Abstract
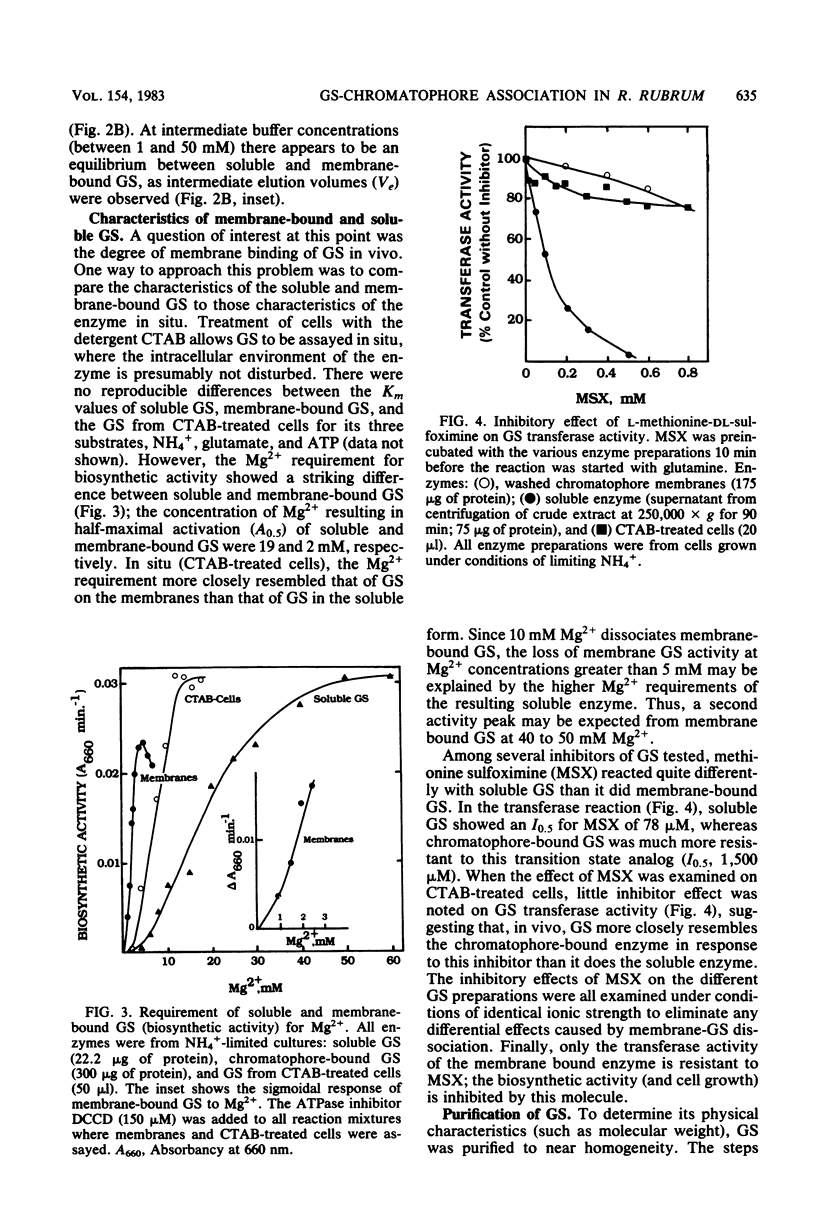
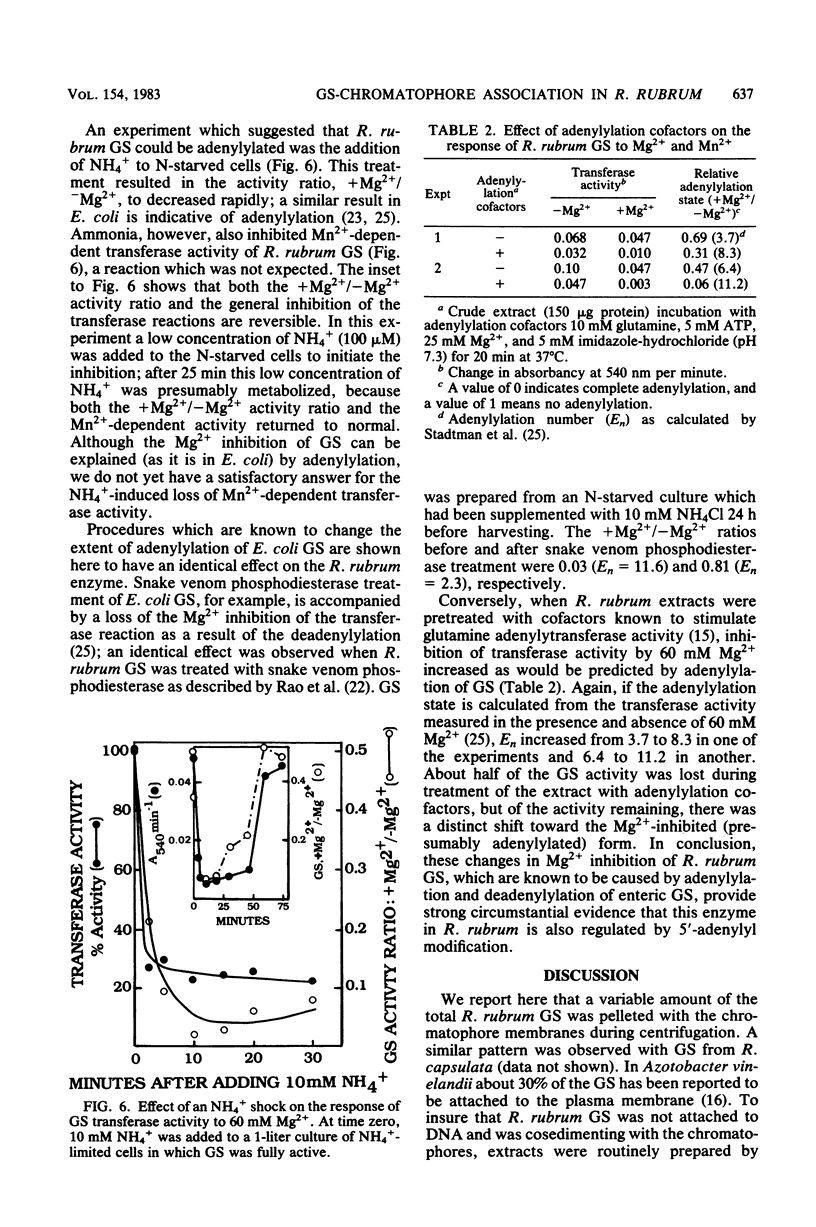
The characteristics of soluble and membrane-bound glutamine synthetase (GS) from Rhodospirillum rubrum were compared with those of the enzyme located in situ (measured in detergent-treated cells). The results suggest that in vivo GS may be associated with, or bound to, the chromatophore membranes. GS was found to reversibly associate and dissociate from purified chromatophores as a function of the ionic strength of the buffer or the Mg2+ concentration. Solubilized GS was purified to homogeneity and found to be similar to the GS of enteric bacteria in that its molecular weight was about 600,000 and it had one type of subunit of 51,000 molecular weight. Removal of GS from the membrane had no effect on the Km values for the substrates of the biosynthetic reaction, but it did have a substantial effect on both its Mg2+ requirement (the Km increased 10-fold) and the sensitivity of the gamma-glutamyl transferase reaction to the inhibitor methionine sulfoximine (the I0.5 decreased from 1,500 to 60 microM). Both observations suggest that the active site of GS is influenced by its association with the membrane. GS activity was shown to respond to NH4+, phosphodiesterase, Mg2+, and adenylylation cofactors in a manner identical to that of the GS of the coliform bacteria, suggesting that the former may also respond to adenylylation and deadenylylation. Finally, R. rubrum GS was also inhibited by NH4+ by a newly observed, as yet undefined, system.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alef K., Burkardt H. J., Horstmann H. J., Zumft W. G. Molecular characterization of glutamine synthetase from the nitrogen-fixing phototrophic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Z Naturforsch C. 1981 Mar-Apr;36(3-4):246–254. doi: 10.1515/znc-1981-3-411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Two forms of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Kaplan S. Isolation and fractionation of the photosynthetic membranous organelles from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):465–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.465-473.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert R. A., Siefert E., Pfennig N. Nitrogen assimilation in Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00407919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Adenylylation/deadenylylation control of the glutamine synthetase of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Kleiner D. The glutamine synthetase from Azotobacter vinelandii: purification, characterization, regulation and localization. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H., Shimizu M., Valentine R. C. The mechanism of ammonia assimilation in nitrogen fixing Bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(2):164–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00424923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman R. A. Membranes of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: interactions of chromatophores with the cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):19–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.19-28.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. R., Darrow R. A., Keister D. L. Effect of oxygen tension on nitrogenase and on glutamine synthetases I and II in Rhizobium jaonicum 61A76. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 15;81(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt H., Holzer H. Biological function of the ammonia-induced inactivation of glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):68–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Ginsburg A., Ciardi J. E., Yeh J., Hennig S. B., Shapiro B. M. Multiple molecular forms of glutamine synthetase produced by enzyme catalyzed adenylation and deadenylylation reactions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:99–118. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Tyler B. Purification of glutamine synthetase from a variety of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):69–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.69-78.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WORDEN P. B., SISTROM W. R. THE PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF BACTERIAL CHROMATOPHORE FRACTIONS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:135–150. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare N. M., Shanmugam K. T. Photoproduction of ammonium ion from N2 in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00690229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolfolk C. A., Shapiro B., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. I. Purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):177–192. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Cantu M. Changes in the regulatory form of Rhodospirillum rubrum nitrogenase as influenced by nutritional and environmental factors. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.899-907.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C. Manganese, an essential trace element for N2 fixation by Rhodospirillum rubrum and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata: role in nitrogenase regulation. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):987–995. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.987-995.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




