Abstract
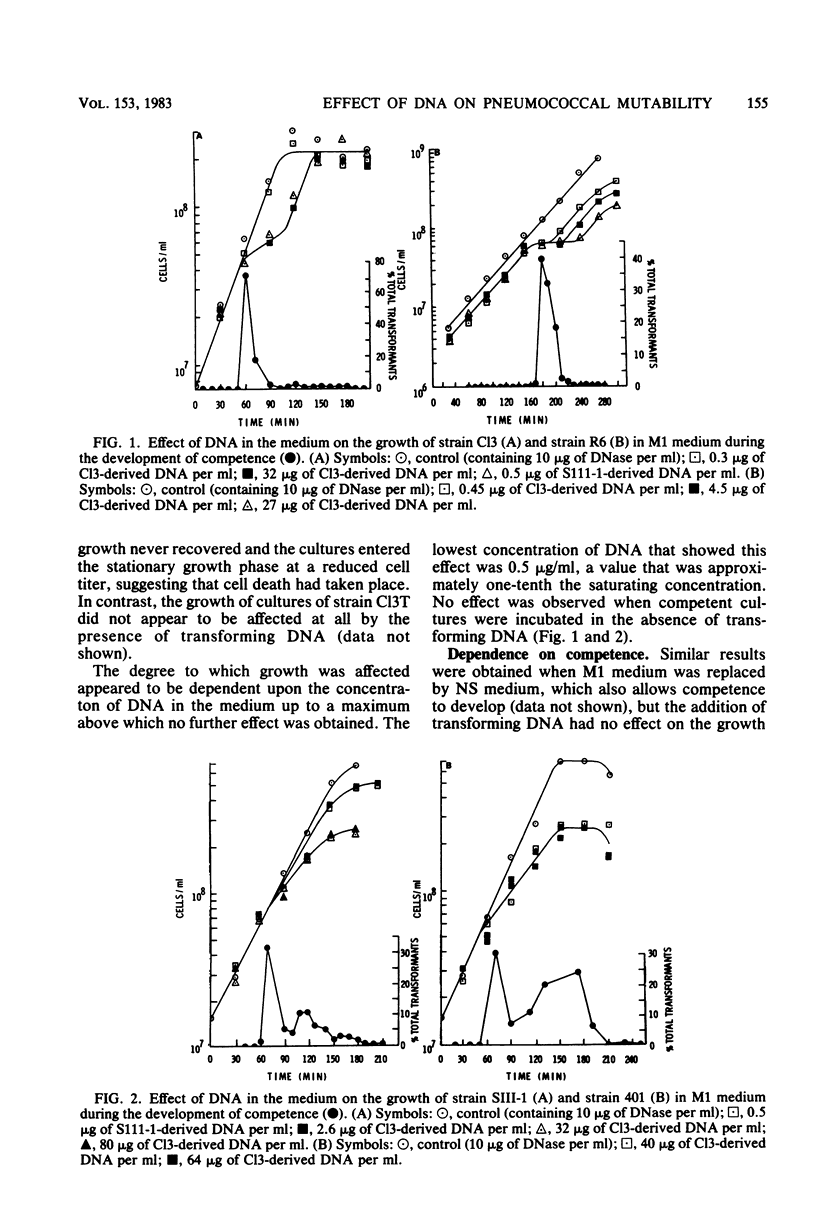
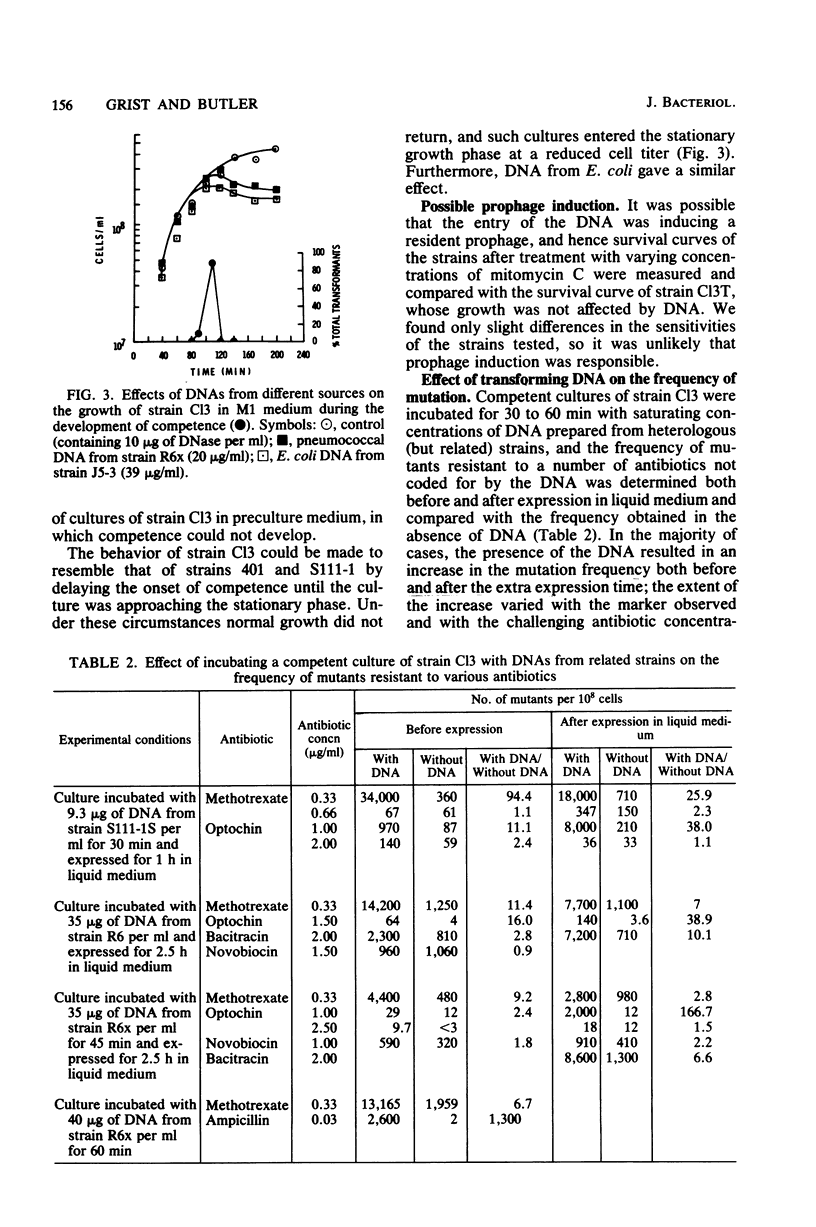
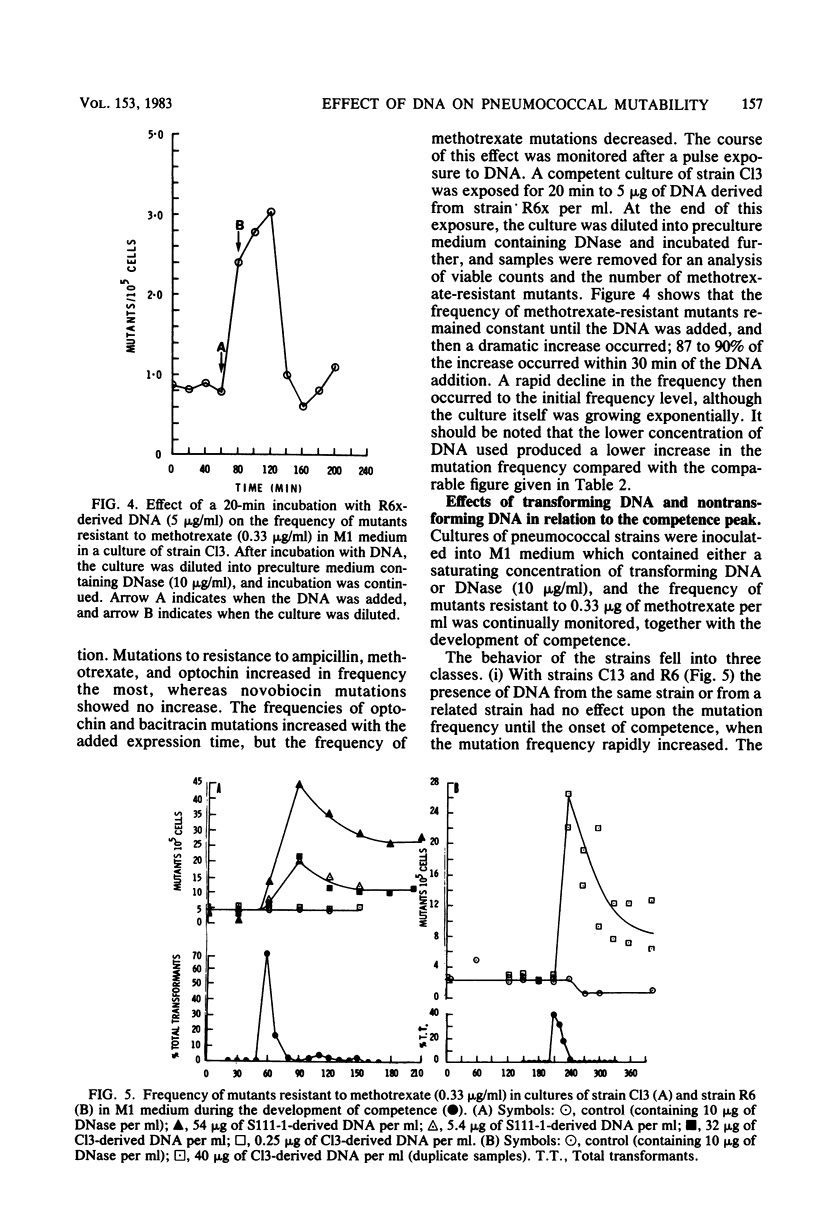
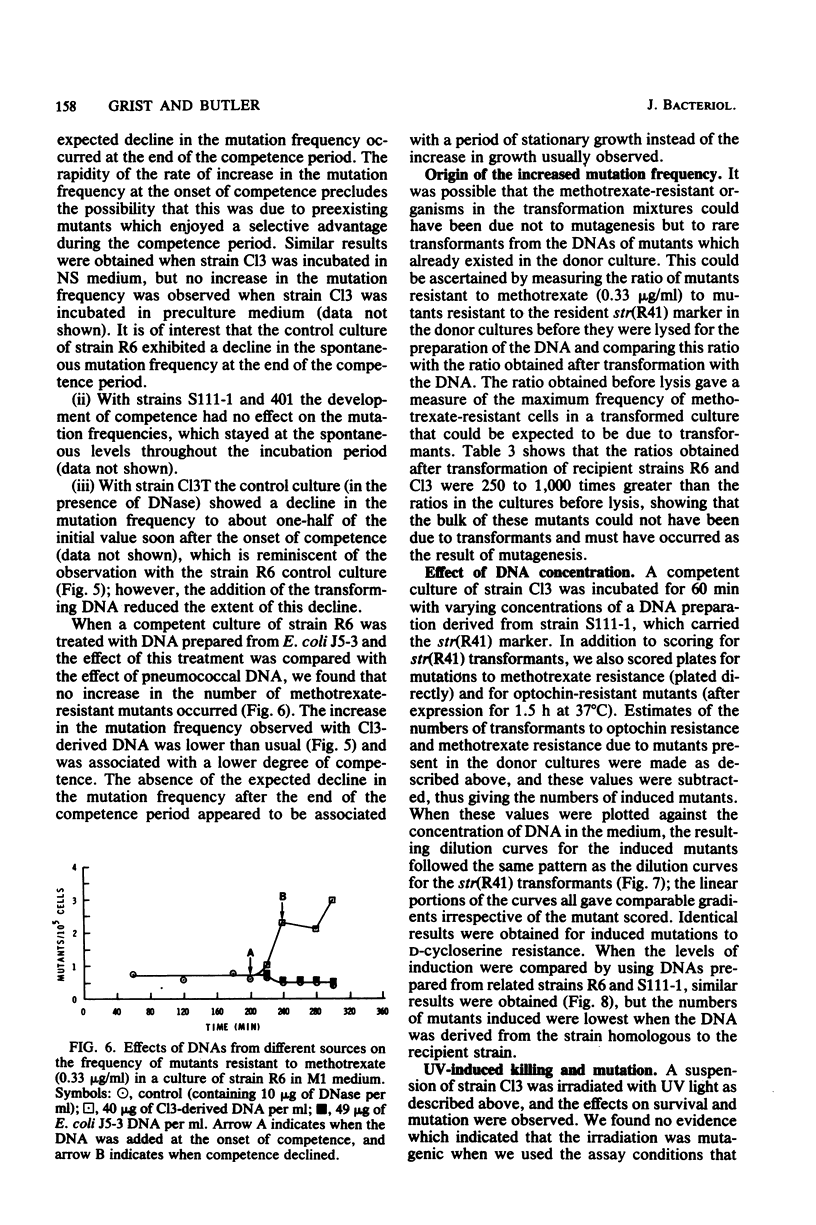
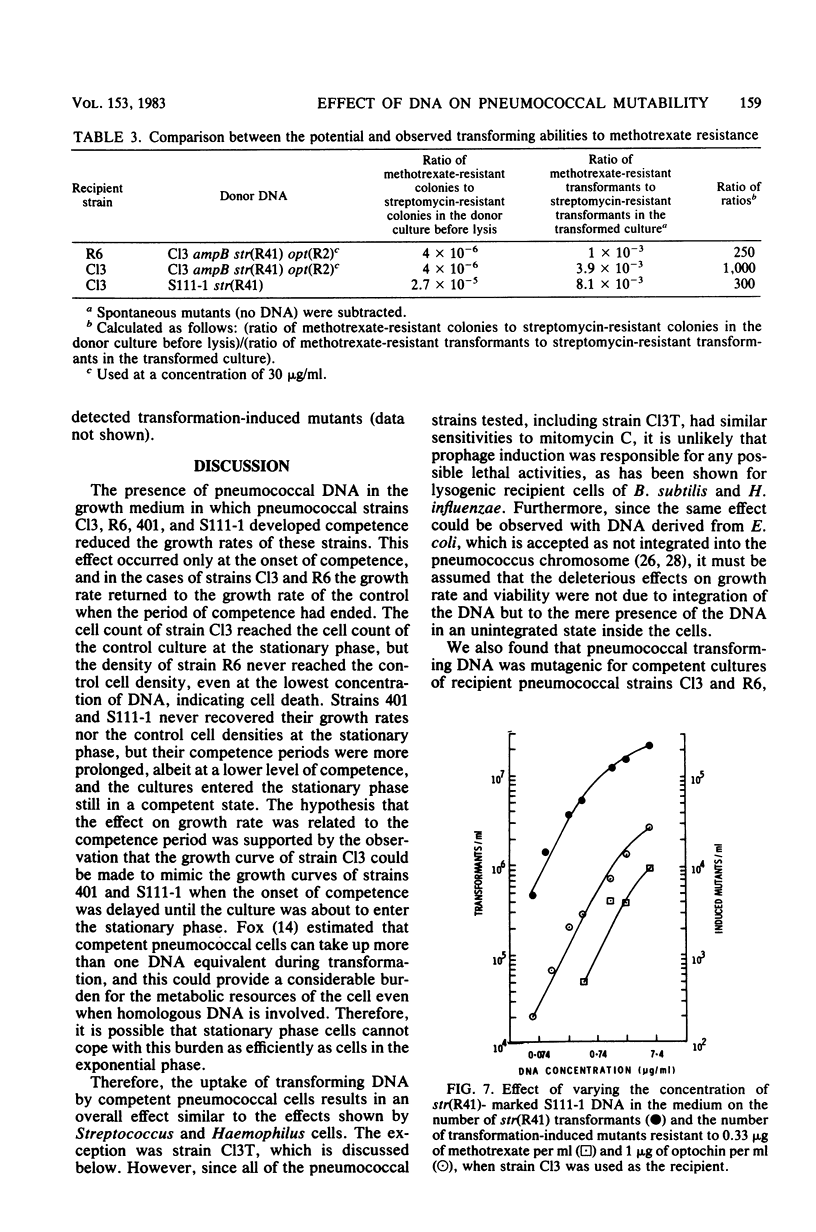
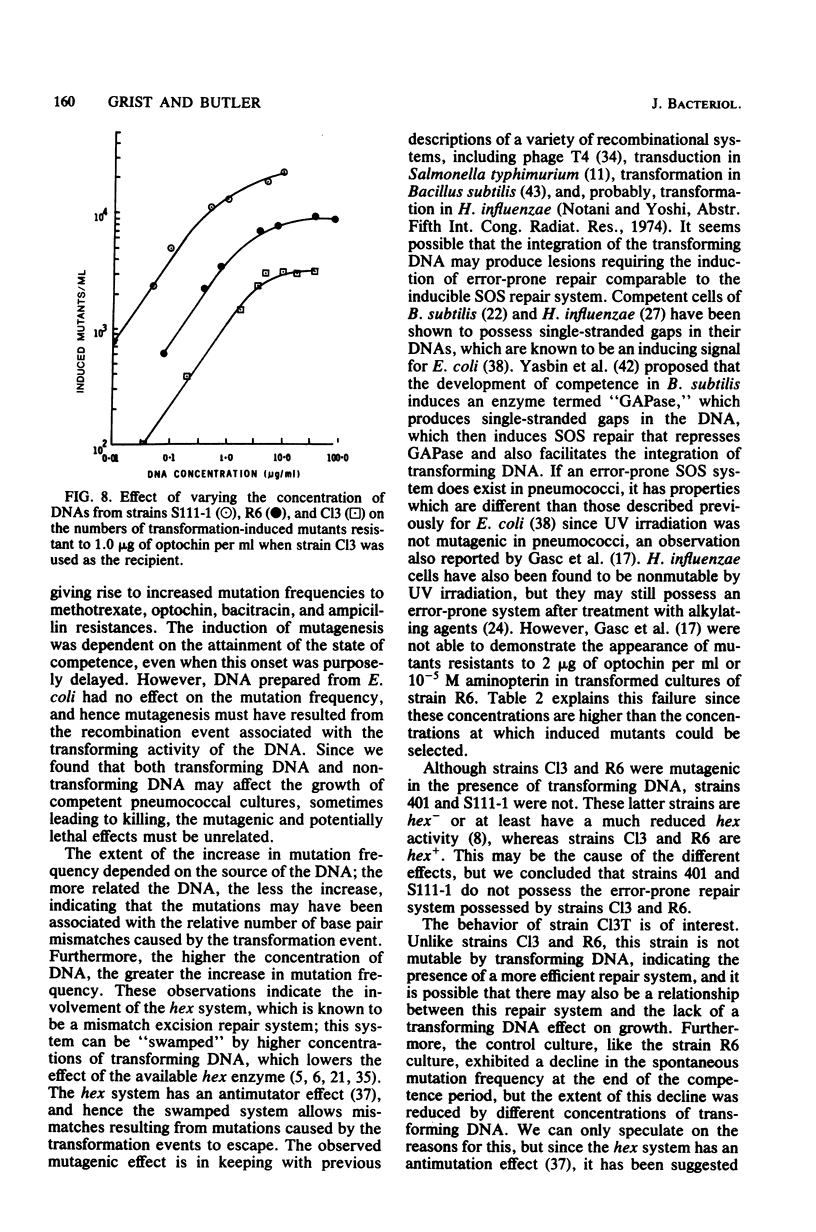
We studied the effect of the presence of homologous transforming DNA on the growth of several transformable strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae and on the frequency of mutation of these strains to various antibiotic resistances. We observed no effect on growth until the strains became competent, when growth was depressed. At the end of the competence period, some strains showed recovery to varying degrees, whereas others showed evidence of cell death. Growth was also depressed by the presence of DNA from Escherichia coli, indicating that recombination was not likely to be the cause of the observed effect. Furthermore, cell death was not caused by the induction of a prophage. Several of the strains showed increased mutation frequencies during the competence period, although treatment with E. coli DNA gave no such effect, indicating that the mutagenesis was due to recombination. We observed no mutagenesis due to UV irradiation of the strains. The possibility that integration of the transforming DNA may produce lesions which induce error-prone repair is discussed. Furthermore, a strain that showed no mutability by transforming DNA, indicating the presence of a more efficient repair system, gave evidence of producing higher amounts of the