Abstract
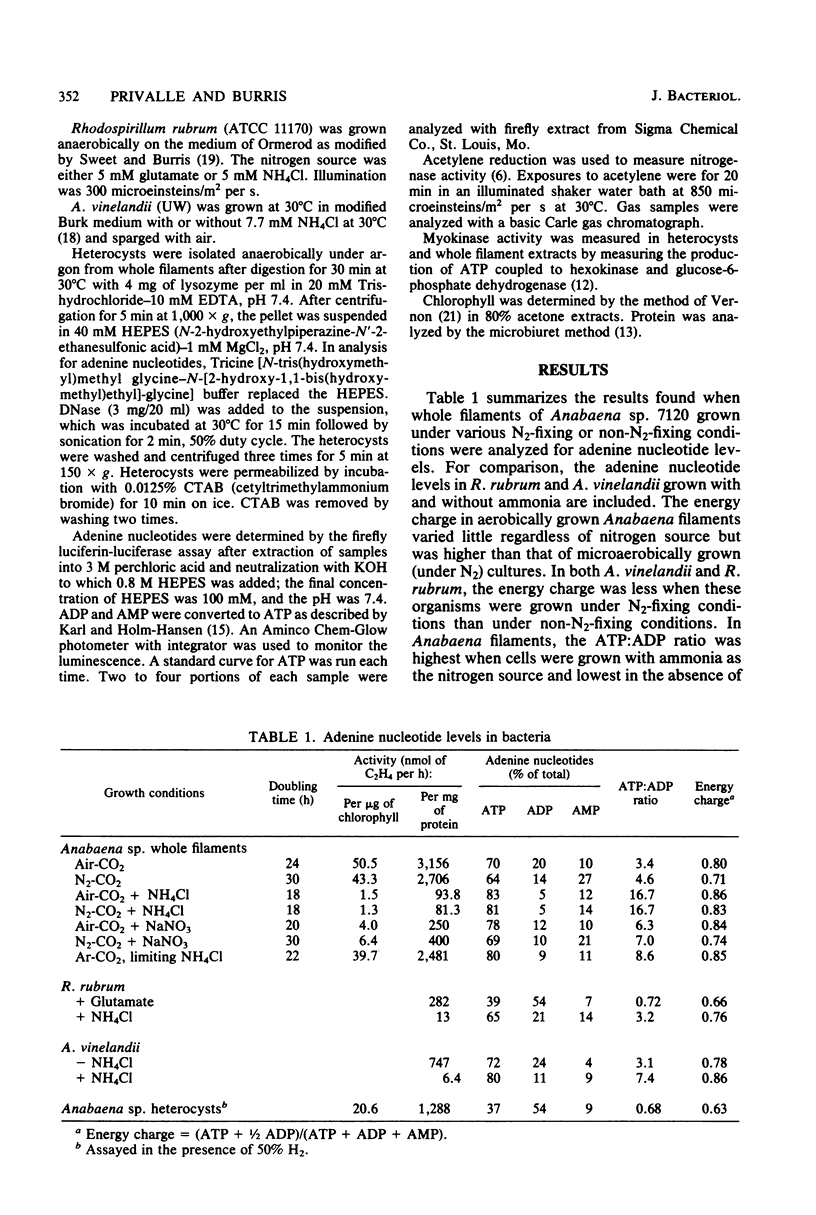
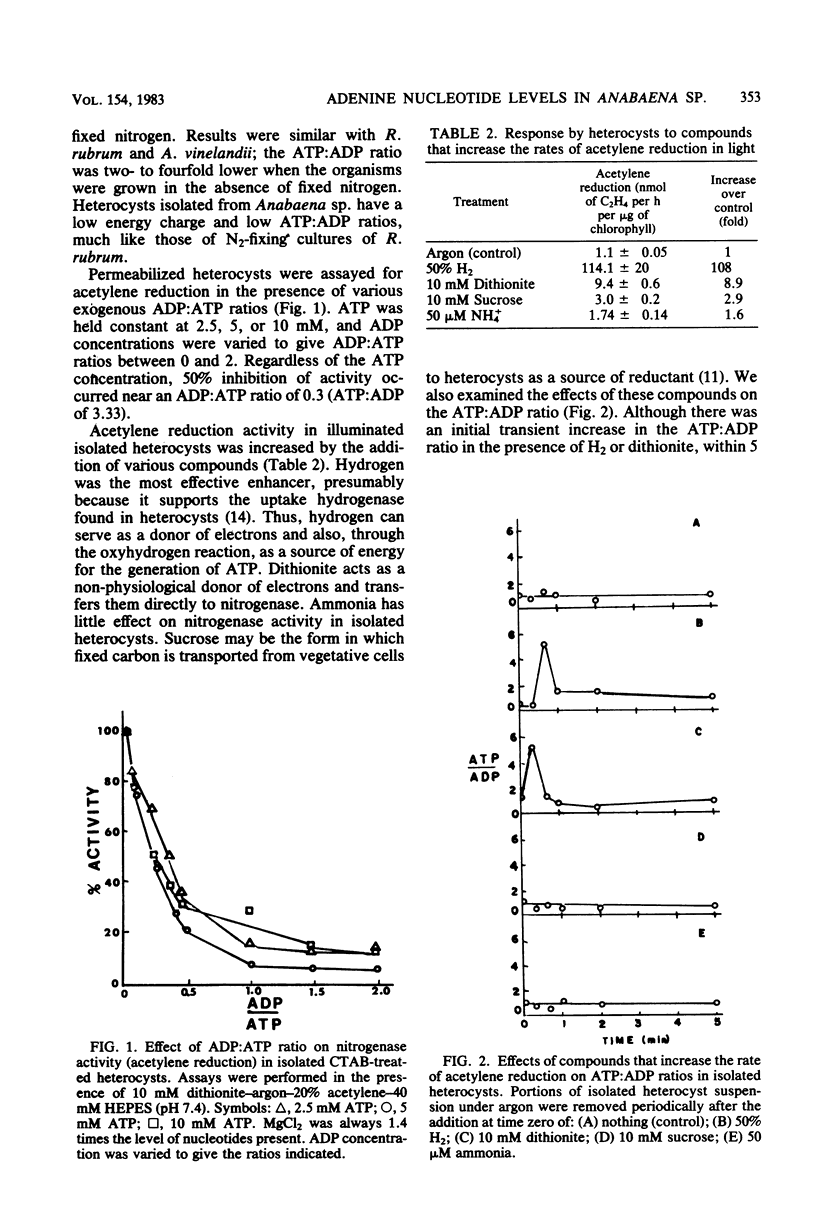
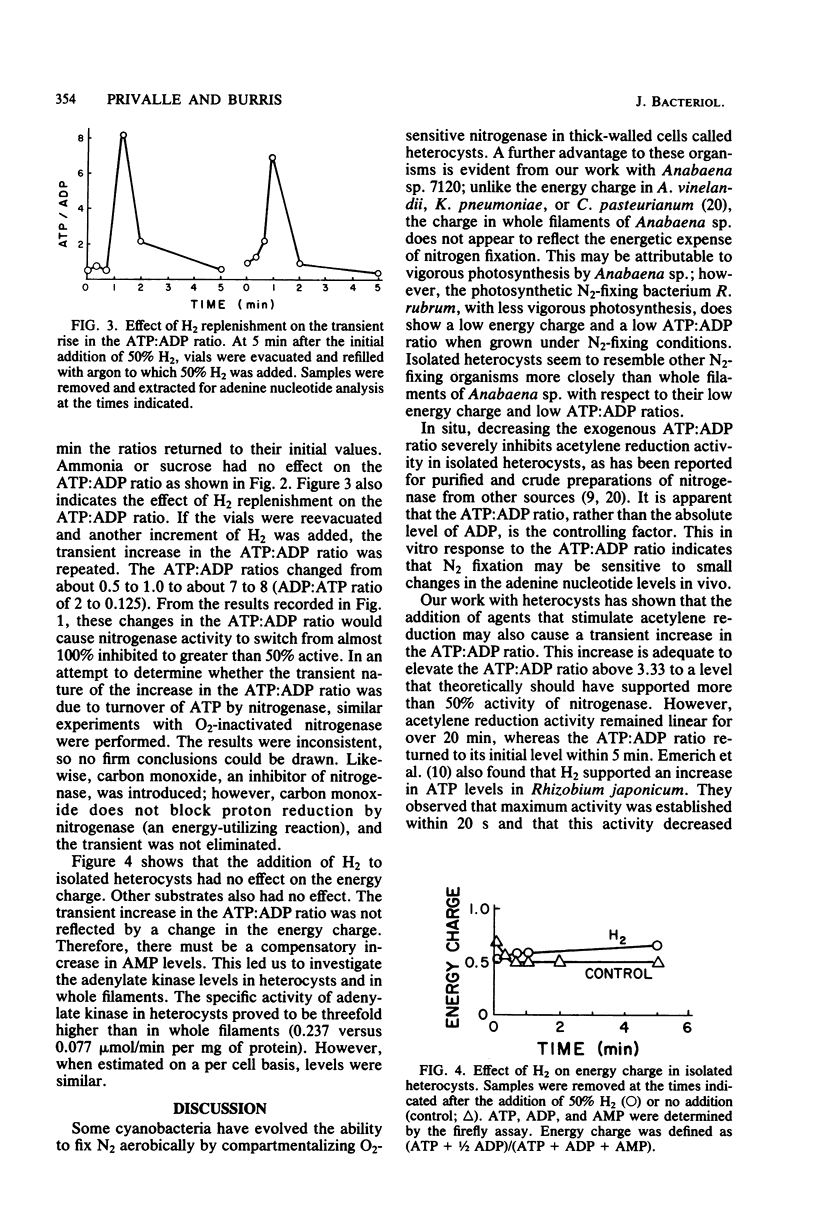
Adenine nucleotide levels were determined in whole filaments of Anabaena sp. 7120 grown under different N2-fixing or non-N2-fixing conditions. These were compared with levels in isolated heterocysts, Rhodospirillum rubrum, and Azotobacter vinelandii. Adenine nucleotides in whole filaments of Anabaena sp. do not reflect the energetic expense of N2 fixation as they do in R. rubrum and A. vinelandii. However, adenine nucleotide levels in heterocysts were similar to the levels found in N2-fixing R. rubrum, i.e., an ATP:ADP ratio near 1 and an energy charge between 0.5 and 0.7. Nitrogenase activity was only 50% of optimal in permeabilized heterocysts at an exogenous ATP:ADP ratio of 3.33. Hydrogen, which increases acetylene reduction activity, also causes a transient increase (2 to 5 min) in the ATP:ADP ratio. Hydrogen has little effect on energy charge.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. J., Stewart W. D. ATP pools and transientss in the blue-green alga, Anabaena cylindrica. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Jul;108(3):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00454849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill W. J. Biochemical genetics of nitrogen fixation. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Sep;44(3):449–467. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.3.449-467.