Abstract
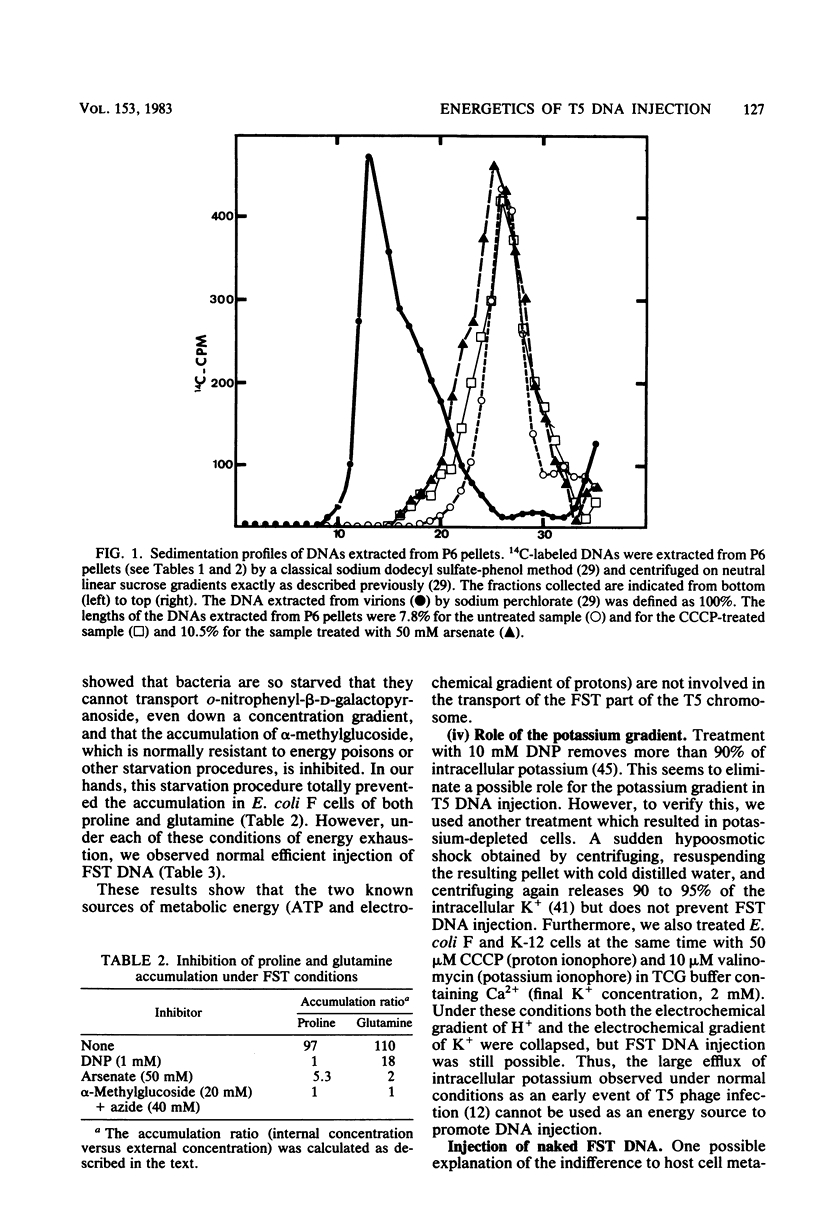
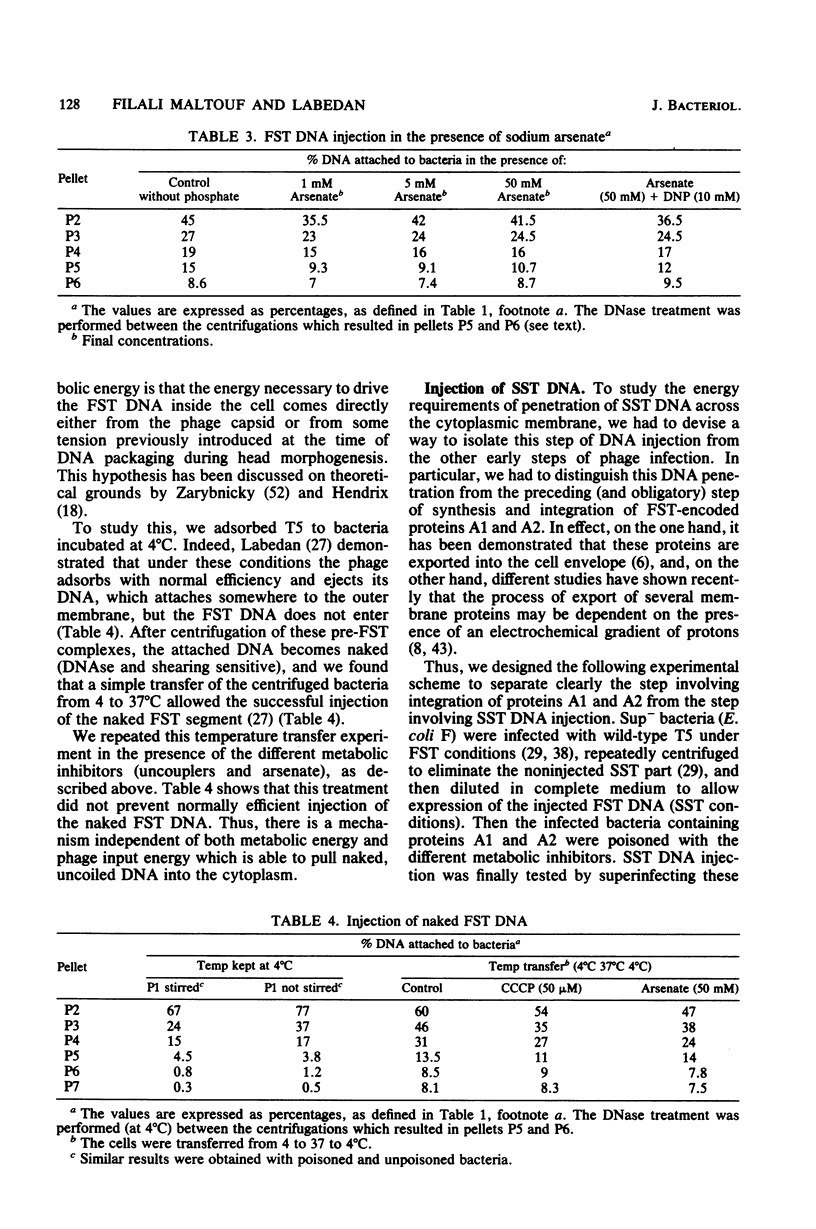
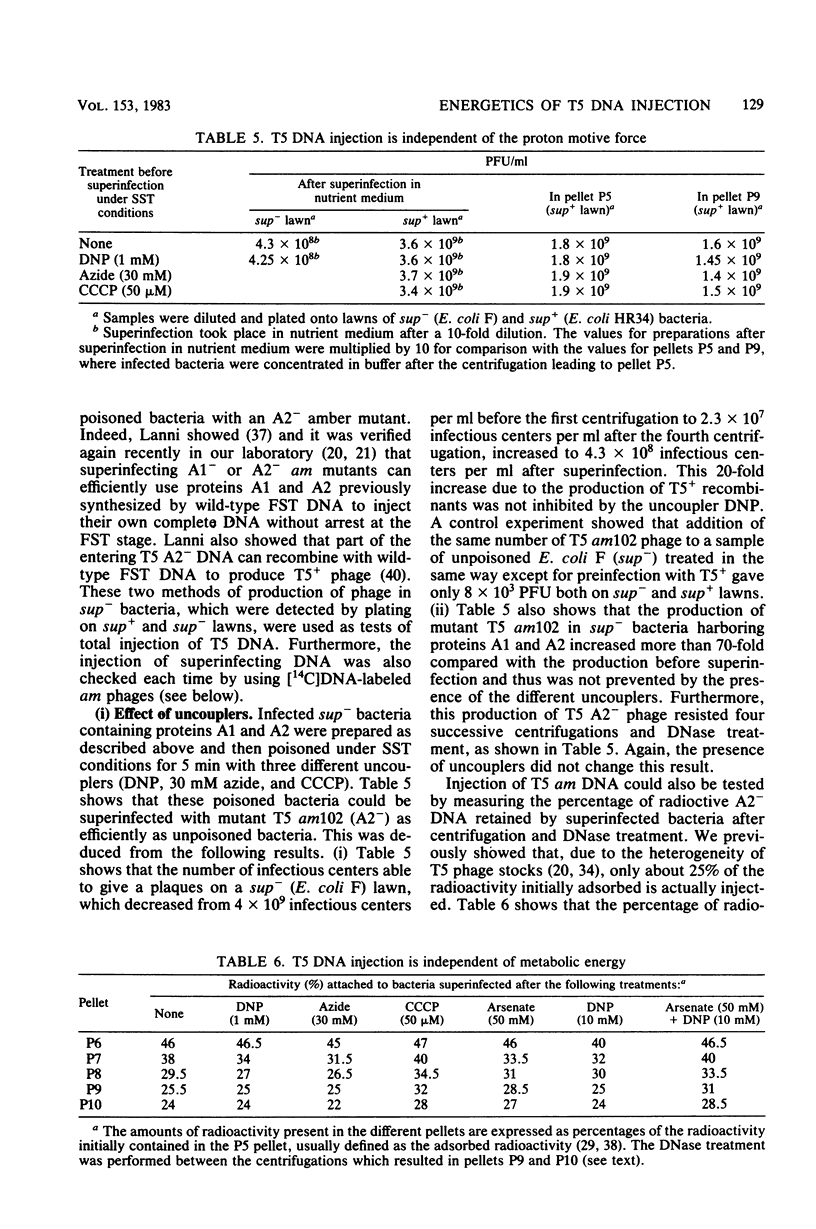
The addition of various metabolic inhibitors (uncouplers, cyanide, arsenate, ionophores) separately or together (for example, arsenate and an uncoupler) or even harsher methods of energy depletion did not prevent bacteriophage T5 from injecting its first-step-transfer DNA (a DNA segment 3 micron long) into the cytoplasm of host cells. The same indifference to metabolic energy was observed if first-step-transfer DNA was decapsidated and uncoiled before injection, thus precluding any energetic help from the phage capsid or from some tension stored in DNA tightly packed in the head. Penetration of the second-step-transfer DNA across the cytoplasmic membrane was studied by determining injection of superinfecting T5 A2- amber phages into Sup- bacteria containing proteins A1 and A2 previously encoded by the first-step-transfer DNA of a primary wild-type phage. The addition of various metabolic inhibitors after synthesis of proteins A1 and A2 but before superinfection did not prevent this penetration of second-step-transfer DNA. Thus, we conclude that traversal of the cytoplasmic membrane by the entire T5 DNA (a molecule 34 micron long) must occur by diffusion through protein channels.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold V., Geider K. Interaction of DNA with DNA-binding proteins. The characterization of protein HD from Escherichia coli and its nucleic acid complexes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec 11;71(2):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Supercoiling energy and nucleosome formation: the role of the arginine-rich histone kernel. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1159–1181. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1159-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaustova L. P., Grinius L. L., Griniuviene B. B., Jasaitis A. A., Kadziauskas J. P., Kiausinyte R. J. Studies on energy supply for genetic processes. Involvement of membrane potential in genetic transformation of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(2):349–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H., Dunn G. B. Membrane protein biosynthesis in T5 bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earhart C. F. The association of host and phage DNA with the membrane of Escherichia coli. