Abstract
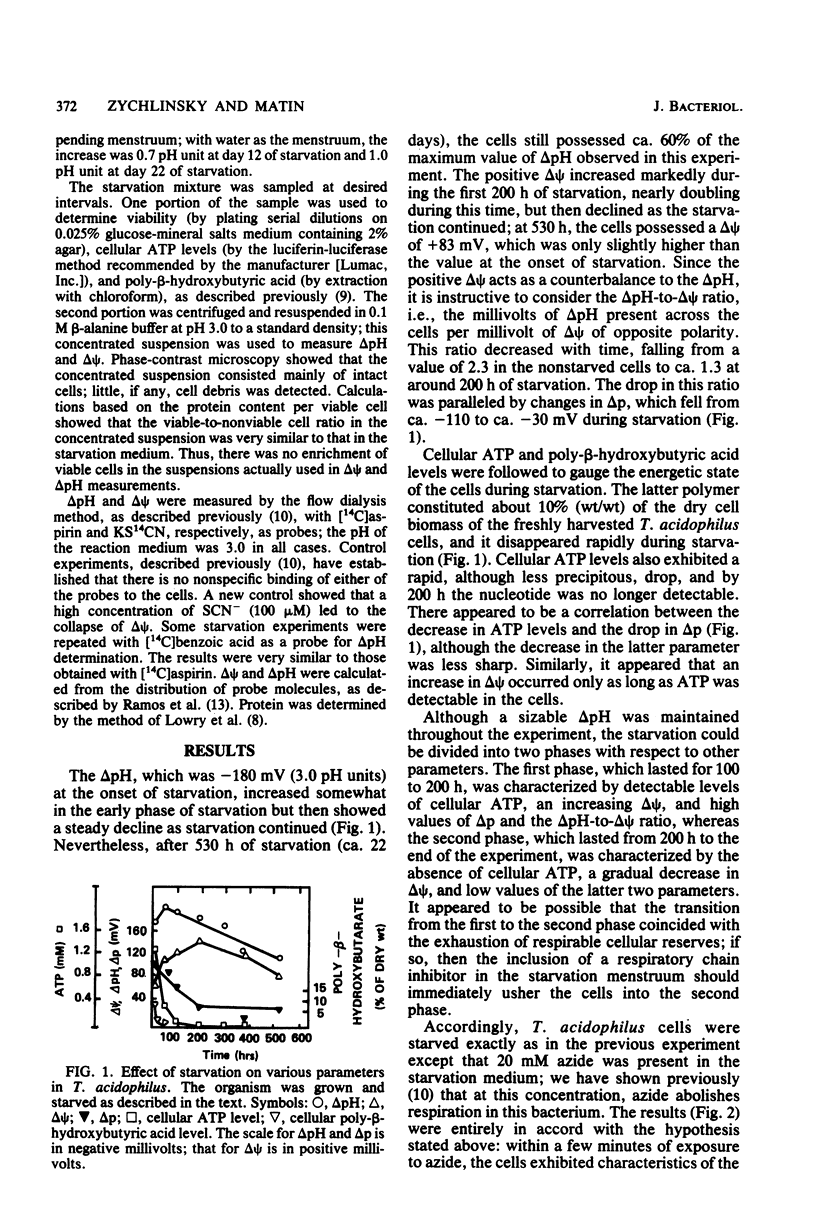
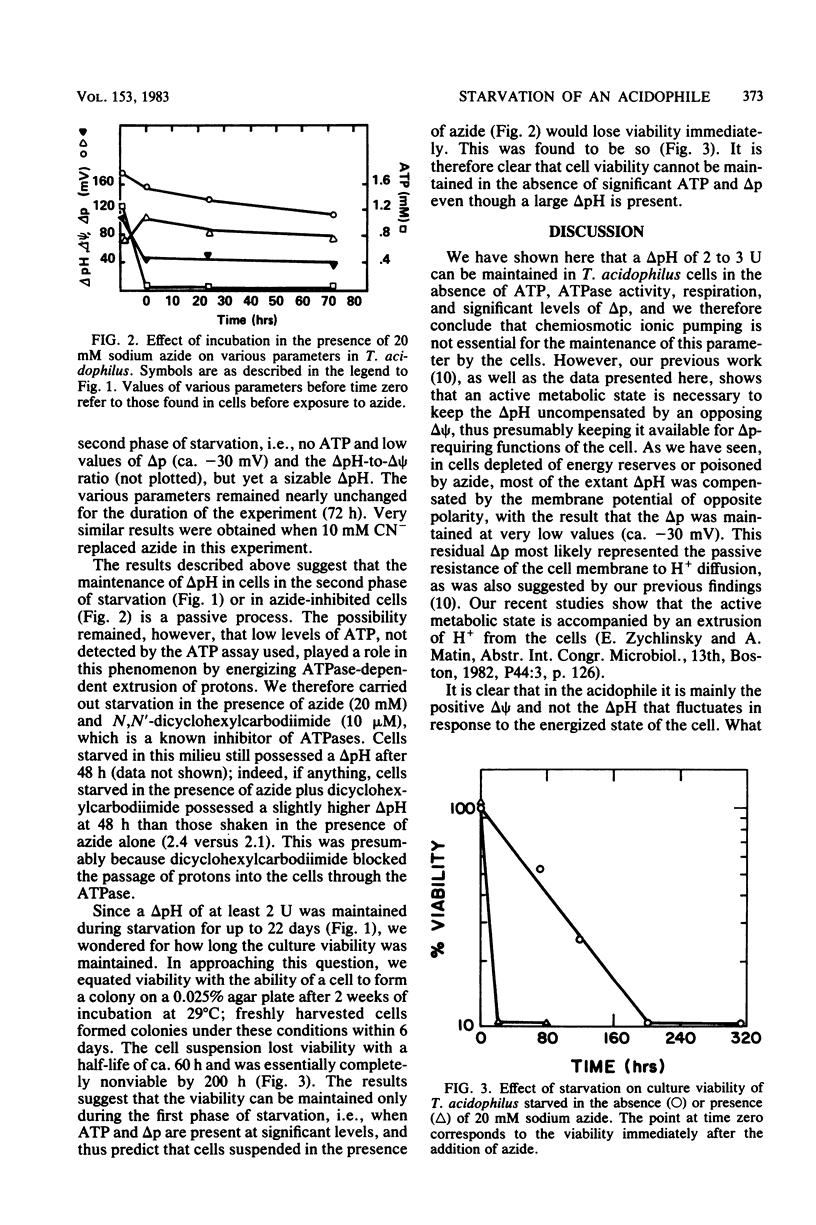
The question of whether Thiobacillus acidophilus maintains its cytoplasmic pH at values close to neutrality by active or passive means was explored by subjecting the organism to long-term starvation (up to 22 days). Starving cells maintained a delta pH of 2 to 3 U throughout starvation, although cellular poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and ATP, the proton motive force, and culture viability were low or not detectable after 200 h. Cells exposed to azide or azide plus N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide immediately exhibited characteristics of cells starved for more than 200 h. Thus, a large delta pH in T. acidophilus was maintained in the absence of ATP, ATPase activity, respiration, significant levels of proton motive force, and cell viability and was therefore not dependent on chemiosmotic ionic pumping. The transition from a metabolically active to an inactive state was accompanied by a large increase in the positive membrane potential, which nearly completely compensated for the delta pH in the inactive cells. The longevity of the acidophile during starvation was comparable to that reported previously for neutrophiles, and the loss of viability occurred not because of the acidification of the cytoplasm but apparently because of energy depletion.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox J. C., Nicholls D. G., Ingledew W. J. Transmembrane electrical potential and transmembrane pH gradient in the acidophile Thiobacillus ferro-oxidans. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):195–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1780195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay R., Silver M. Thiobacillus acidophilus sp. nov.; isolation and some physiological characteristics. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):281–288. doi: 10.1139/m75-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan N. J., Midgley M., Dawes E. A. Effect of starvation on transport, membrane potential and survival of Staphylococcus epidermidis under anaerobic conditions. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):223–230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsung J. C., Haug A. Intracellular pH of Thermoplasma acidophila. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 21;389(3):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsung J. C., Haug A. Membrane potential of Thermoplasma acidophila. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):47–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A., Davidson L. F., Filip S. J., Jr, Zuckerman R. S., Guffanti A. A. The protonmotive force and beta-galactoside transport in Bacillus acidocaldarius. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4599–4603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Veldhuis C., Stegeman V., Veenhuis M. Selective advantage of a Spirillum sp. in a carbon-limited environment. Accumulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and its role in starvation. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jun;112(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Wilson B., Zychlinsky E., Matin M. Proton motive force and the physiological basis of delta pH maintenance in thiobacillus acidophilus. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):582–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.582-591.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague M. D., Dawes E. A. The survival of Peptococcus prévotii in relation to the adenylate energy charge. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):291–299. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima T., Arakawa H., Baba M. Biochemical studies on an acidophilic, thermophilic bacterium, Bacillus acidocaldarius: isolation of bacteria, intracellular pH, and stabilities of biopolymers. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):1107–1113. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The use of flow dialysis for determinations of deltapH and active transport. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:680–688. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searcy D. G. Thermoplasma acidophilum: intracellular pH and potassium concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 18;451(1):278–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



