Abstract
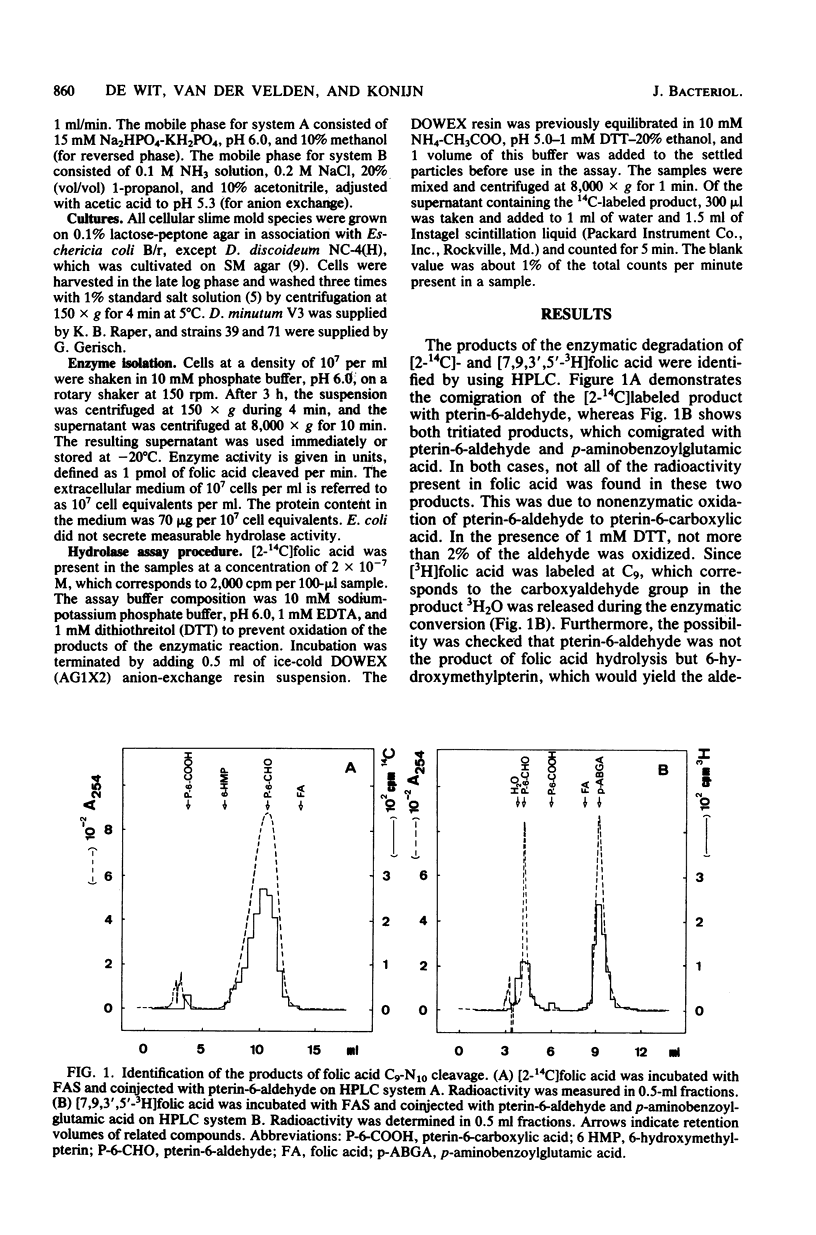
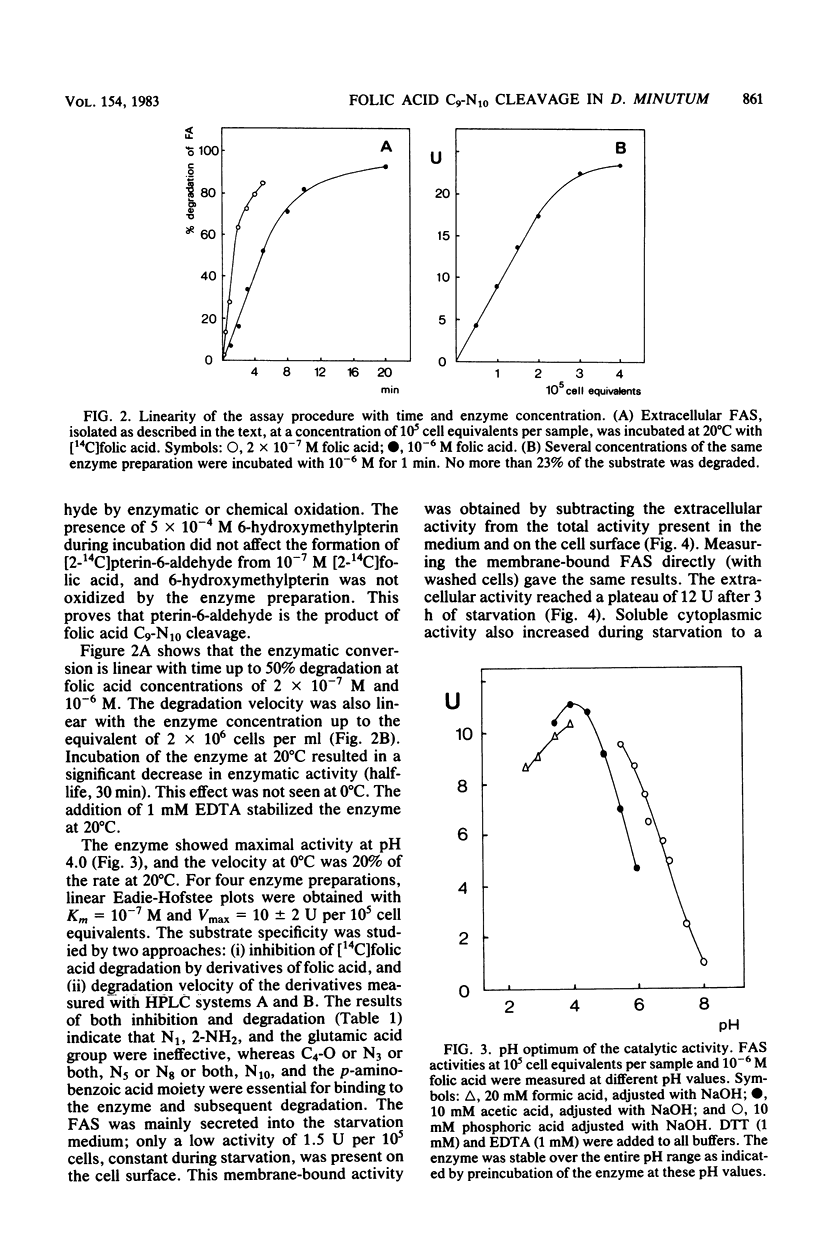
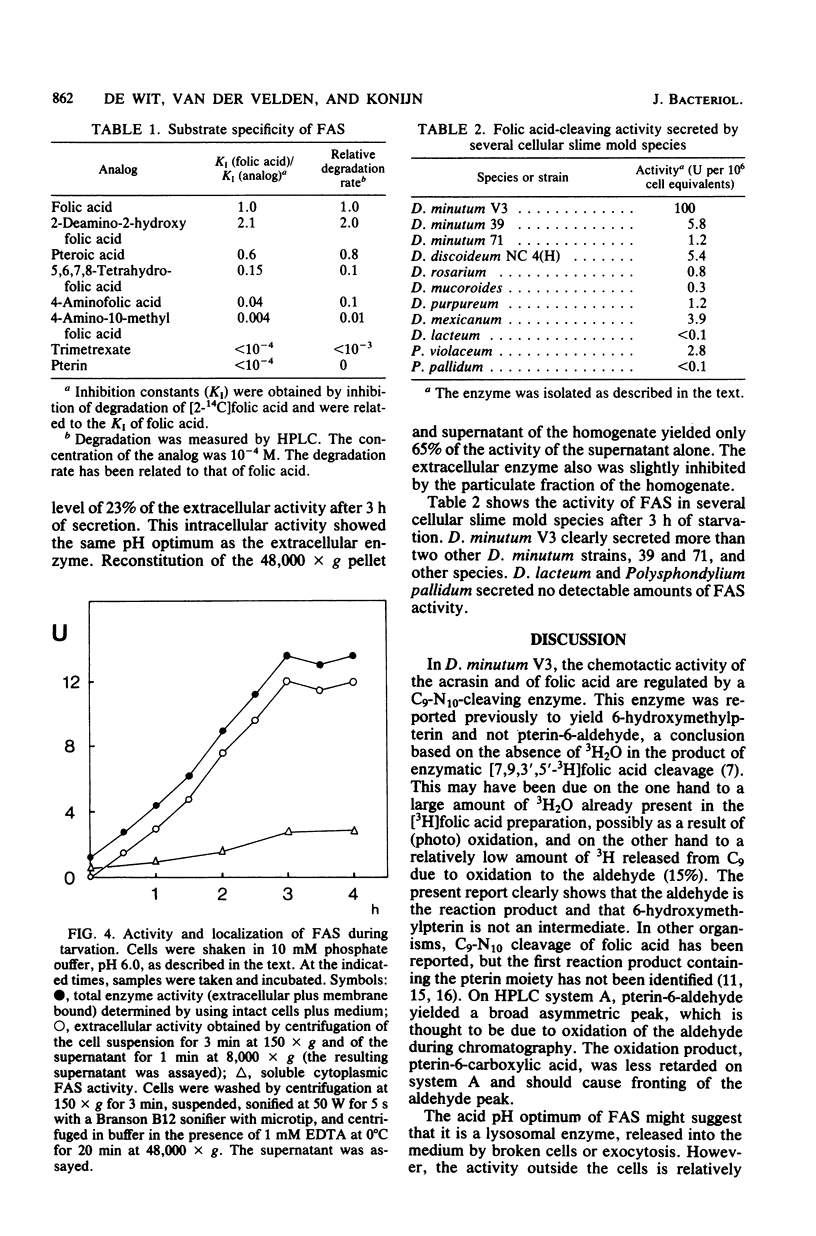
Folic acid is a chemoattractant for the slime mold Dictyostelium minutum V3. The activity of extracellular folic acid is regulated by a folic acid C9-N10 splitting enzyme (FAS). The products were identified as pterin-6-aldehyde and p-amino-benzoylglutamic acid. The enzyme was stabilized by EDTA. For the extracellular enzyme, the Km was 10(-7) M, and the optimal pH was 4.0. During starvation, FAS activity was mainly secreted into the medium; after 3 h, a plateau was reached. The membrane-bound activity was constant, but only 12% of the extracellular activity at 3 h. Intracellular activity also increased up to 3 h to a level of 23% of the extracellular FAS. The substrate recognition of FAS was found to be based on 4-O or N3 or both, N5 or N8 or both, N10, and the p-aminobenzoic acid moiety, whereas 2-NH2, N1, and the glutamic acid moiety were not recognized. Other slime mold species were found to secrete FAS with 20-fold or more reduced activity than D. minutum V3.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkley D. S. Adenosine-3',5'-phosphate: identification as acrasin in a species of cellular slime mold. Science. 1969 Sep 12;165(3898):1133–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3898.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. L., Rossier C., van Driel R., Brunner M., Gerisch G. Folate deaminase and cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium discoideum: their regulation by extracellular cyclic AMP and folic acid. Cell Differ. 