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):420–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enequist H. G., Hirst T. R., Harayama S., Hardy S. J., Randall L. L. Energy is required for maturation of exported proteins in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazi A., Schechter E., Letellier L., Labedan B. Probes of membrane potential in Escherichia coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80717-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J., Duckworth D. H. Ion fluxes during T5 bacteriophage infection of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 May;201(2):576–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L., Berzinskiene J. Studies on DNA transport during bacterial conjugation. Role of protonmotive force-generating H+-ATPase and respiratory chain. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 15;72(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80833-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. Nucleic acid transport driven by ion gradient across cell membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Apr 21;113(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Symmetry mismatch and DNA packaging in large bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulen C., Labedan B., Legault-Demare J. Evidence for heterogeneity in populations of T5 bacteriophage. II. Some particles are unable to inject their second-step-transfer DNA. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):633–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.633-638.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulen C., Legault-Demare J. Rescue of first-step-transfer amber mutants by "second-step-transfer-blocked" bacteriophage T5 on an su- strain. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):602–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.602-604.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Lutz H., Kornberg A. Novel histone H2A-like protein of escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5097–5101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalasauskaite E., Grinius L., Kadisaite D., Jasaitis A. Electrochemical H+ gradient but not phosphate potential is required for Escherichia coli infection by phage T4. