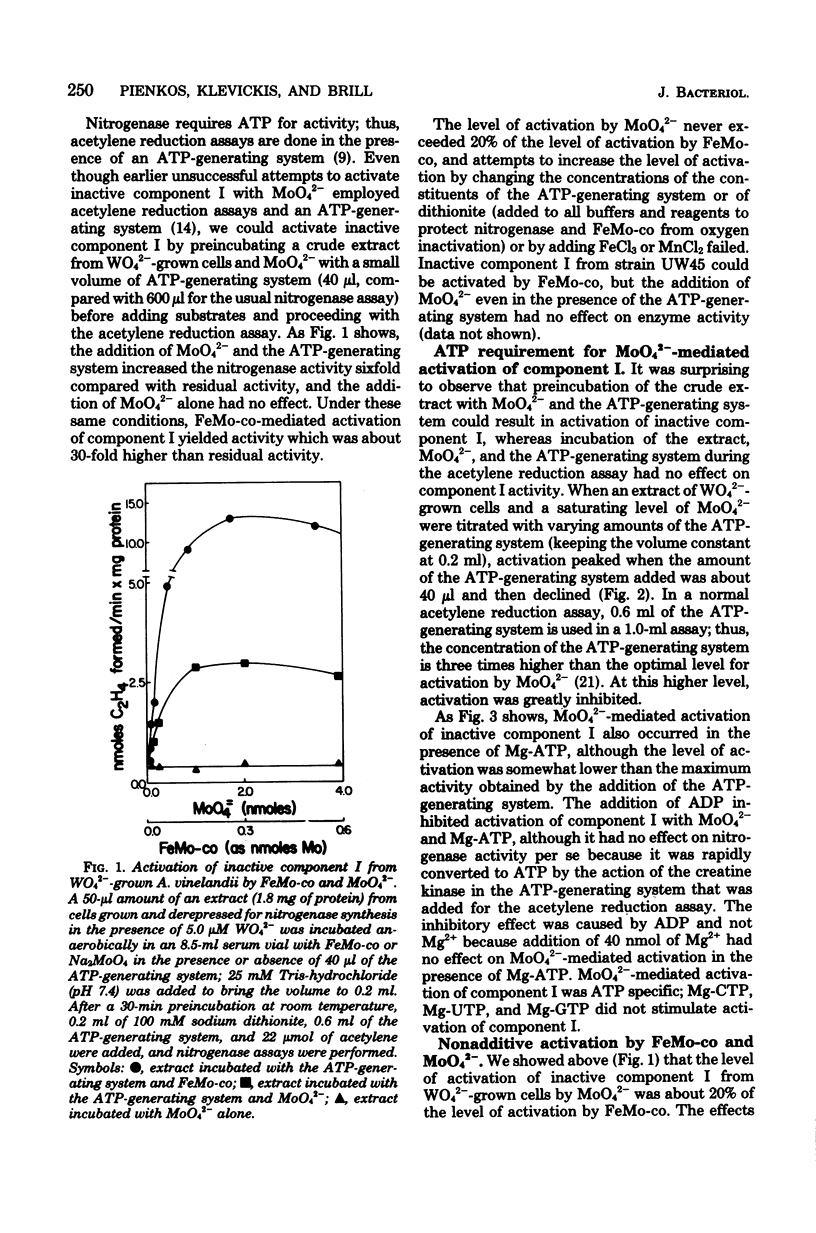
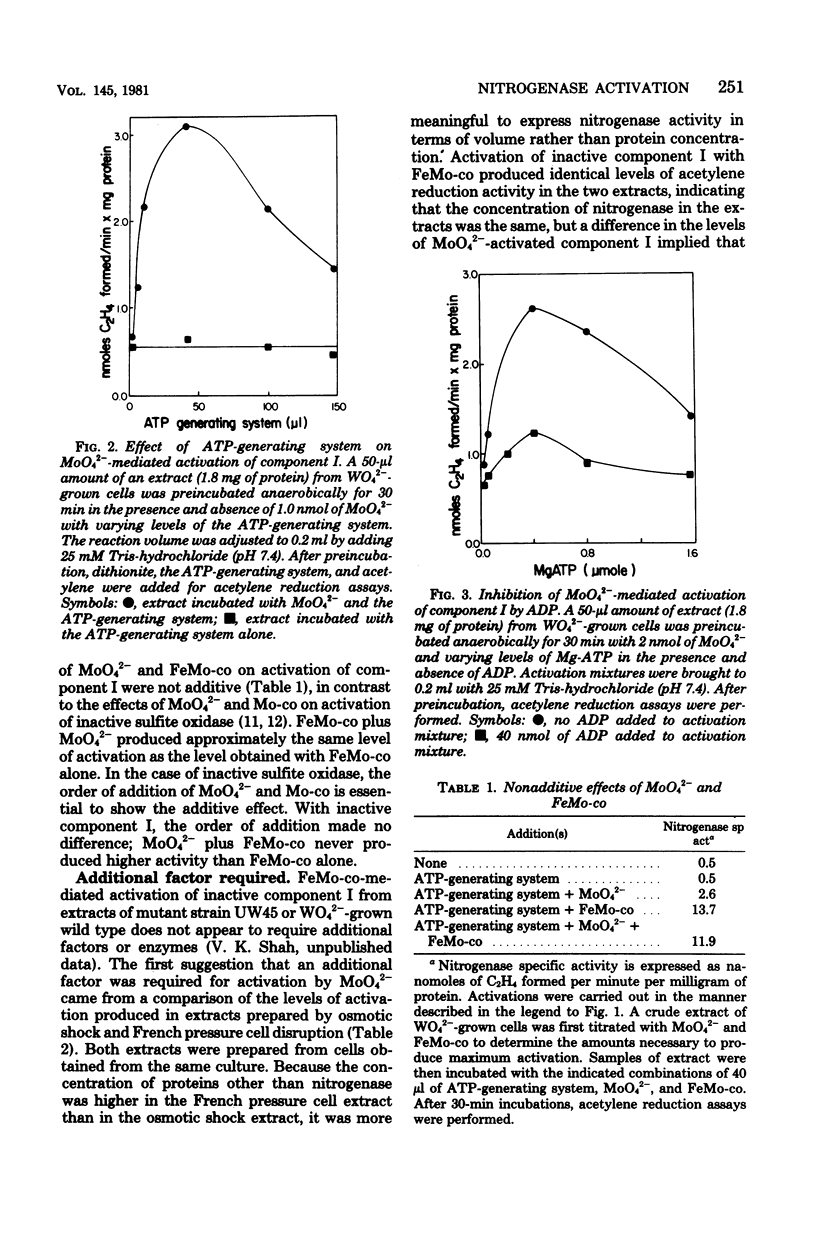
When Azotobacter vinelandii was derepressed for nitrogenase synthesis in the presence of WO42- rather than MoO42-, it synthesized active component II and inactive component I of nitrogenase. This inactive component I could be activated in vitro with the iron-molybdenum cofactor or with MoO42-. The latter reaction required adenosine 5'-triphosphate and was inhibited by adenosine 5'-diphosphate. FeMo cofactor and MoO42- produced different levels of activation, but there was no evidence that they acted upon different species of demolybdo component I. Rather, it may be that an additional factor necessary for MoO42-mediated activation but not for FeMo cofactor-mediated activation was limiting. Mo was inserted into component I during both FeMo cofactor- and MoO42- mediated activations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy N. K., Rajagopalan K. V. Characterization of molybdenum cofactor from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):114–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.114-124.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L. Kinetic studies of nitrogenase from soya-bean root-nodule bacteroids. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):61–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1310061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulen W. A., LeComte J. R. The nitrogenase system from Azotobacter: two-enzyme requirement for N2 reduction, ATP-dependent H2 evolution, and ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):979–986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):805–810. doi: 10.1038/249805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Jones H. P., Rajagopalan K. V. In vitro reconstitution of demolybdosulfite oxidase by a molybdenum cofactor from rat liver and other sources. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4994–5003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. P., Johnson J. L., Rajagopalan K. V. In vitro reconstitution of demolybdosulfite oxidase by molybdate. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4988–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase V. The effect of Mo, W and V on the synthesis of nitrogenase components in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 7;362(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H. H., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Activation of inactive nitrogenase by acid-treated component I. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):697–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.697-701.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pienkos P. T., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Molybdenum cofactors from molybdoenzymes and in vitro reconstitution of nitrogenase and nitrate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5468–5471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBRISH S. A., MARR A. G. Location of enzymes in Azotobacteragilis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:158–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.158-168.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., MacNeil T., MacNeil D., Brill W. J. Regulation and characterization of protein products coded by the nif (nitrogen fixation) genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):267–279. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.267-279.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Sperl G. T., DeMoss J. A. In vitro incorporation of molybdate into demolybdoproteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):719–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.719-726.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. IV. Simple method of purification to homogeneity of nitrogenase components from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):445–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis I. C., Gordon J. K., Orme-Johnson W. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. 3. Nitrogenaseless mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii: activities, cross-reactions and EPR spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. Y., Burris R. H. The binding of ATP and ADP by nitrogenase components from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]