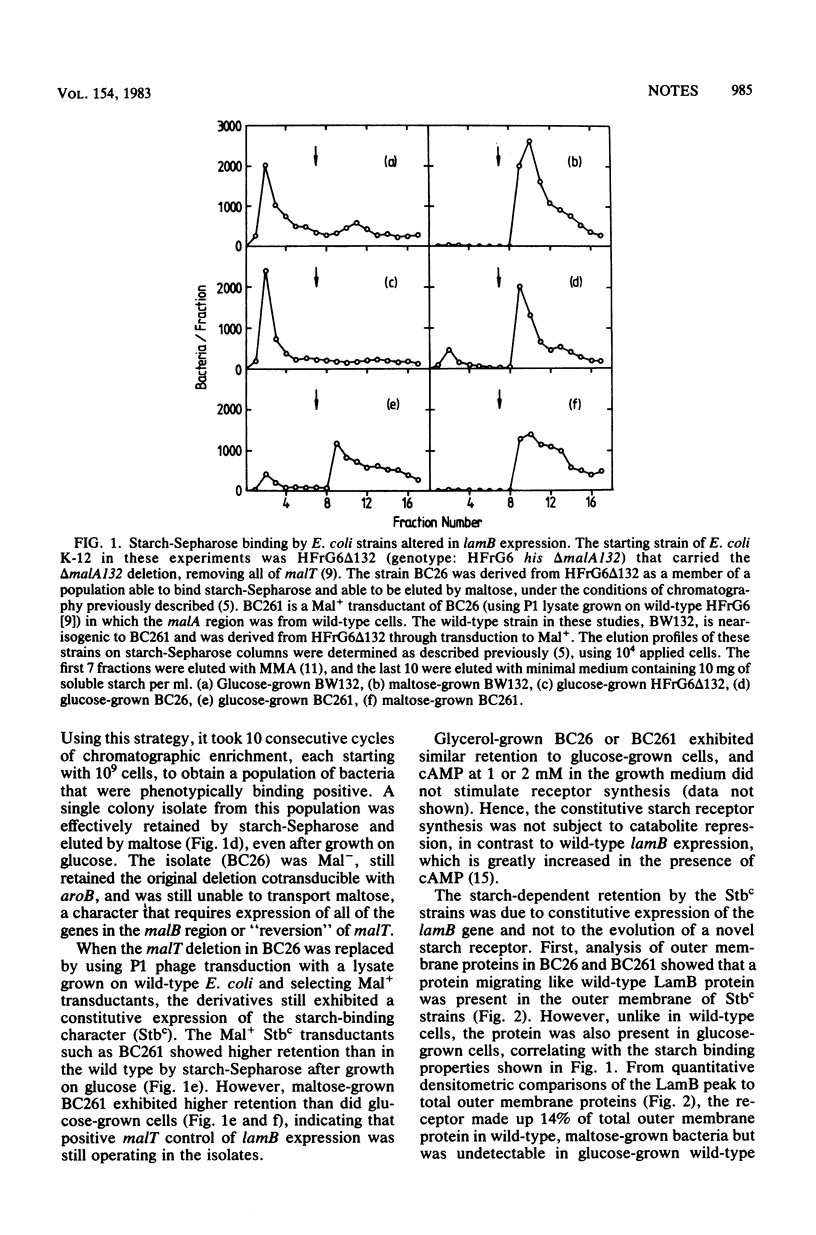
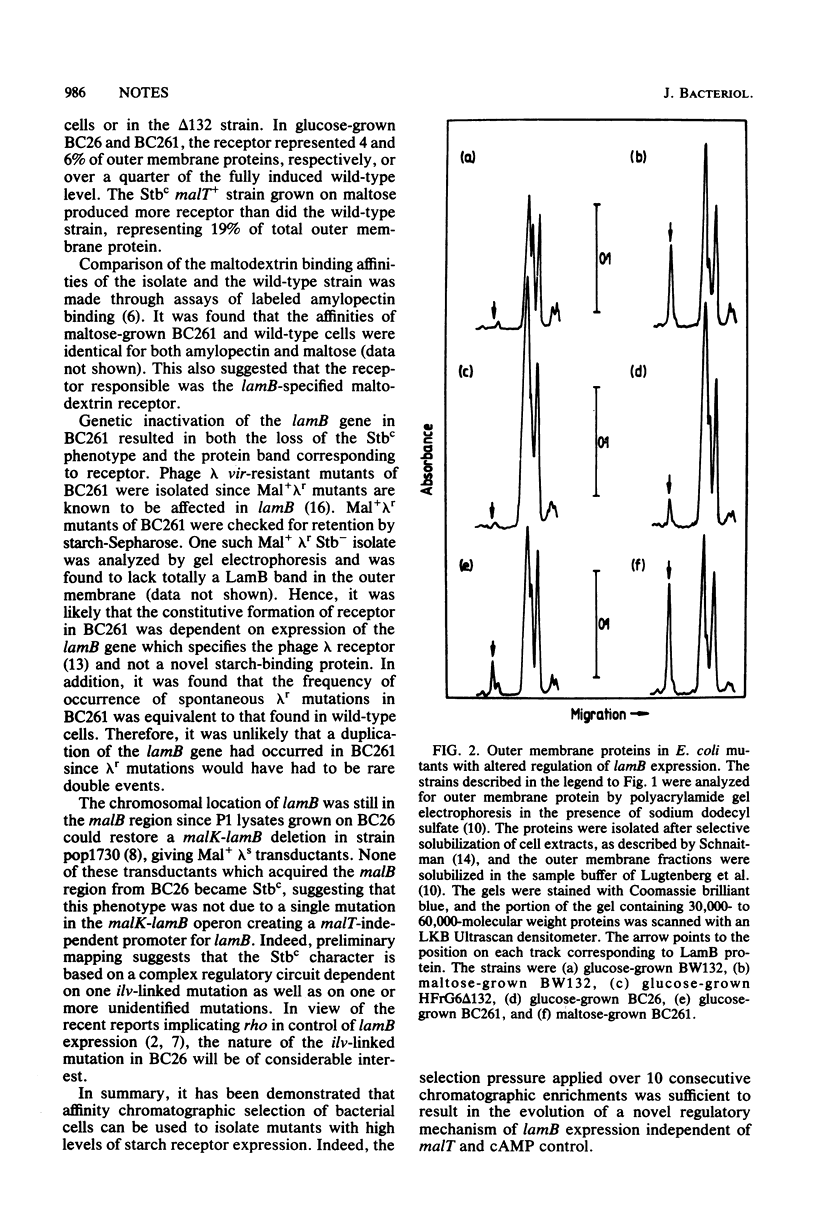
Abstract
Affinity chromatography was used as a positive genetic selection technique for the isolation of cells exhibiting high levels of surface receptor expression. Starting from a large population of Escherichia coli with no maltodextrin receptor due to a deletion of malT, the positive regulator gene required for receptor synthesis, cells were chromatographically enriched that could bind to starch-Sepharose, an immobilized ligand of the receptor. One such isolate showed over 25% of wild-type-induced levels of receptor in the absence of malT and levels higher than that of the wild type in a malT+ background. In contrast to wild-type cells, receptor expression in the isolate was insensitive to control by cAMP. The maltodextrin receptor synthesized by the mutant was identical to wild-type protein in terms of ligand affinity and electrophoretic mobility and was dependent on lamB, the structural gene for the receptor. The directed evolution of this novel form of lamB expression was dependent on at least two mutations in the isolate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapon C. Role of the catabolite activator protein in the maltose regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):722–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.722-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna B., Hofnung M. rho Mutations restore lamB expression in E. coli K12 strains with an inactive malB region. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):479–483. doi: 10.1007/BF00352526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Débarbouillé M., Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Schwartz M. Dominant constitutive mutations in malT, the positive regulator gene of the maltose regulon in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):359–371. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Boos W. The role of the Escherichia coli lambda receptor in the transport of maltose and maltodextrins. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(1):101–116. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Lee K. S. Directed evolution of the lambda receptor of Escherichia coli through affinity chromatographic selection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 25;160(3):431–444. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Schwentorat M., Ullrich S., Vilmart J. Lambda receptor in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a binding protein for maltodextrins and starch polysaccharides. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):521–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.521-526.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Hatfield D., Schwartz M. malB region in Escherichia coli K-12: characterization of new mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.40-47.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofnung M., Schwartz M., Hatfield D. Complementation studies in the maltose-A region of the Escherichia coli K12 genetic map. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Meijers J., Peters R., van der Hoek P., van Alphen L. Electrophoretic resolution of the "major outer membrane protein" of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):254–258. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Roa M., Braun-Breton C., Schwartz M. Structure of the malB region in Escherichia coli K12. I. Genetic map of the malK-lamB operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 24;174(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00267796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall-Hazelbauer L., Schwartz M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda receptor from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1436–1446. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1436-1446.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. The adsorption of coliphage lambda to its host: effect of variations in the surface density of receptor and in phage-receptor affinity. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 25;103(3):521–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirion J. P., Hofnung M. On some genetic aspects of phage lambda resistance in E. coli K12. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):207–216. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