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80952-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalasauskaite E., Grinius L. The role of energy-yielding ATPase and respiratory chain at early stages of bacteriophage T4 infection. FEBS Lett. 1979 Mar 15;99(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80974-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L., Boyer P. D. Energization of active transport by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7257–7265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Energy expenditure is obligatory for the downhill transport of galactosides. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):447–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B. A very early step in the T5 DNA injection process. Virology. 1976 Dec;75(2):368–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Crochet M., Legault-Demare J., Stevens B. J. Location of the first step transfer fragment and single-strand interruptions in T5stO bacteriophage DNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):213–234. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Goldberg E. B. Requirement for membrane potential in injection of phage T4 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Heller K. B., Jasaitis A. A., Wilson T. H., Goldberg E. B. A membrane potential threshold for phage T4 DNA injection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Mar 28;93(2):625–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B. In vitro study of the phage T5 DNA injection process: use of columns of Escherichia coli membranes immobilized on kieselguhr. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90455-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Legault-Demare J. Evidence for heterogeneity in populations of T5 bacteriophage. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1093-1100.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Legault-Demare J. Penetration into host cells of naked, partially injected (post-FST) DNA of bacteriophage T5. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):226–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.226-229.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labedan B., Letellier L. Membrane potential changes during the first steps of coliphage infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):215–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. T. DNA transfer from phage T5 to host cells: dependence on intercurrent protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):969–973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. T. First-step-transfer deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteriophage T5. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):227–242. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.227-242.