Abstract
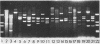
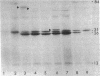
Mutations which affect the activity of polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase) map near 69 min on the bacterial chromosome. This region of the chromosome has been cloned by inserting the kanamycin-resistant transposon Tn5 near the argG and mtr loci at 68.5 min. Large SalI fragments of chromosomal DNA containing the Tn5 element were inserted into pBR322, and selection was made for kanamycin-resistant recombinant plasmids. Two of these plasmids were found to produce high levels of PNPase activity in both wild-type and host strains lacking PNPase activity. The pnp gene was further localized and subcloned on a 4.8 kilobase HindIII-EcoRI fragment. This fragment was shown to encode an 84,000-molecular weight protein which comigrated with purified PNPase during sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The orientation of the pnp gene was determined by insertion of Tn5 into the 4.8 kilobase fragment cloned in pBR322. Some of the insertions had lost the ability to elevate the level of PNPase activity in the host bacterium. Restriction mapping of the positions of the Tn5 insertions and analysis of plasmid-encoded polypeptides in UV-irradiated maxi-cells indicated that the pnp gene is oriented in the counterclockwise direction on the bacterial chromosome.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Davies J., Allet B., Rochaix J. D. Transposition of R factor genes to bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Mizuno D. Effect of sRNA and related compounds on the phosphorolysis of polynucleotide phosphorylase in the degradation of messenger ribonucleic acids. J Biochem. 1966 May;59(5):521–523. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Har-El R., Silberstein A., Kuhn J., Tal M. Synthesis and degradation of lac mRNA in E. coli depleted of 30S ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jun 7;173(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. D., Heilig J. S., Martinez I. I., Calendar R., Isaksson L. A. Temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant producing a temperature-sensitive sigma subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hautala J. A., Bassett C. L., Giles N. H., Kushner S. R. Increased expression of a eukaryotic gene in Escherichia coli through stabilization of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S., Ito K., Matsuyama T., Ozaki H., Yura T. 5-methyltryptophan-resistant mutations lniked with the arginine G marker in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1880–1881. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1880-1881.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Apirion D. The involvement of ribonuclease I, ribonuclease II, and polynucleotide phosphorylase in the degradation of stable ribonucleic acid during carbon starvation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):149–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitakawa M., Dabbs E. R., Isono K. Genes coding for ribosomal proteins S15, L21, and L27 map near argG in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):832–838. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.832-838.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna R. V., Apirion D. Polynucleotide phosphorylase has a role in growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1235–1239. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1235-1239.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN D. H., THANG M. N., GRUNBERG-MANAGO M. SYNTHESIS IN VIVO OF POLYNUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORYLASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. I. EFFECT OF AMINO ACIDS ON POLYNUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHORYLASE ACTIVITY IN A CHLORAMPHENICOL-INHIBITED SYSTEM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 20;76:558–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori S., Mizuno D. Turnover of ribosomal RNA in a ribonuclease I-less mutant of Escherichia coli, Q-13, which was found to possess polynucleotide phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., van Rapenbusch R., Minh-Nguy-Thang, Grunberg-Manago M. Quaternary structure of polynucleotide phosphorylase from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Dec 3;40(1):77–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Characterization of polynucleotide phosphorylase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1437–1443. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1437-1443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein S. J., Jorgensen R. A., Postle K., Reznikoff W. S. The inverted repeats of Tn5 are functionally different. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):795–805. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80055-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEKIGUCHI M., COHEN S. S. The selective degradation of phage-induced ribonucleic acid by polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Littauer U. Z. Purification and characterization of polynucleotide phosphorylase from Escherichia coli. Probe for the analysis of 3' sequences of RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6885–6888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T. A model for three-point analysis of random general transduction. Genetics. 1966 Aug;54(2):405–410. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]