Abstract
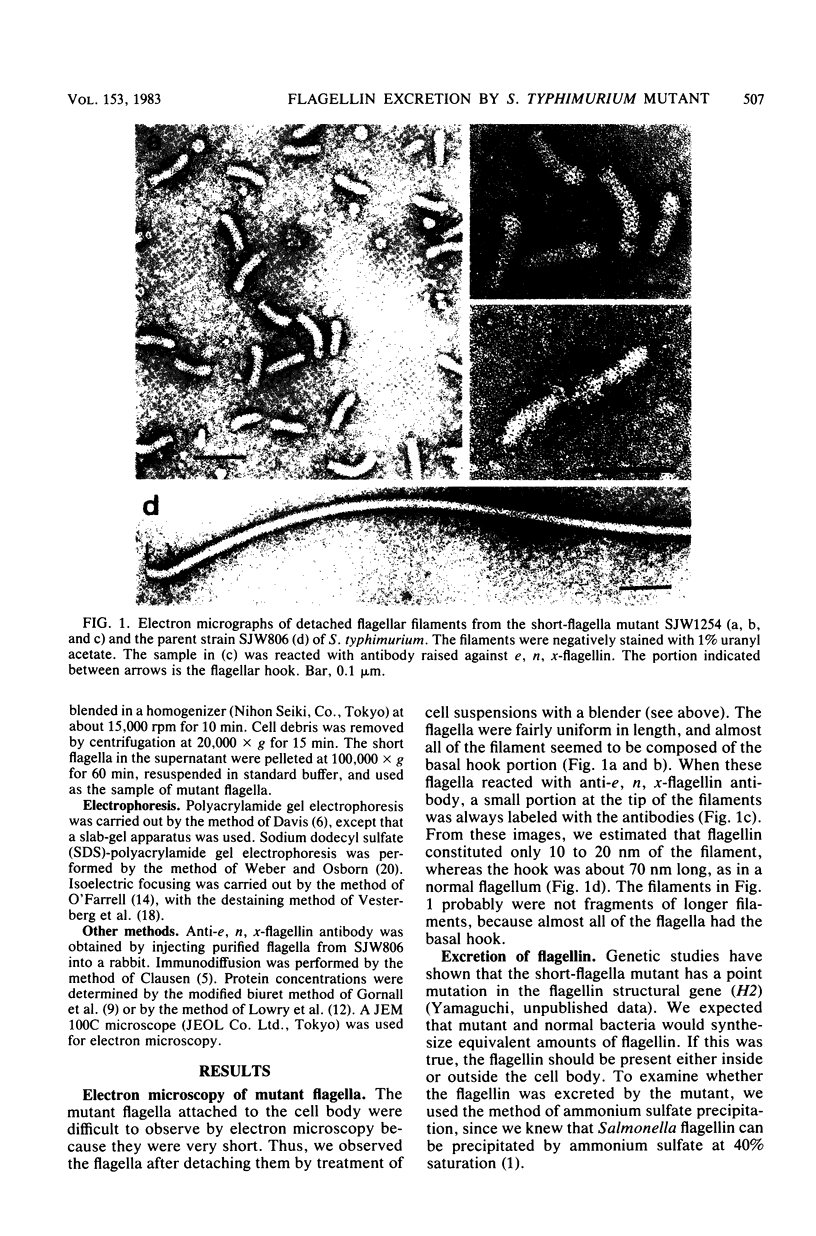
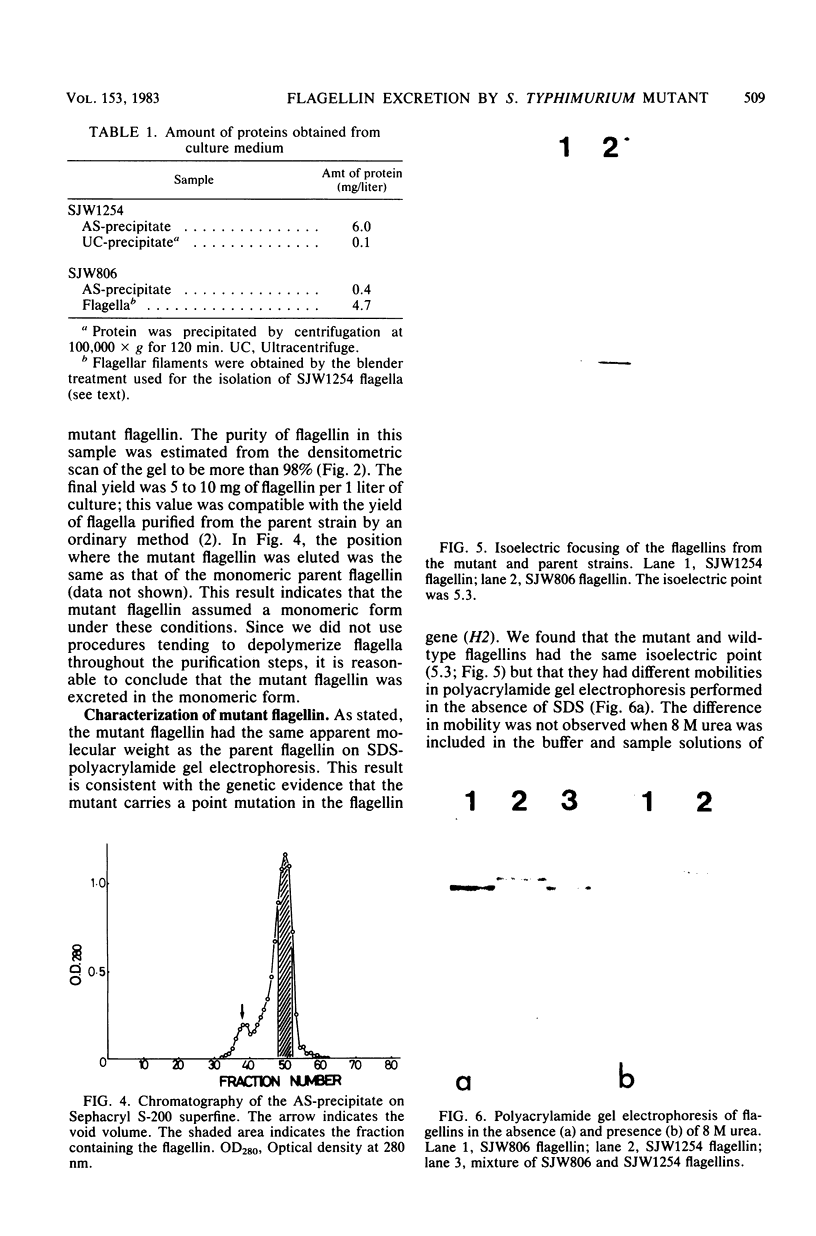
A nonmotile mutant of Salmonella typhimurium, SJW1254, has very short flagella (less than 0.1 micron long) due to a mutation in the structural gene of flagellin (H2). When ammonium sulfate was added to the culture medium of SJW1254 grown to the late-log phase, a large amount of protein precipitated. Gel electrophoresis and immunodiffusion showed that more than 90% (wt/wt) of the precipitated protein was flagellin. The mutant flagellin appeared to be excreted in the monomeric form, in an amount comparable to the amount in the flagellar filaments of wildtype bacteria. No such precipitate was obtained from the medium of wild-type bacteria. The mutant flagellin had the same apparent molecular weight (55,000) and isoelectric point (5.3) as the wild-type flagellin, but differed in mobility in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nondenaturing conditions. Moreover, the mutant flagellin did not polymerize in vitro under various conditions in which wild-type flagellin polymerized. These results suggested that the mutant bacteria excreted flagellin because the flagellin polymerized poorly and therefore could not be trapped at the tip of the flagellar filament. This short-flagella mutant should be useful for studying the mechanism of flagellin transport.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J., ABBOT A. BEHAVIOUR OF ACTIVE BACTERIAL ANTIGENS DURING THE INDUCTION OF THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. I. PROPERTIES OF FLAGELLAR ANTIGENS FROM SALMONELLA. Nature. 1963 Sep 28;199:1257–1259. doi: 10.1038/1991257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASAKURA S., EGUCHI G., IINO T. RECONSTITUTION OF BACTERIAL FLAGELLA IN VITRO. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:42–56. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakura S., Iino T. Polymorphism of Salmonella flagella as investigated by means of in vitro copolymerization of flagellins derived from various strains. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):251–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90334-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Engel J., Winklmair D. A model of bacterial flagella based on small-angle x-ray scattering and hydrodynamic data which indicated an elongated shape of the flagellin protomer. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 11;26(3):313–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. U., Tokuyasu K., Simon M. I. Bacterial flagella: polarity of elongation. Science. 1970 Jul 10;169(3941):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3941.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Taira T., Iino T. A simple method for the isolation of flagellar shape mutants in Salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jul;125(1):213–216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-1-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Polarity of flagellar growth in salmonella. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 May;56(2):227–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-56-2-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komeda Y., Iino T. Regulation of expression of the flagellin gene (hag) in Escherichia coli K-12: analysis of hag-lac gene fusions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):721–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.721-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakihara Y., Wakabayashi T. Three-dimensional image reconstruction of straight flagella from a mutant Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 5;131(3):485–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleytr U. B., Glauert A. M. Evidence for an empty core in a bacterial flagellum. Nature. 1973 Feb 23;241(5391):542–543. doi: 10.1038/241542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Iino T. Appearance of straight flagellar filaments in the presence of p-fluorophenylalanine in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):527–529. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.527-529.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O., Hansén L., Sjösten A. Staining of proteins after isoelectric focusing in gels by new procedures. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., DeRosier D., Shapiro L., Weissborn A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the flagellar hook from Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):439–465. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]