Abstract
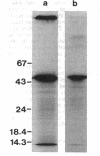
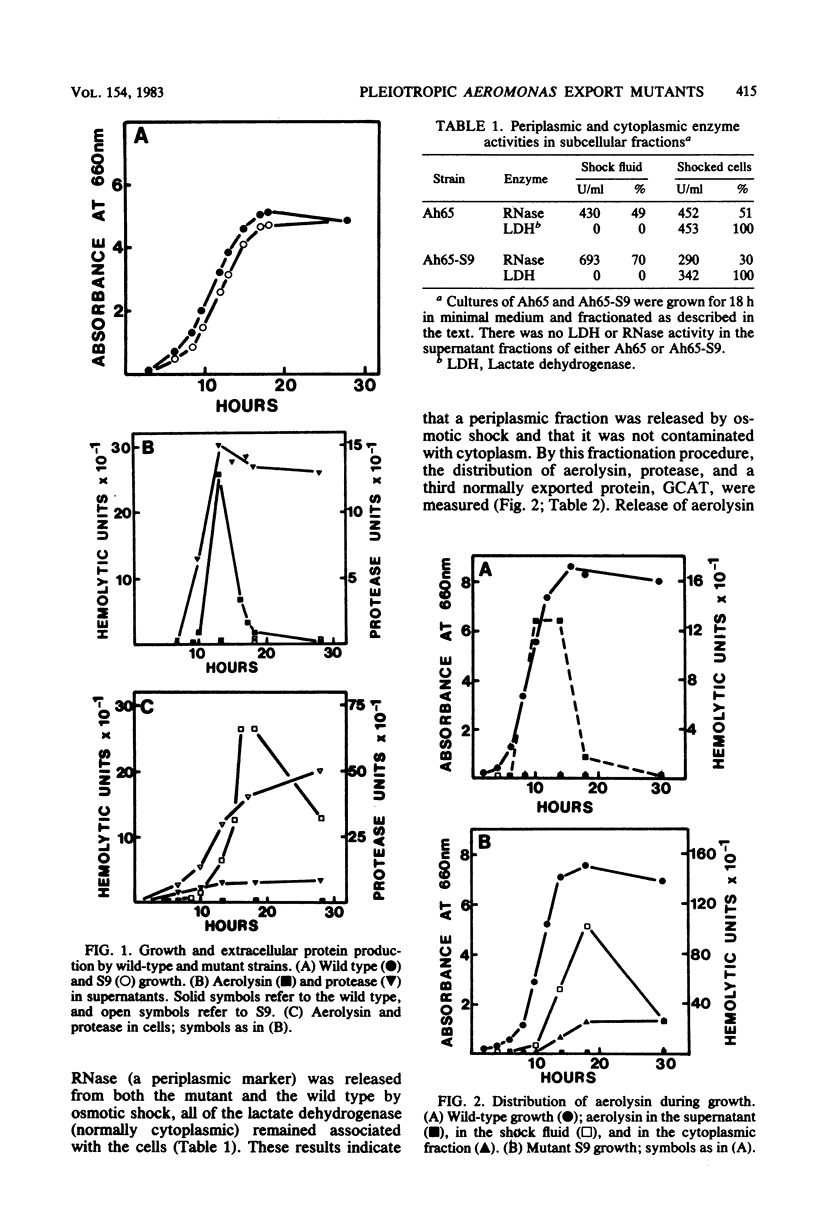
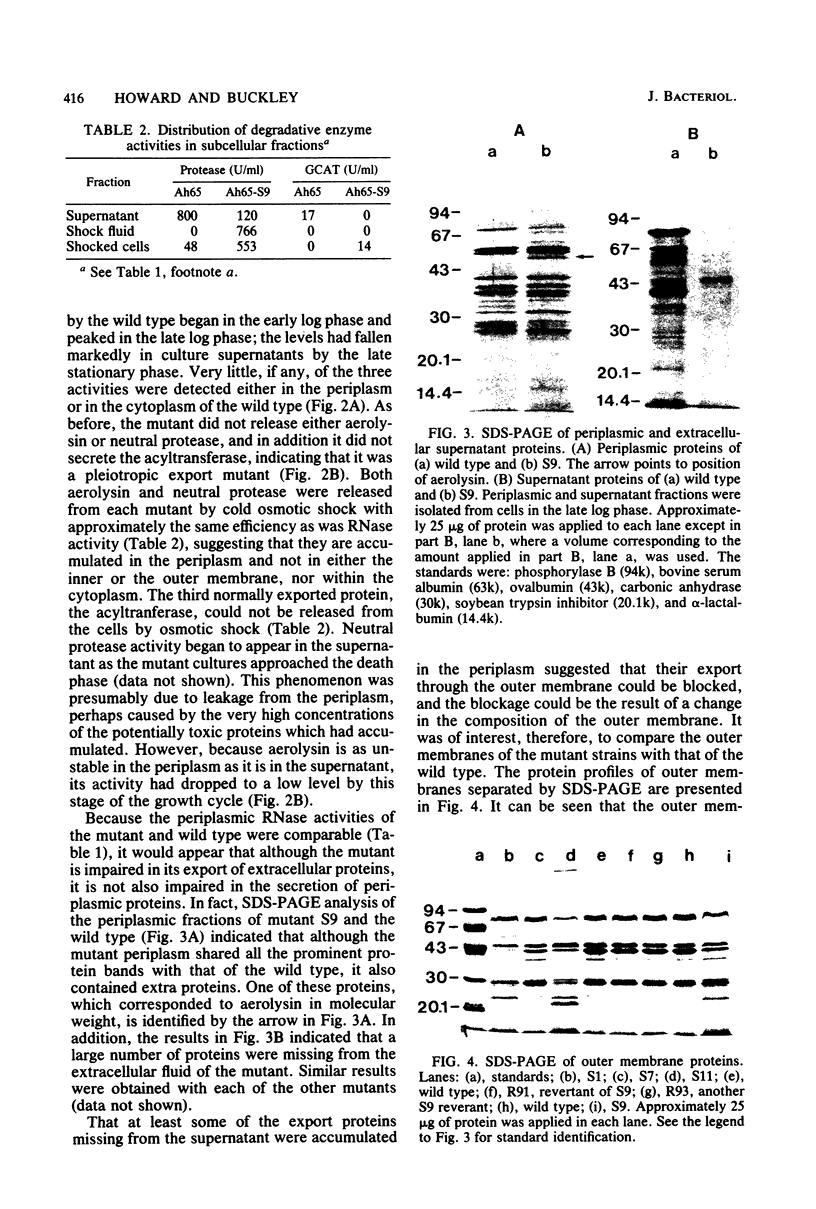
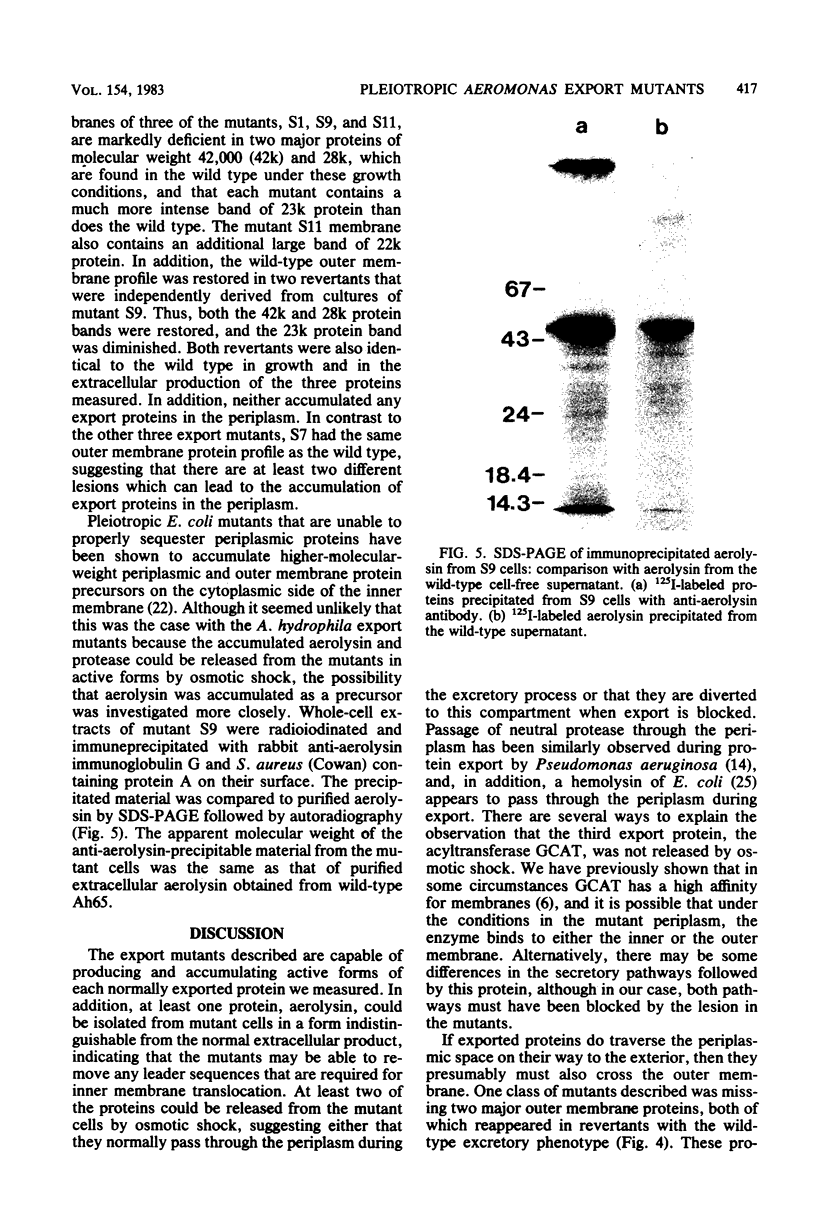
Pleiotropic export mutants of Aeromonas hydrophila were obtained which are unable to release protease, hemolysin, and glycerophospholipid:cholesterol acyltransferase. The synthesis of the proteins was not impaired; they were accumulated in active forms inside the mutant cells. The hemolysin could be isolated from cell contents by immunoprecipitation in a form with the same apparent molecular weight as the wild-type extracellular product, as determined by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Because both the protease and the hemolysin could be released from the mutant cells by osmotic shock, it was concluded that they were accumulated in the periplasmic space. Some mutants were missing two major outer membrane proteins, both of which reappeared in revertants with the wild-type excretory phenotype. Another mutant class had a normal outer membrane protein profile. That two different mutant classes could be obtained indicates that at least two gene products may be needed for export after protein translocation through the inner membrane. The accumulation of proteins which can be released by osmotic shock suggests that the periplasm may be part of the normal route for protein export.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annapurna E., Sanyal S. C. Enterotoxicity of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):317–323. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S., Avigad G. Interactions between aerolysin, erythrocytes, and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1312–1319. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1312-1319.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Halasa L. N., Lund K. D., MacIntyre S. Purification and some properties of the hemolytic toxin aerolysin. Can J Biochem. 1981 Jun;59(6):430–435. doi: 10.1139/o81-059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley J. T., Halasa L. N., MacIntyre S. Purification and partial characterization of a bacterial phospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3320–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Weiss J., Konrad M., White T., Bahl C., Yu S. D., Marks D., Steiner D. F. Biosynthesis and periplasmic segregation of human proinsulin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5401–5405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filip C., Fletcher G., Wulff J. L., Earhart C. F. