Abstract
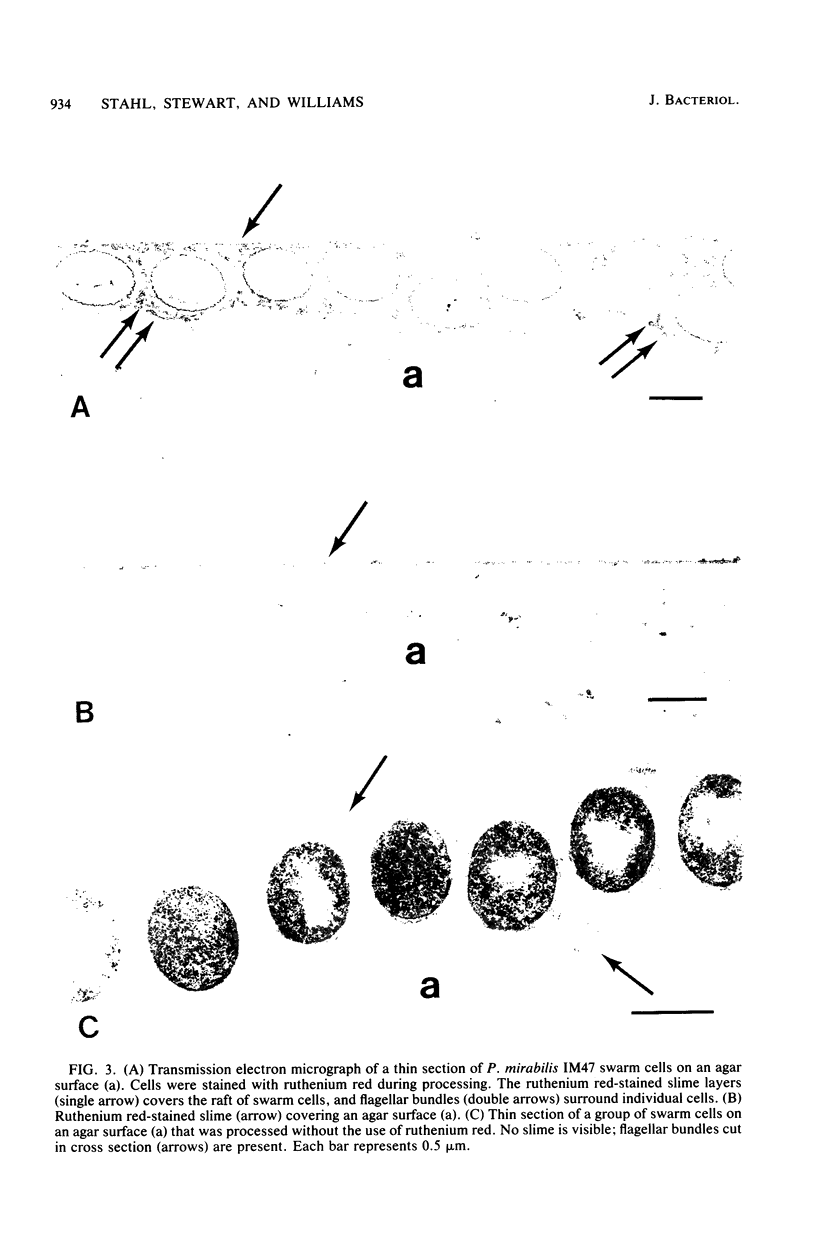
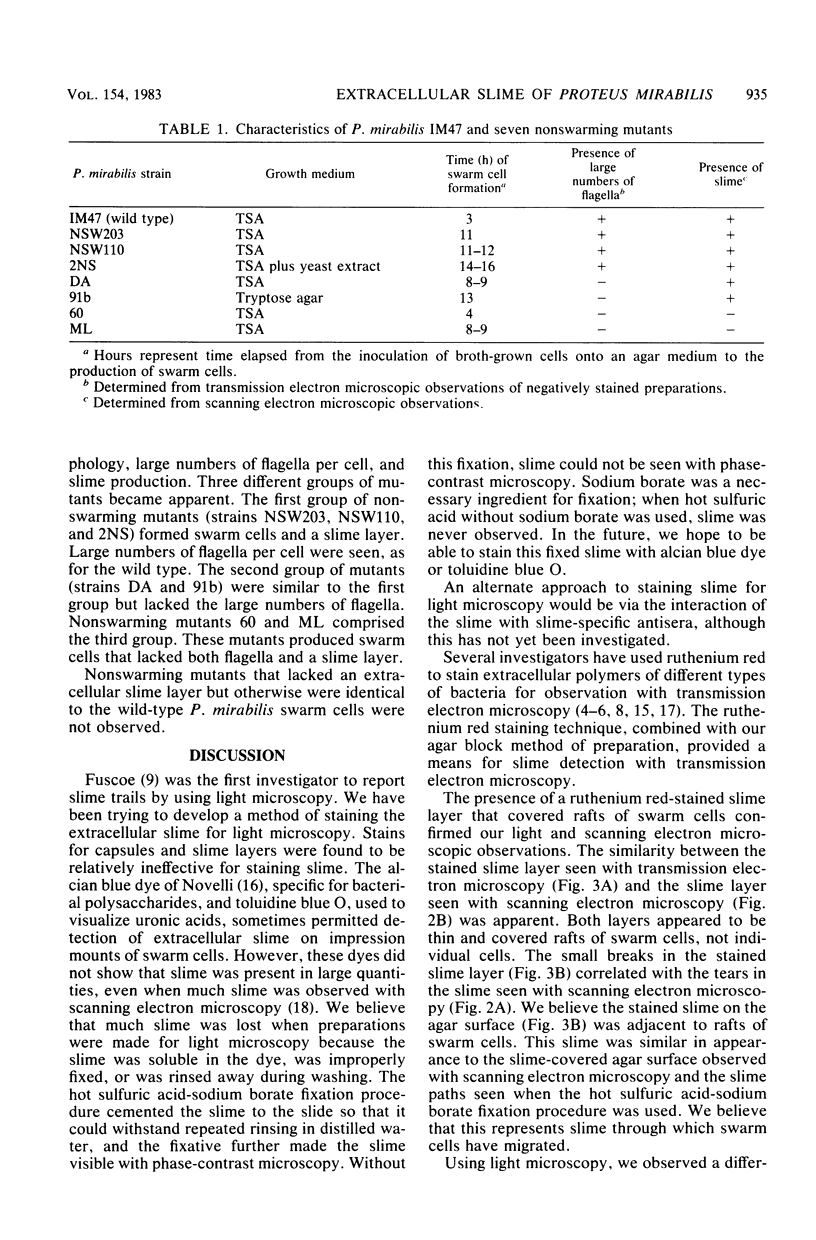
Light microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy were used to visualize the extracellular slime of Proteus mirabilis swarm cells. Slime was observed with phase-contrast microscopy after fixation in hot sulfuric acid-sodium borate. Ruthenium red was used to stain slime for transmission electron microscopy. Copious quantities of extracellular slime were observed surrounding swarm cells; the slime appeared to provide a matrix through which the cells could migrate. Swarm cells were always found embedded in slime. These observations support the argument that swarming of P. mirabilis is associated with the production of large quantities of extracellular slime. Examination of nonswarming mutants of P. mirabilis revealed that a number of morphological changes, including cell elongation and increased flagellum synthesis, were required for swarm cell migration. It is still unclear whether extracellular slime production also is required for migration.
