Abstract
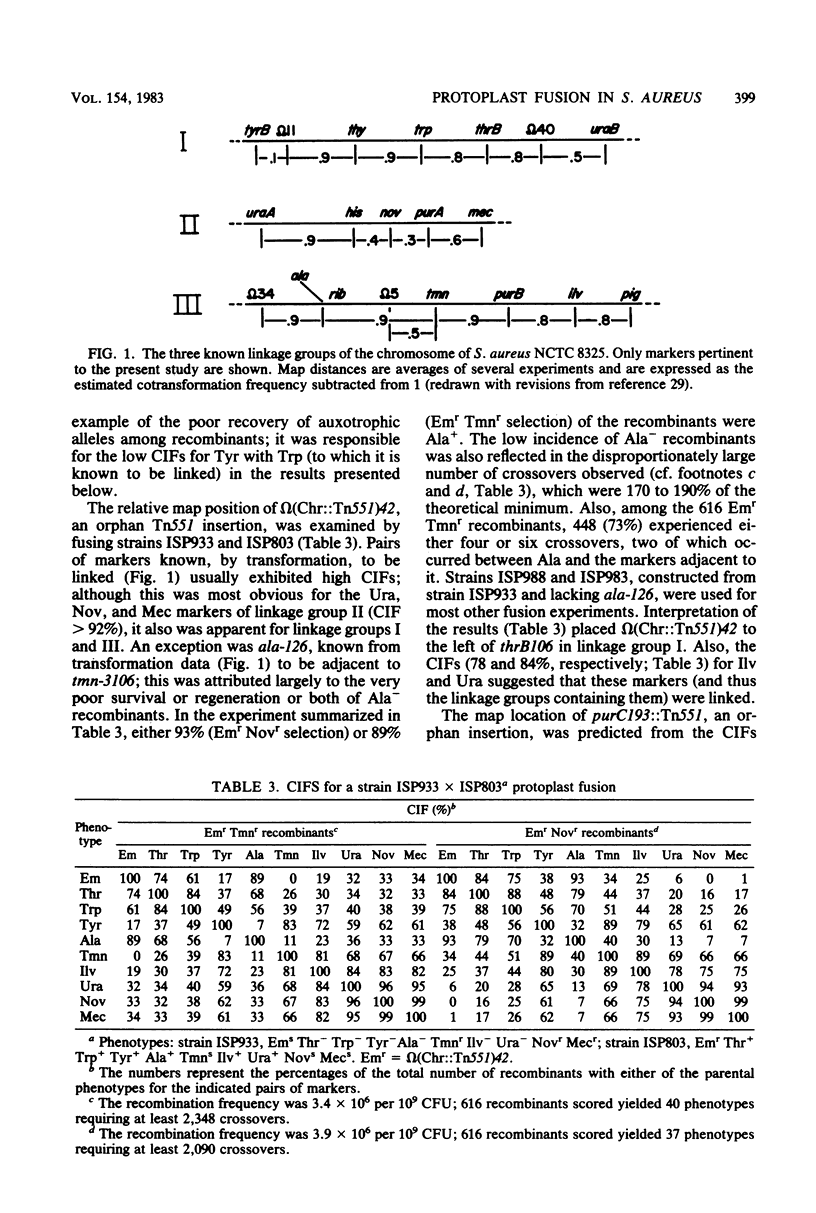
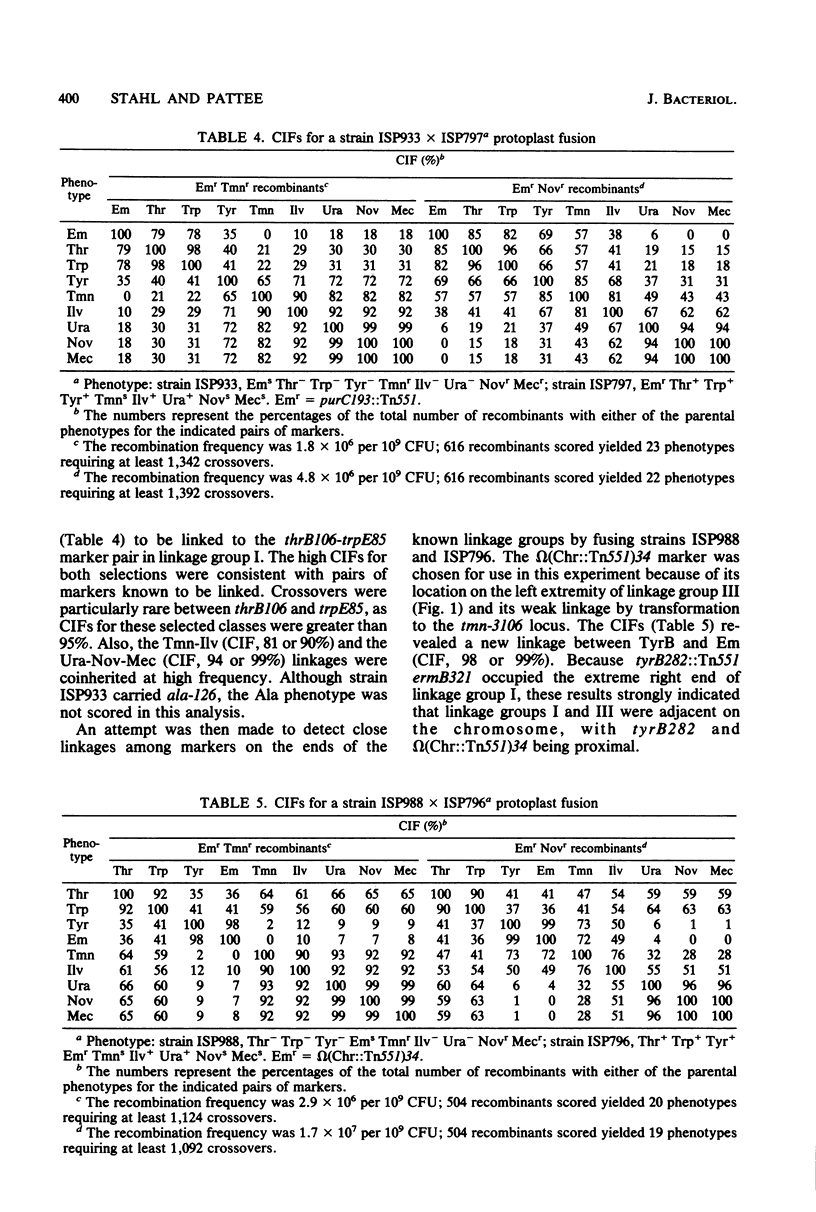
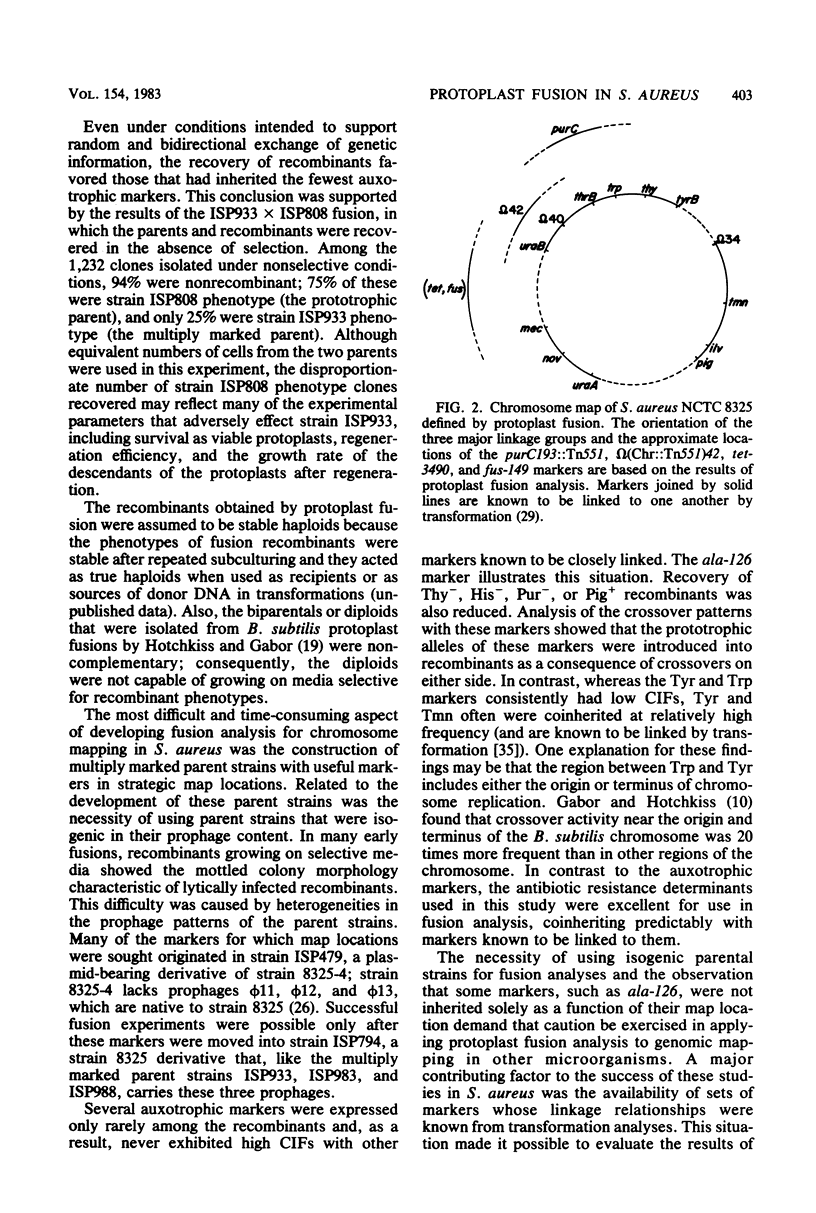
Protoplasts of genetically marked derivatives of Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8325 were fused with polyethylene glycol and regenerated without selection. Recombinants possessing one specific resistance marker from each parent were selected from the regenerated population and scored for seven or eight unselected markers. The results of these 9- and 10-factor crosses were entered directly into a programmed microcomputer from prescored replica plates. The data then were condensed into an array of phenotypes, together with the frequency with which each occurred. Further analyses by computer included the calculation of coinheritance frequencies for all possible pairs of markers; after entering a proposed order for the markers being analyzed, the minimum number of crossover events required to generate each phenotypic class was calculated. The linkage relationships of markers, based on the protoplast fusion data, were entirely consistent with the linkage relationships of markers already known to exist within each of the three linkage groups previously defined by transformation. The fusion data defined an arrangement of the three linkage groups into a circular chromosome map and predicted the approximate location of four previously unmapped markers (tet-3490, fus-149, purC193::Tn551, and omega [Chr::Tn551]42) on this map.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltz R. H. Genetic recombination in Streptomyces fradiae by protoplast fusion and cell regeneration. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Jul;107(1):93–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-107-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz R. H., Matsushima P. Protoplast fusion in Streptomyces: conditions for efficient genetic recombination and cell regeneration. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Nov;127(1):137–146. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Pattee P. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of alpha-toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):36–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.36-42.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Sirgel F. A., Lecatsas G. Genetic recombination in fused spheroplasts of Providence alcalifaciens. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):313–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCastro-Costa M. R., Landman O. E. Inhibitory protein controls the reversion of protoplasts and L forms of Bacillus subtilis to the walled state. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):678–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.678-689.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Fusion of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2147–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Polyethylene-glycol induced fusion of bacterial protoplasts: direct selection of recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):55–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00267933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey O., Ford L., Huber M. L. Interspecies matings of Streptomyces fradiae with Streptomyces bikiniensis mediated by conventional and protoplast fusion techniques. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Aug;24(8):994–997. doi: 10.1139/m78-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Ahrné S., Lindberg M. Plasmid transfer and genetic recombination by protoplast fusion in staphylococci. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.74-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirachi Y., Kurono M., Kotani S. Further evidence of polyethylene glycol-induced cell fusion of Staphylococcus aureus L-forms. Biken J. 1980 Mar;23(1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirachi Y., Kurono M., Kotani S. Polyethylene glycol-induced fusion of L-forms of Staphylococcus aureus. Biken J. 1979 Mar;22(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. Genetic studies with bacterial protoplasts. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:237–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M. Bacterial protoplast fusion: recombination in fused protoplasts of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 4;162(3):307–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00268856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Wright H. M., Bibb M. J., Cohen S. N. Genetic recombination through protoplast fusion in Streptomyces. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):171–174. doi: 10.1038/268171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D., Gabor M. H. Biparental products of bacterial protoplast fusion showing unequal parental chromosome expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3553–3557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl S. A., Pattee P. A., Baldwin J. N. Chromosomal map location of the methicillin resistance determinant in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):460–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.460-465.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg M., Sjöström J. E., Johansson T. Transformation of chromosomal and plasmid characters in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):844–847. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.844-847.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. L. TRANSDUCTION BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL BACTERIOPHAGE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 May;45(5):722–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Edelman I., Schwesinger M. D., Gruss A. D., Swanson E. C., Pattee P. A. Genetic translocation in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Studies on plasmid replication. III. Isolation and characterization of replication-defective mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(2):131–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00264781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A. Distribution of Tn551 insertion sites responsible for auxotrophy on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):479–488. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.479-488.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Glatz B. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of enterotoxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):186–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.186-193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A., Thompson N. E., Haubrich D., Novick R. P. Chromosomal map locations of integrated plasmids and related elements in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITZ H. L., BALDWIN J. N. A transduction analysis of complex loci governing the synthesis of tryptophan by Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:667–671. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Cami B., Hotchkiss R. D. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Pattee P. A. Confirmation of protoplast fusion-derived linkages in Staphylococcus aureus by transformation with protoplast DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):406–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.406-412.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