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by the ionic detergent sodium-lauryl sarcosinate. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.717-722.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. L., Berka R. M., Vasil M. L. A Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutant non-derepressible for orthophosphate-regulated proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):675–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.675-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard S. P., Buckley J. T. Membrane glycoprotein receptor and hole-forming properties of a cytolytic protein toxin. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1662–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Halegoua S. Secretion and membrane localization of proteins in Escherichia coli. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1980;7(4):339–371. doi: 10.3109/10409238009105465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen S. E., Fecycz I. T., Stemke G. W., Campbell J. N. Demonstration of a cell-associated, inactive precursor of an exocellular protease produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Jan;26(1):87–93. doi: 10.1139/m80-013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIN E. C., LERNER S. A., JORGENSEN S. E. A method for isolating constitutive mutants for carbohydrate-catabolizing enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 2;60:422–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Gottfried S., Rothfield L. Leakage of periplasmic enzymes by mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of "periplasmic leaky" mutants. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):520–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.520-525.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Buckley J. T. Presence of glycerophospholipid: cholesterol acyltransferase and phospholipase in culture supernatant of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):402–407. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.402-407.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre S., Trust T. J., Buckley J. T. Identification and characterization of outer membrane fragments released by Aeromonas sp. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):1018–1025. doi: 10.1139/o80-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord C. E., Sjöberg L., Wadström T., Wretlind B. Characterization of three Aeromonas and nine pseudomonas species by extracellular enzymes and haemolysins. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1975;161(2):79–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02121748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes by osmotic shock from Escherichia coli in exponential phase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver D. B., Beckwith J. E. coli mutant pleiotropically defective in the export of secreted proteins. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):765–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz D., Scharmann W., Blobel H. Leucocidic substances for Aeromonas hydrophila. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;228(3):312–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W., Goebel W. Synthesis and secretion of hemolysin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):53–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.53-59.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stambaugh R., Post D. Substrate and product inhibition of rabbit muscle lactic dehydrogenase heart (H4) and muscle (M4) isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1462–1467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Ljungh A., Wretlind B. Enterotoxin, haemolysin and cytotoxic protein in Aeromonas hydrophila from human infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):112–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Hedén L., Wadström T. Formation of extracellular haemolysin by Aeromonas hydrophila in relation to protease and staphylolytic enzyme. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Sep;78(1):57–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-78-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Möllby R., Wadström T. Separation of two hemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila by isoelectric focusing. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):503–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.503-505.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato I., Anraku Y., Hirosawa K. Cytoplasmic membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. A simple method for preparing the cytoplasmic and outer membranes. J Biochem. 1975 Apr;77(4):705–718. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]