Full text
PDF


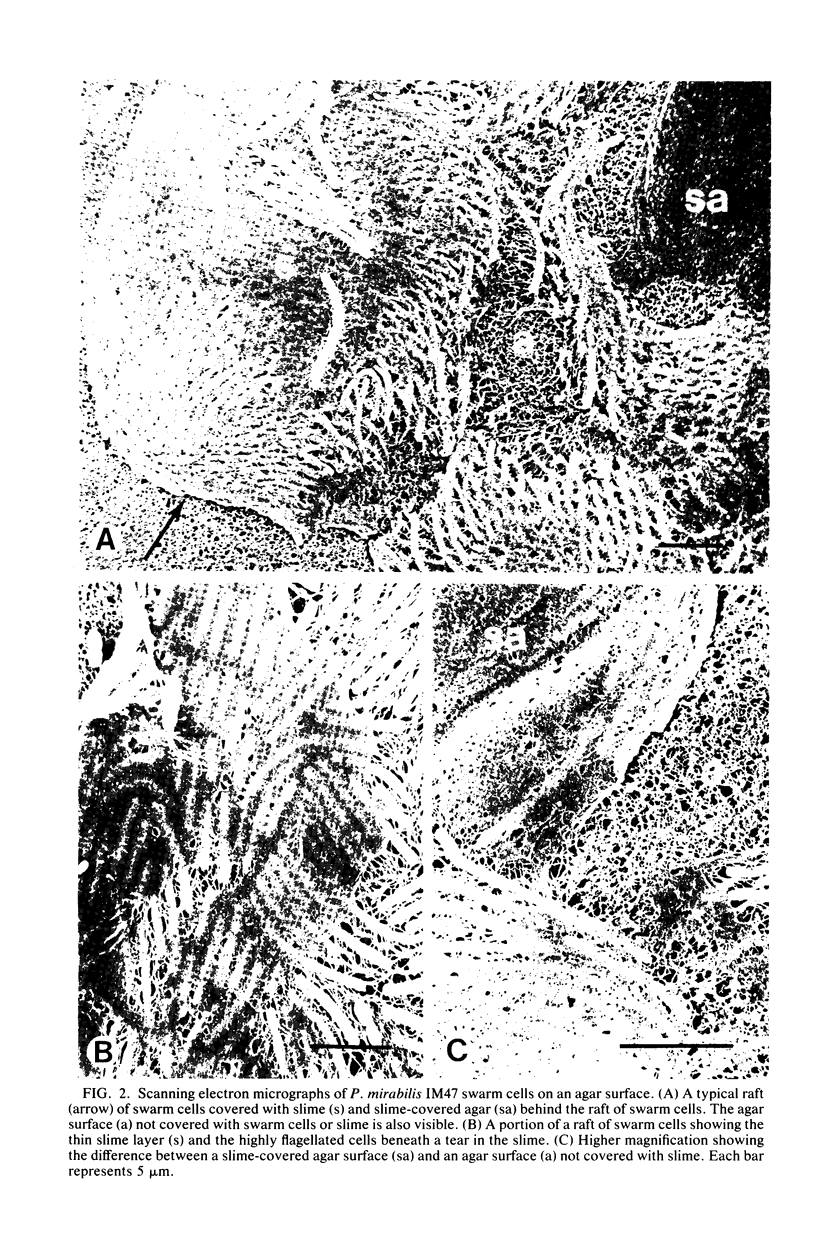


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRENNER S., HORNE R. W. A negative staining method for high resolution electron microscopy of viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisset K. A. The motion of the swarm in Proteus mirabilis. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Feb;6(1):33–35. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagle G. D. An improved method for the study of bacterial extracellular polymers by electron microscopy. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 1974 Apr;73(8):679–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cagle G. D. Fine structure and distribution of extracellular polymer surrounding selected aerobic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):395–408. doi: 10.1139/m75-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. The formation of microcolonies by rumen bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Sep;26(9):1104–1113. doi: 10.1139/m80-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Ultrastructure of cell envelopes of bacteria of the bovine rumen. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):841–849. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.841-849.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. W., Bisset K. A. Development of concentric zones in the Proteus swarm colony. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):497–500. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuscoe F. J. The role of extracellular slime secretion in the swarming of Proteus. Med Lab Technol. 1973 Oct;30(4):373–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOENIGER J. F. CELLULAR CHANGES ACCOMPANYING THE SWARMING OF PROTEUS MIRABILIS. I. OBSERVATIONS OF LIVING CULTURES. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Feb;10:1–9. doi: 10.1139/m64-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeniger J. F. Cellular changes accompanying the swarming of Proteus mirabilis. II. Observations of stained organisms. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):113–123. doi: 10.1139/m66-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. E., Park R. W. The short forms and long forms of Proteus. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jun;47(3):359–367. doi: 10.1099/00221287-47-3-359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCowan R. P., Cheng K. J., Bailey C. B., Costerton J. W. Adhesion of bacteria to epithelial cell surfaces within the reticulo-rumen of cattle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):149–155. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.149-155.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVELLI A. [New method of staining of bacterial capsules in films and sections]. Experientia. 1953 Jan 15;9(1):34–35. doi: 10.1007/BF02147711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson H., Irvin R., Costerton J. W., Cheng K. J. Ultrastructure and adhesion properties of Ruminococcus albus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):278–287. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.278-287.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Anderson D. M., Hoffman P. S., Schwarzhoff R. H., Leonard S. Evidence against the involvement of chemotaxis in swarming of Proteus mirabilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):237–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.237-248.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. D., Schwarzhoff R. H. Nature of the swarming phenomenon in Proteus. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:101–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]