Abstract
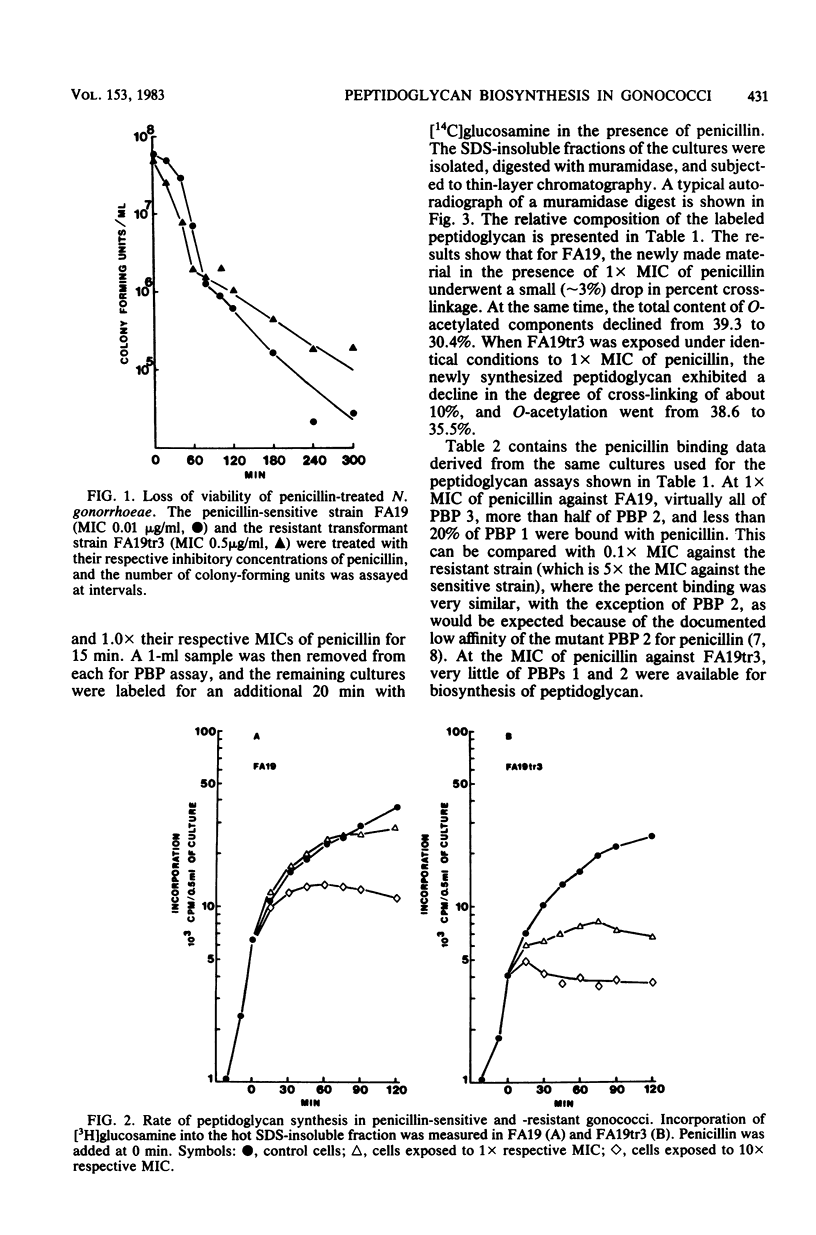
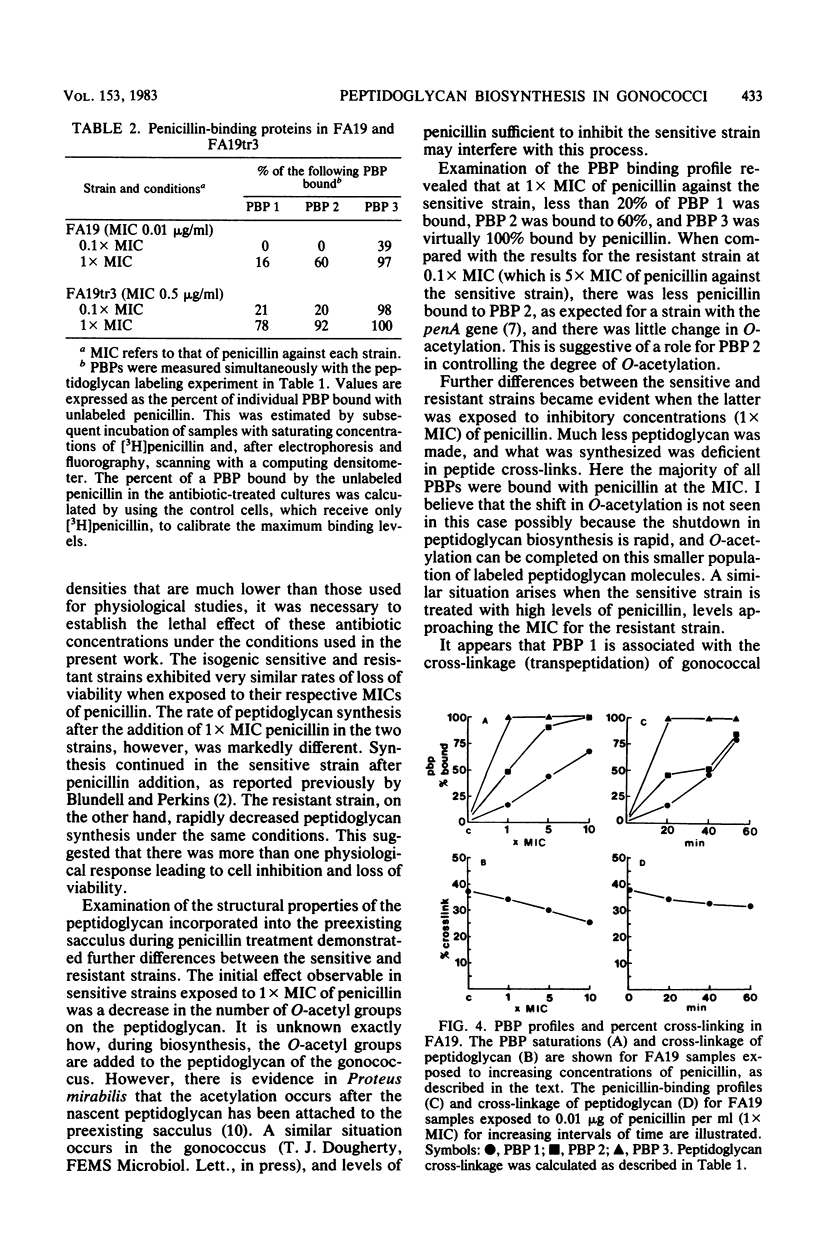
Treatment of penicillin-sensitive and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains with their respective inhibitory concentrations of penicillin caused rapid cell death. When the peptidoglycan syntheses of these two strains were examined in the presence of penicillin, the sensitive strain continued to make this cell wall polymer for an extended time, whereas the resistant strain underwent a rapid and marked depression in synthesis. Examination of the labeled sodium dodecyl sulfate-insoluble peptidoglycan made in the presence of inhibitory concentrations of penicillin revealed further differences. The primary effect on the penicillin-sensitive gonococcus was a slight change in peptide cross-linking and a sharp decline in the degree of O-acetylation. In contrast, the resistant strain exhibited a substantial decline in cross-linking, with a very moderate change in O-acetylation. The degree of saturation of the individual penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) was assessed under these conditions. PBP 2, which exhibits a reduced affinity for penicillin in the resistant strain, appeared to be related to O-acetylation, whereas PBP 1 was implicated in the transpeptidation reaction.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G. Properties of penicillin-binding proteins in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):316–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell J. K., Perkins H. R. Effects of beta-lactam antibiotics on peptidoglycan synthesis in growing Neisseria gonorrhoeae, including changes in the degree of O-acetylation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):633–641. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.633-641.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. A., Perkins H. R. In vitro synthesis of peptidoglycan by beta-lactam-sensitive and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: effects of beta-lactam and other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Kroll H. P. Murein biosynthesis and O-acetylation of N-acetylmuramic acid during the cell-division cycle of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Fazio M., Tomasz A. Effect of benzylpenicillin on the synthesis and structure of the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):514–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hash J. H., Rothlauf M. V. The N,O-diacetylmuramidase of Chalaropsis species. I. Purification and crystallization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5586–5590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaya M., Strominger J. L. Simultaneous deletion of D-alanine carboxypeptidase IB-C and penicillin-binding component IV in a mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Gmeiner J. Modification of peptidoglycan structure by penicillin action in cell walls of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Maruyama I. N., Takagaki Y., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. Isolation of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase IA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2631–2635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Rosenthal R. S. Effect of penicillin G on release of peptidoglycan fragments by Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization of extracellular products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Rosenthal R. S. Release of soluble peptidoglycan from growing conococci: demonstration of anhydro-muramyl-containing fragments. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):914–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.914-925.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Biochemical and genetical approaches to the mechanism of action of penicillin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 May 16;289(1036):273–283. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1980.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: penicillin enhancement of peptidoglycan hydrolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):717–725. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.717-725.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