hex system when competent, and the possible relationship between these properties is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER L. O. A CO-PRECIPITATION METHOD FOR THE PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DNA FROM SMALL SAMPLES OF LOW DENSITY BACTERIAL CULTURES. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 May;39:247–252. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie K. L., Setlow J. K. Killing of Haemophilus influenzae cells by integrated ultraviolet-induced lesions from transforming deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1284–1288. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1284-1288.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. O., George Y. The effect of both homologous and heterologous DNA on integration efficiencies in pneumococcal transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):140–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00271210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. O., Nicholas G., Grist R. W. Mapping of the pneumococcus chromosome: differences between recipient strains varying in hex property and the location of the opt-r2 gene. Genet Res. 1979 Feb;33(1):1–14. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300018127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. O., Nicholas G. Mapping of the pneumococcus chromosome. Linkage between the genes conferring resistances to erythromycin and tetracycline and its implication to the replication of the chromosome. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Nov;79(1):31–44. doi: 10.1099/00221287-79-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler L. O., Smiley M. B. Characterization by transformation of an ampicillin-resistant mutant of pneumococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):189–195. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMEREC M. SELFER MUTANTS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Genetics. 1963 Nov;48:1519–1531. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.11.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX M. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid incorporation by transformed bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):83–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J. DNA-mediated prophage induction in Bacillus subtilis lysogenic for phi 105c4. J Virol. 1973 Jul;12(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.1.18-24.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garro A. J., Law M. F. Relationship between lysogeny, spontaneous induction, and transformation efficiencies in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasc A. M., Sicard N., Claverys J. P., Sicard A. M. Lack of SOS repair in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mutat Res. 1980 Apr;70(2):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(80)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild W. R., Shoemaker N. B. Intracellular competition for a mismatch recogition system and marker-specific rescue