Abstract
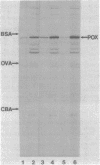
Mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 deficient in pyruvate oxidase were isolated from an aceEF (pyruvate dehydrogenase-deficient) strain by selection for a complete absence of growth on medium lacking acetate. Extracts of two of the mutants were shown to contain normal levels of pyruvate oxidase antigen, although the enzymatic activities of the extracts were reduced or absent. The poxB locus was mapped by using closely linked transposon insertions to min 18.7 of the E. coli linkage map between the cmlA and aroA loci, a location far removed from that of the regulatory gene, poxA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Jones-Mortimer M. C., Kornberg H. L. The enzymic interconversion of acetate and acetyl-coenzyme A in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Oct;102(2):327–336. doi: 10.1099/00221287-102-2-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber J. P. Radioimmunoassay of polypeptide hormones and enzymes. Methods Biochem Anal. 1974;22:1–94. doi: 10.1002/9780470110423.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feutrier J., Lepelletier M., Pascal M. C., Chippaux M. Tn10 insertions directed in the pyr D - ser C region and improved mapping of pep N in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):518–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00334153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNING U. EIN REGULATIONSMECHANISMUS BEIM ABBAU DER BRENZTRAUBENSAEURE DURCH ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochem Z. 1963 Jul 26;337:490–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNING U., HERZ C. EIN STRUKTURGEN-KOMPLEX FUER DEN PYRUVAT-DEHYDROGENASE-KOMPLEX VON ESCHERICHIA COLI K 12. Z Vererbungsl. 1964 Nov 11;95:260–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Roth J. Electrolyte effects on the activity of mutant enzymes in vivo and in vitro. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1386–1392. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeMaster D. M., Cronan J. E., Jr Biosynthetic production of 13C-labeled amino acids with site-specific enrichment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M. Immunoaffinity chromatography of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:723–731. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Rapid mapping of conditional and auxotrophic mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):798–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.798-812.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low K. B. Escherichia coli K-12 F-prime factors, old and new. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):587–607. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.587-607.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather M., Blake R., Koland J., Schrock H., Russell P., O'Brien T., Hager L. P., Gennis R. B., O'Leary M. Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase: interaction of a peripheral membrane protein with lipids. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):87–88. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84613-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recny M. A., Hager L. P. Reconstitution of native Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase from apoenzyme monomers and FAD. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12878–12886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve E. C., Suttie D. R. Chromosomal location of a mutation causing chloramphenicol resistance in Escherichia coli K 12. Genet Res. 1968 Feb;11(1):97–104. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Schrock H. L., Gennis R. B. Lipid activation and protease activation of pyruvate oxidase. Evidence suggesting a common site of interaction on the protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7883–7887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrock H. L., Gennis R. B. High affinity lipid binding sites on the peripheral membrane enzyme pyruvate oxidase. Specific ligand effects on detergent binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5990–5995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. R., Hager L. P. Crystalline flavin pyruvate oxidase from Escherichia coli. I. Isolation and properties of the flavoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C., LENNOX E. S. Transduction and recombination study of linkage relationships among the genes controlling tryptophan synthesis in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1959 Aug;8:425–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]