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching T. M., Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L. Energy status, growth and nitrogenase activity in continuous cultures of Rhizobium sp. strain CB756 supplied with NH+4 and various rates of aeration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 12;636(1):82–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C., Kotake S. Regulation of nitrogenase activity in aerobes by Mg2+ availability: an hypothesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):934–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. C., Orhme-Johnson W. H. Nitrogenase IX. Effect of the MgATP generator on the catalytic and EPR properties of the enzyme in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 8;452(1):42–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Ruiz-Argüeso T., Ching T. M., Evans H. J. Hydrogen-dependent nitrogenase activity and ATP formation in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.153-160.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOA J. A micro biuret method for protein determination; determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1953;5(3):218–222. doi: 10.3109/00365515309094189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glembotski C. C., Chapman A. G., Atkinson D. E. Adenylate energy charge in Escherichia coli CR341T28 and properties of heat-sensitive adenylate kinase. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1374–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1374-1385.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houchins J. P., Burris R. H. Occurrence and localization of two distinct hydrogenases in the heterocystous cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain 7120. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):209–214. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.209-214.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T. Nitrogen fixation and bioenergetics: the role of ATP in nitrogenase catalysis. FEBS Lett. 1979 Feb 1;98(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori M., Hattori A. Transient change in the ATP pool of Anabaena cylindrica associated with ammonia assimilation. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):17–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00689345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandberg G. W., Wilson P. W. Formation of the nitrogen-fixing enzyme system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1139/m68-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet W. J., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase activity by NH+4 in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):824–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.824-831.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upchurch R. G., Mortenson L. E. In vivo energetics and control of nitrogen fixation: changes in the adenylate energy charge and adenosine 5'-diphosphate/adenosine 5'-triphosphate ratio of cells during growth on dinitrogen versus growth on ammonia. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):274–284. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.274-284.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