of transforming DNA from inactivation by ultraviolet irradiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(4):291–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00268517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTCHKISS R. D. Transfer of penicillin resistance in pneumococci by the desoxyribonucleate derived from resistant cultures. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:457–461. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. J., Barr G. C. Some properties of DNA in competent Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan;39(2):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball R. F., Perdue S. W., Boling M. E. The role of pre-replication and post-replication processes in mutation induction in Haemophilus influenzae by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Mutat Res. 1978 Oct;52(1):57–72. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(78)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LERMAN L. S., TOLMACH L. J. Genetic transformation. I. Cellular incorporation of DNA accompanying transformation in Pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):68–82. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClerc J. E., Setlow J. K. Single-strand regions in the deoxyribonucleic acid of competent Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):1091–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.1091-1102.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTTOLENGHI E., HOTCHKISS R. D. Release of genetic transforming agent from pneumococcal cultures during growth and disintegration. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:491–519. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechowska M., Shugar D. Influence of DNA on growth and viability of transformable group H streptococci. Acta Biochim Pol. 1967;14(2):277–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow J. K., Boling M. E., Allison D. P., Beattie K. L. Relationship between prophage induction and transformation in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):153–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.153-161.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhart W. L., Herriott R. M. Genetic integration in the heterospecific transformation of Haemophilus influenzae cells by Haemophilus parainfluenzae deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1725–1731. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1725-1731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strigini P. On the mechanism of spontaneous reversion and genetic recombination in bacteriophage T4. Genetics. 1965 Oct;52(4):759–776. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby G., Fox M. S., Bernheimer H. Marker discrimination in deoxyribonucleic acid-mediated transformation of various Pneumococcus strains. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):608–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.608-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby G., Sicard M. A. Integration efficiencies of spontaneous mutant alleles of amiA locus in pneumococcal transformation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1130–1135. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1130-1135.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiraby J. G., Fox M. S. Marker discrimination in transformation and mutation of pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3541–3545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E. DNA repair in Bacillus subtilis. I. The presence of an inducible system. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 8;153(2):211–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E. DNA repair in Bacillus subtilis. II. Activation of the inducible system in competent bacteria. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 8;153(2):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):540–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.540-548.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasbin R. E., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Transformation and transfection in lysogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis: evidence for selective induction of prophage in competent cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):296–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.296-304.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa H. Mutations Resulting from the Transformation of BACILLUS SUBTILIS. Genetics. 1966 Nov;54(5):1201–1214. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



