Abstract
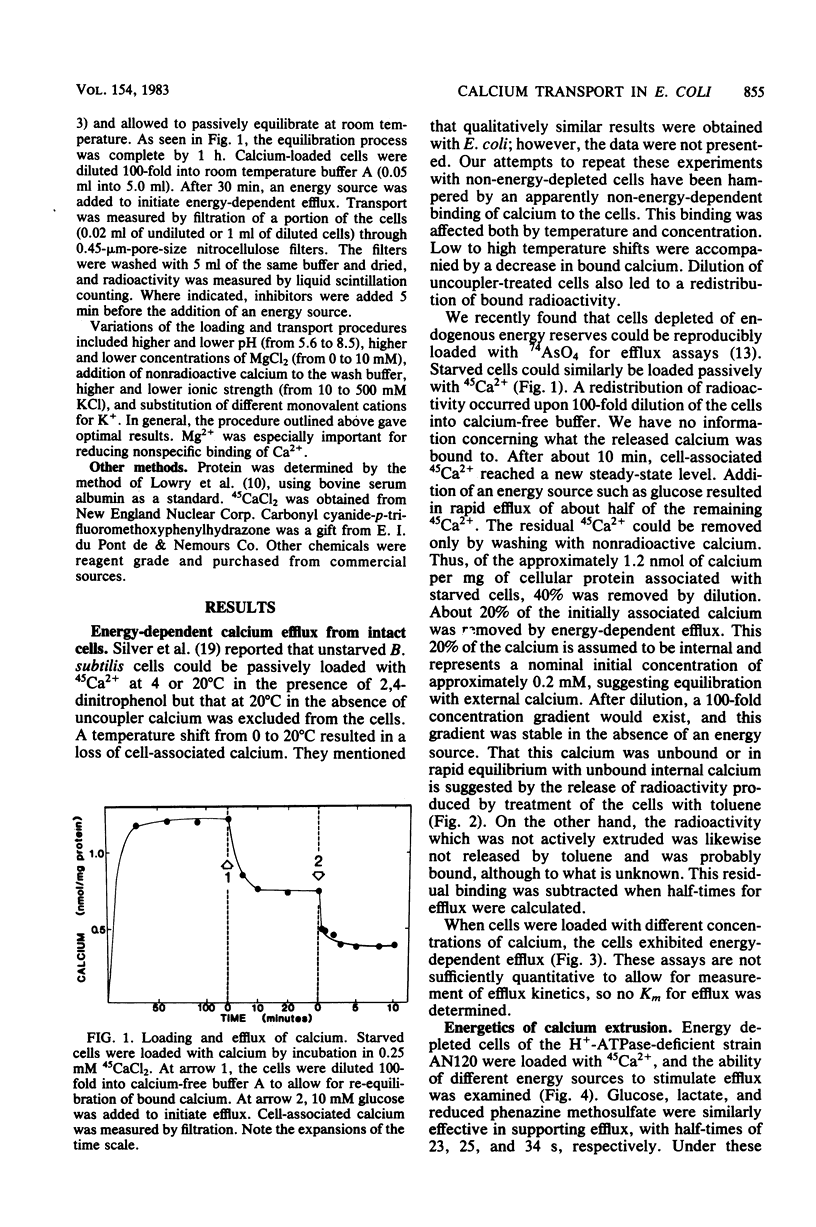
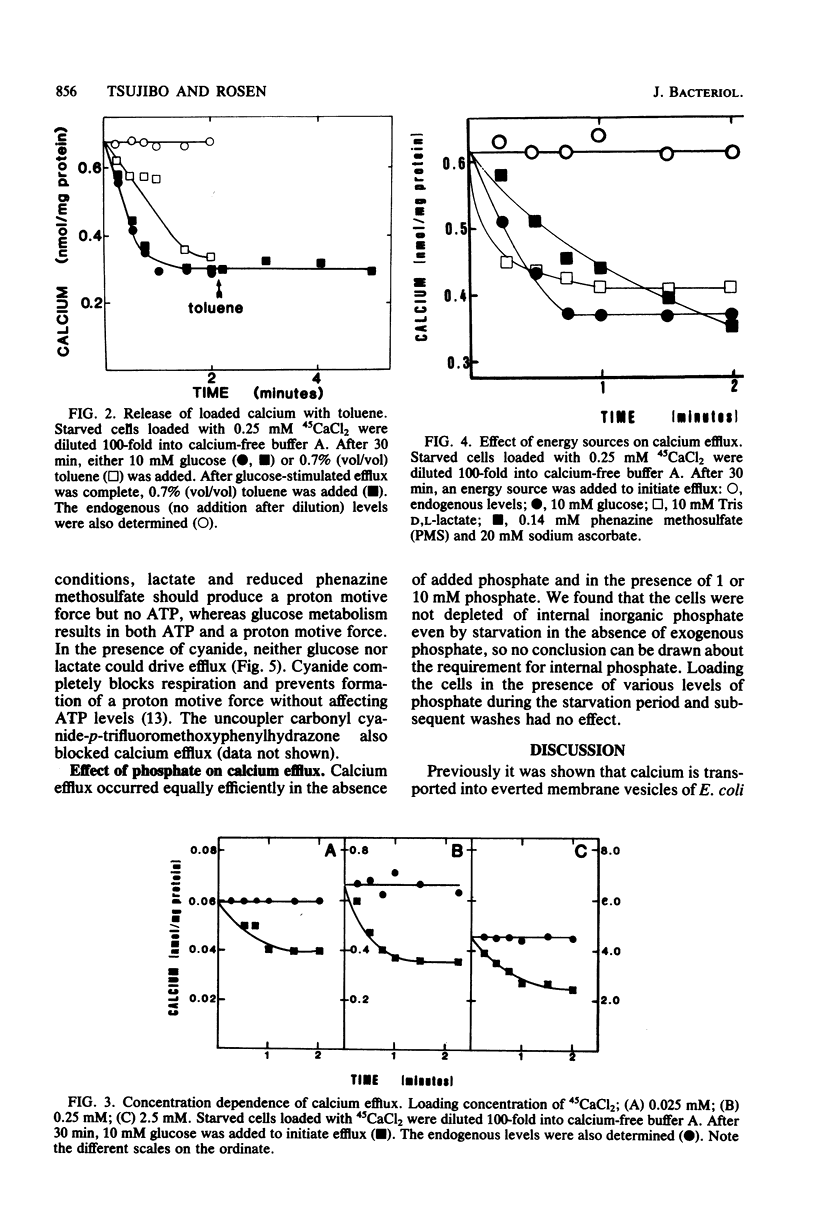
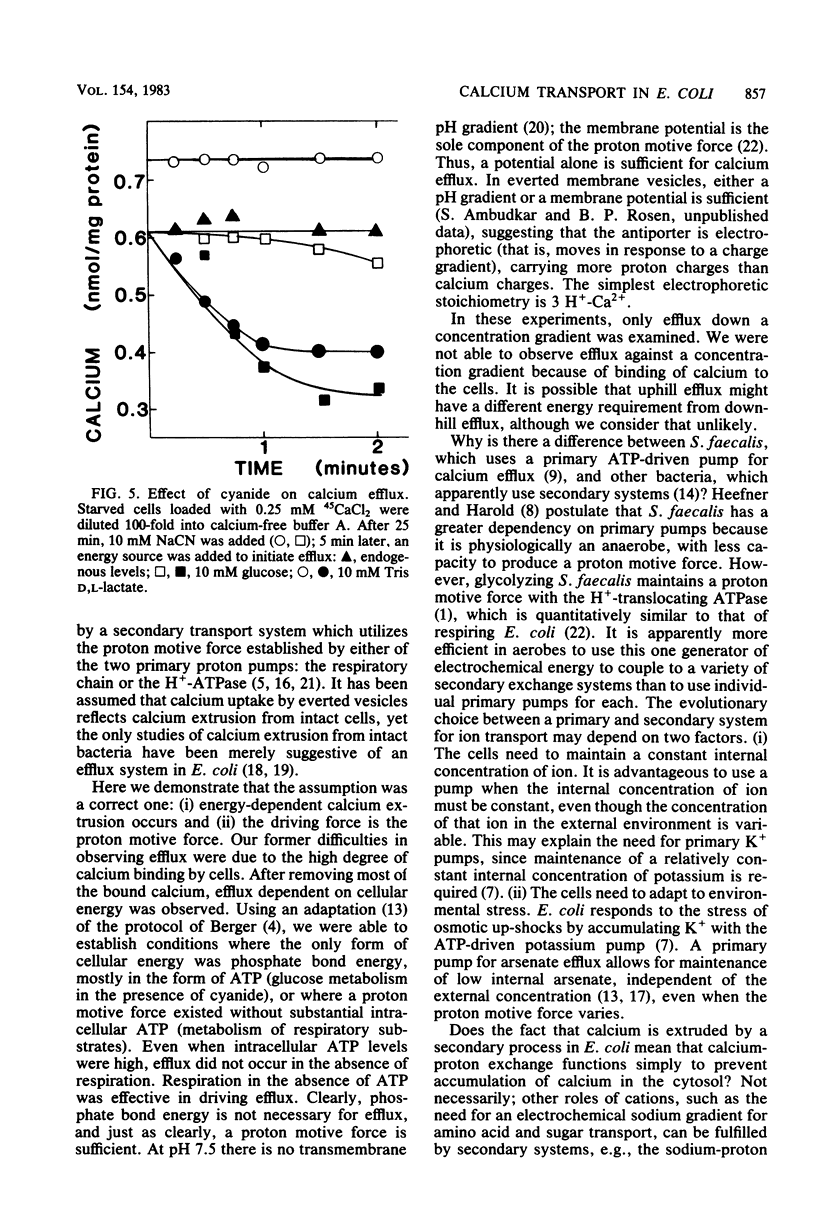
Intact cells of a H+-translocating ATPase-deficient strain of Escherichia coli were starved of endogenous energy reserves and passively loaded with 45CaCl2. Energy-dependent efflux of calcium was observed upon addition of glucose or respiratory substrates. Addition of cyanide or uncouplers prevented efflux. It is concluded that calcium efflux in intact cells is coupled to the proton motive force via secondary calcium-proton exchange.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. C., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in escherichia coli: properties of the sodium/proton antiporter. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belliveau J. W., Lanyi J. K. Calcium transport in Halobacterium halobium envelope vesicles. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):98–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A. Different mechanisms of energy coupling for the active transport of proline and glutamine in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1514–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the calcium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1957–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butlin J. D., Cox G. B., Gibson F. Oxidative phosphorylation in Escherichia coli K12. Mutations affecting magnesium ion- or calcium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):75–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1240075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Harold F. M. ATP-driven sodium pump in Streptococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2798–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. ATP-linked calcium transport in cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley H. L., Rosen B. P. Energetics of plasmid-mediated arsenate resistance in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6119–6122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P., McClees J. S. Active transport of calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5042–5046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Keach D. Energy-dependent arsenate efflux: the mechanism of plasmid-mediated resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Kralovic M. L. Manganese accumulation by Escherichia coli: evidence for a specific transport system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 10;34(5):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90786-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Toth K., Scribner H. Facilitated transport of calcium by cells and subcellular membranes of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):880–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.880-885.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonczewski J. L., Rosen B. P., Alger J. R., Macnab R. M. pH homeostasis in Escherichia coli: measurement by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of methylphosphonate and phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6271–6275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya T., Rosen B. P. Characterization of an active transport system for calcium in inverted membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7687–7692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S., Padan E. Proton electrochemical gradient in Escherichia coli cells and its relation to active transport of lactose. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):669–673. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