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. T., Lanni F., Tevethia M. J. Bacteriophage T5 chromosome fractionation: genetic specificity of a DNA fragment. Science. 1966 Apr 8;152(3719):208–210. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3719.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanni Y. Functions of two genes in the first-step-transfer DNA of bacteriophage T5. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Lebail S., Kepes A. Opening of potassium channels in Escherichia coli membranes by thiol reagents and recovery of potassium tightness. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):33–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORE A., POLLARD E. Physical mechanism of bacteriophage injection. Science. 1956 Sep 7;124(3219):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3219.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate C. A., Suit J. L., Jetten A. M., Luria S. E. Effects of colicin K on a mutant of Escherichia coli deficient in Ca 2+, Mg 2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6138–6143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Waters F. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. VIII. Potassium transport mutants. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):325–341. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Yaniv M., Germond J. E. E. coli DNA binding protein HU forms nucleosomelike structure with circular double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabelnikov A. G., Domaradsky I. V. Effect of metabolic inhibitors on entry of exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid into Ca2+-treated Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.435-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Kaback H. R. Involvement of the proton electrochemical gradient in genetic transformation in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 30;99(4):1153–1160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel P. J., Schaechter M. The role of the host cell membrane in the replication and morphogenesis of bacteriophages. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:261–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Ponta H., Schweiger M. Development of Escherichia coli virus T1. The role of the proton-motive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zárybnický V. Mechanism of T-even DNA ejection. J Theor Biol. 1969 Jan;22(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