1981 Mar;10(2):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(81)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. L., Tabler M., Vestweber D., Van Driel R. Extracellular folate deaminase of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 12;677(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S., Hall E. M., Konijn T. M., Mason J. W., O'Keefe G., 3rd, Wolfe P. B. Acrasin, Acrasinase, and the sensitivity to acrasin in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1969 Jul;20(1):72–87. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIJN T. M., RAPER K. B. Cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1961 Dec;3:725–756. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(61)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakebeeke P. I., de Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. A novel chemotaxis regulating enzyme that splits folic acid into 6-hydroxymethylpterin and P-aminobenzoylgutamic acid. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakebeeke P. I., de Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. Folic acid deaminase activity during development in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):307–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.307-312.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M., Boyle P. H., Weir D. G., Scott J. M. The identification of the products of folate catabolism in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1978 Feb;38(2):211–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb01037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Determination of the active portion of the folic acid molecule in cellular slime mold chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.185-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Folic acid as second chemotactic substance in the cellular slime moulds. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):181–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio237181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Wurster B. Inactivation of the chemoattractant folic acid by cellular slime molds and identification of the reaction product. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):955–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.955-959.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold H., Bacher A. Bacterial degradation of folic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):283–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea B., Backlund P. S., Jr, Berkey P. B., Cho A. K., Halpern B. C., Halpern R. M., Smith R. A. Folate and pterin metabolism by cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J., Grijpma Y., Konijn T. M. Identification of a pterin as the acrasin of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium lacteum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6270–6274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Bek F., Butz U. Folic acid and pterin deaminases in Dictyostelium discoideum: kinetic properties and regulation by folic acid, pterin, and adenosine 3',5'-phosphate. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):183–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.183-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Pan P., Tyan G. G., Bonner J. T. Preliminary characterization of the acrasin of the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium violaceum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):795–799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. Identification of the acrasin of Dictyostelium minutum as a derivative of folic acid. Cell Differ. 1983 Apr;12(4):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(83)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. Antagonists of chemoattractants reveal separate receptors for cAMP, folic acid and pterin in Dictyostelium. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Aug;140(2):453–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



