Abstract
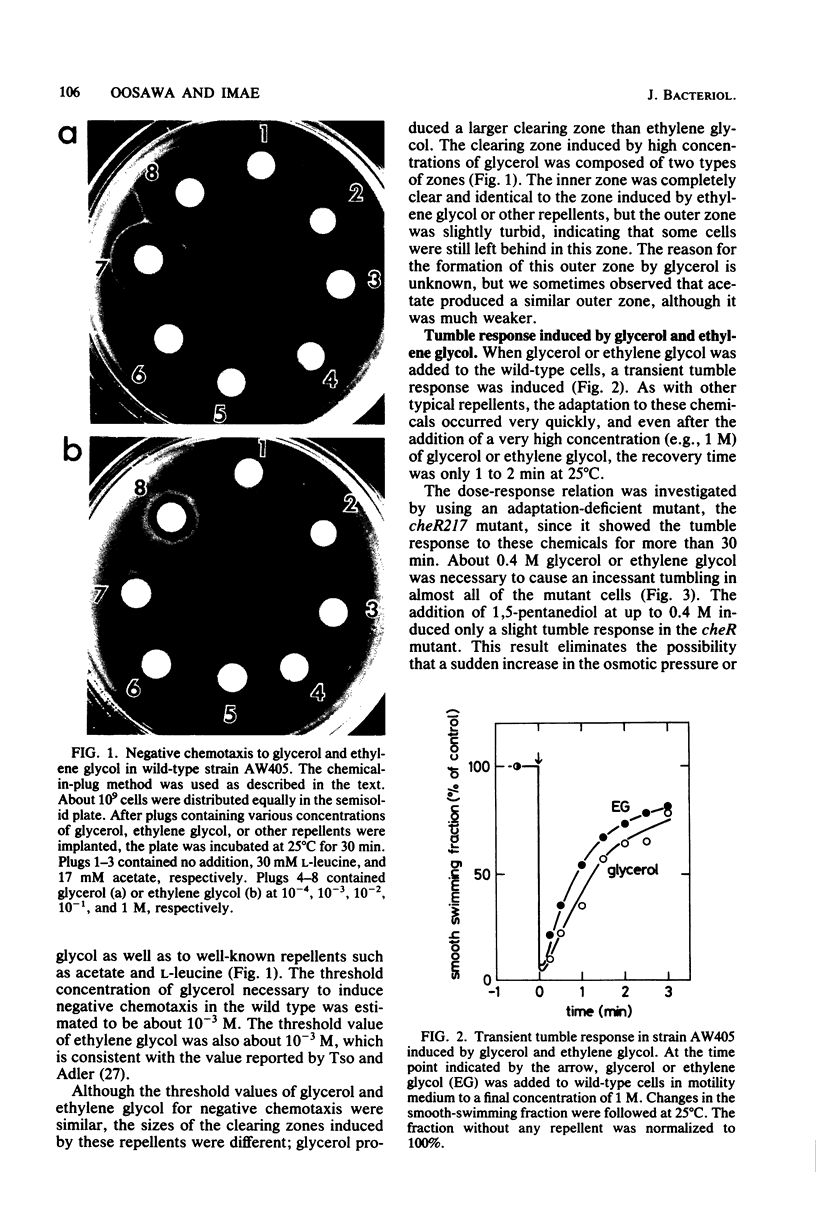
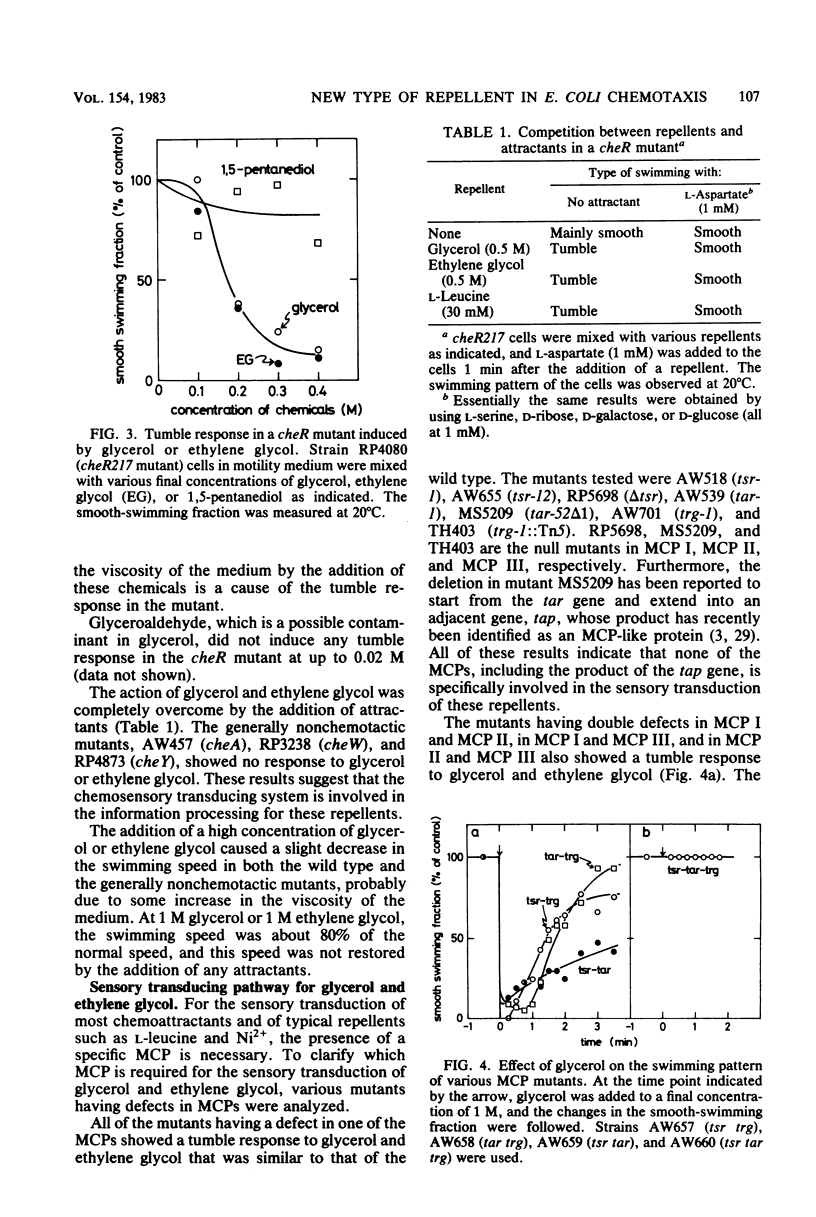
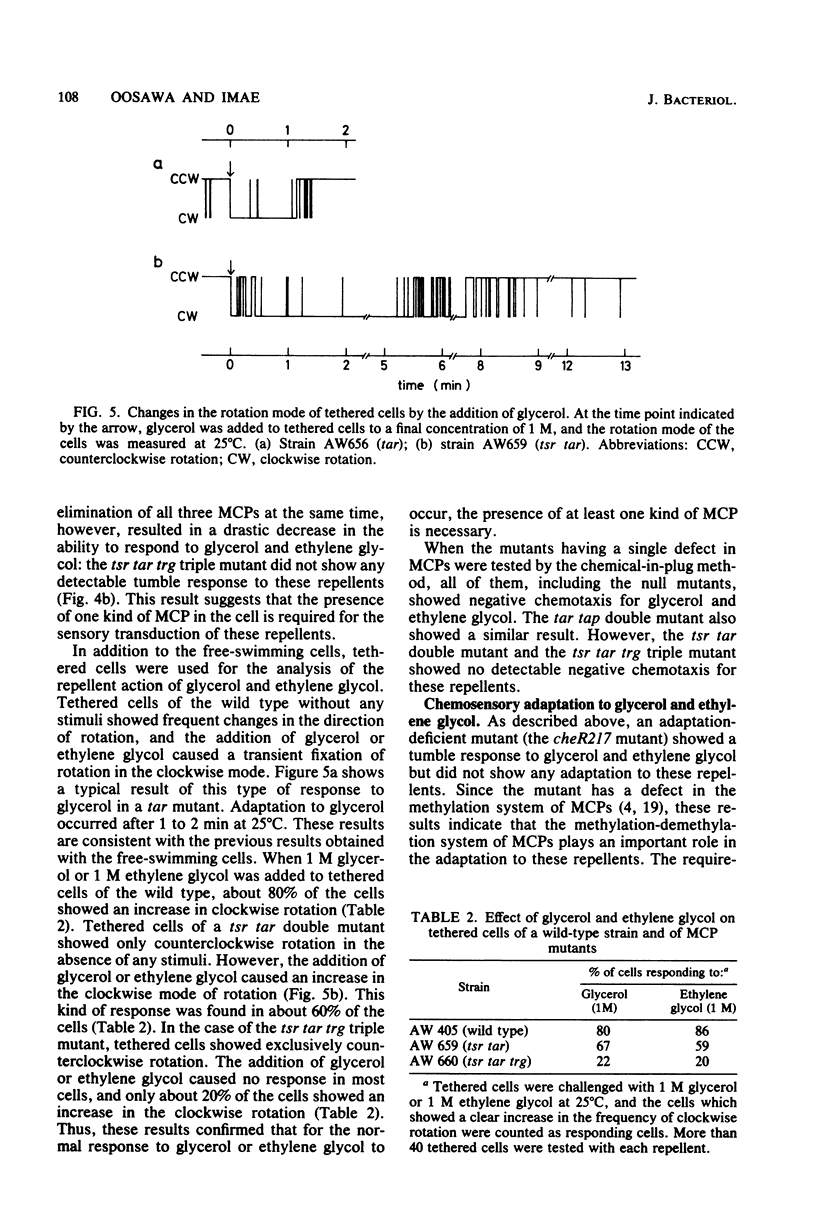
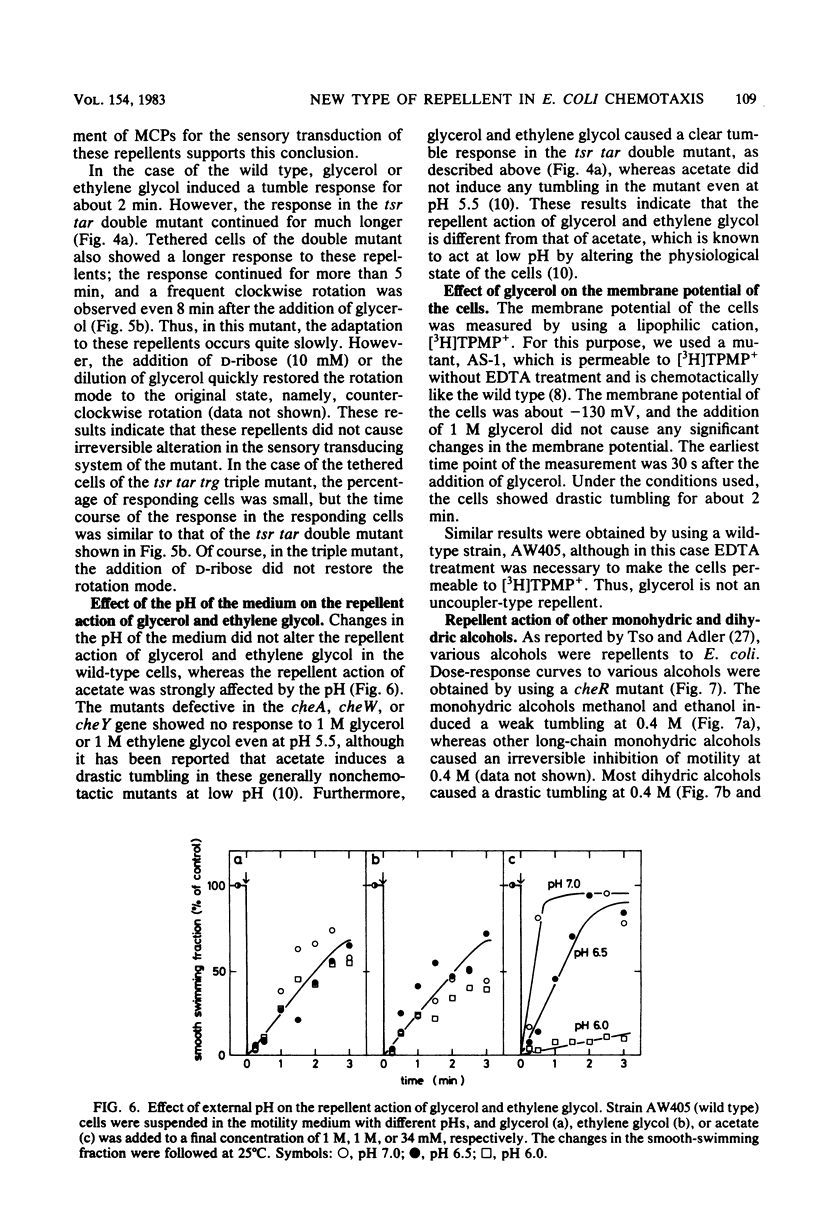
By using the chemical-in-plug method, we found that glycerol and ethylene glycol caused negative chemotaxis in wild-type cells of Escherichia coli; the threshold concentration was about 10(-3) M for both chemicals. As with other known repellents, the addition of glycerol or ethylene glycol induced a brief tumble response in wild-type cells but not in generally nonchemotactic mutants. Experiments with mutants defective in various methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins (MCPs) revealed that the presence of any one of three kinds of MCPs (MCP I, MCP II, or MCP III) was necessary to give a tumble response to these repellents. Consistently, it was found that the methylation-demethylation system of MCPs was involved in the adaptation of the cells to these repellents. The effect of glycerol or ethylene glycol was not enhanced by lowering the pH of the medium, and glycerol did not alter the membrane potential of the cells. All of these results suggest that glycerol and ethylene glycol are members of a new class of repellents which produce a tumble response in the cells by perturbing the MCPs in the membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:341–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J., Hazelbauer G. L., Dahl M. M. Chemotaxis toward sugars in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):824–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.824-847.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A., Krikos A., Simon M. Sensory transducers of E. coli are encoded by homologous genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy M. F., Springer M. S., Adler J. Failure of sensory adaptation in bacterial mutants that are defective in a protein methylation reaction. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Palva E. T., Hazelbauer G. L. Transposon-insertion mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in a component common to galactose and ribose chemotaxis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 20;171(2):193–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00270005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Engström P. Parallel pathways for transduction of chemotactic signals in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):98–100. doi: 10.1038/283098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedblom M. L., Adler J. Genetic and biochemical properties of Escherichia coli mutants with defects in serine chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1048–1060. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1048-1060.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota N., Matsuura S., Mochizuki N., Mutoh N., Imae Y. Use of lipophilic cation-permeable mutants for measurement of transmembrane electrical potential in metabolizing cells of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):399–405. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.399-405.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Macnab R. M. The steady-state counterclockwise/clockwise ratio of bacterial flagellar motors is regulated by protonmotive force. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):563–597. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihara M., Macnab R. M. Cytoplasmic pH mediates pH taxis and weak-acid repellent taxis of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1209–1221. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1209-1221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koiwai O., Hayashi H. Studies on bacterial chemotaxis. IV. Interaction of maltose receptor with a membrane-bound chemosensing component. J Biochem. 1979 Jul;86(1):27–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh H., Ball C. B., Adler J. Identification of a methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein for the ribose and galactose chemoreceptors of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr Biochemistry of sensing and adaptation in a simple bacterial system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:765–782. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S. H., Reader R. W., Kort E. N., Tso W. W., Adler J. Change in direction of flagellar rotation is the basis of the chemotactic response in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):74–77. doi: 10.1038/249074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Ornston M. K. Normal-to-curly flagellar transitions and their role in bacterial tumbling. Stabilization of an alternative quaternary structure by mechanical force. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Shioi J. I., Imae Y., Iida S. Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis motile system driven by an artificially created proton motive force. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.28-36.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Complementation analysis and deletion mapping of Escherichia coli mutants defective in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):45–53. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.45-53.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Revello P. T. Sensory adaptation mutants of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1221–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske D. R., Adler J. Change in intracellular pH of Escherichia coli mediates the chemotactic response to certain attractants and repellents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1196–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1196-1208.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G. Interaction of the maltose-binding protein with membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.662-667.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioi J. I., Matsuura S., Imae Y. Quantitative measurements of proton motive force and motility in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):891–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.891-897.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman M., Simon M. Flagellar rotation and the mechanism of bacterial motility. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):73–74. doi: 10.1038/249073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Sensory transduction in Escherichia coli: two complementary pathways of information processing that involve methylated proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3312–3316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso W. W., Adler J. Negative chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):560–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.560-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Koshland D. E., Jr Receptor structure in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. A., Mowry K. L., Clegg D. O., Koshland D. E., Jr Tandem duplication and multiple functions of a receptor gene in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4673–4676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




