Abstract
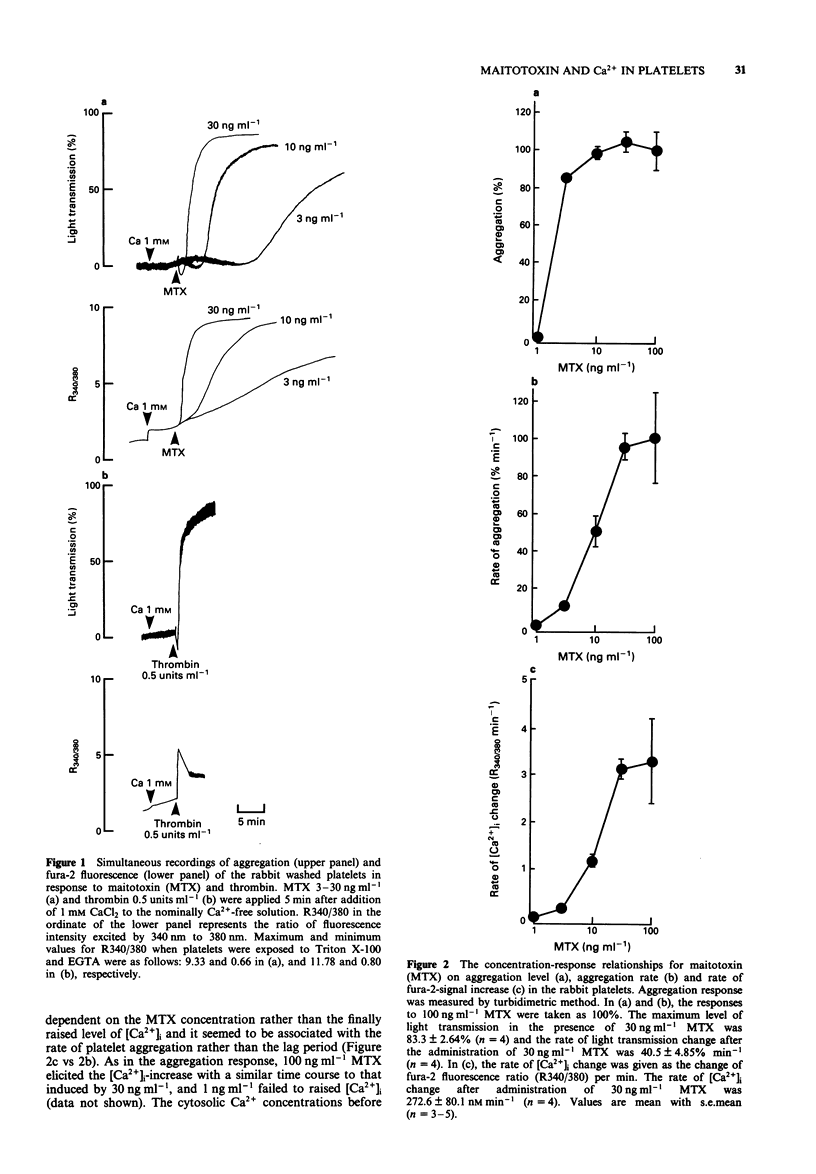
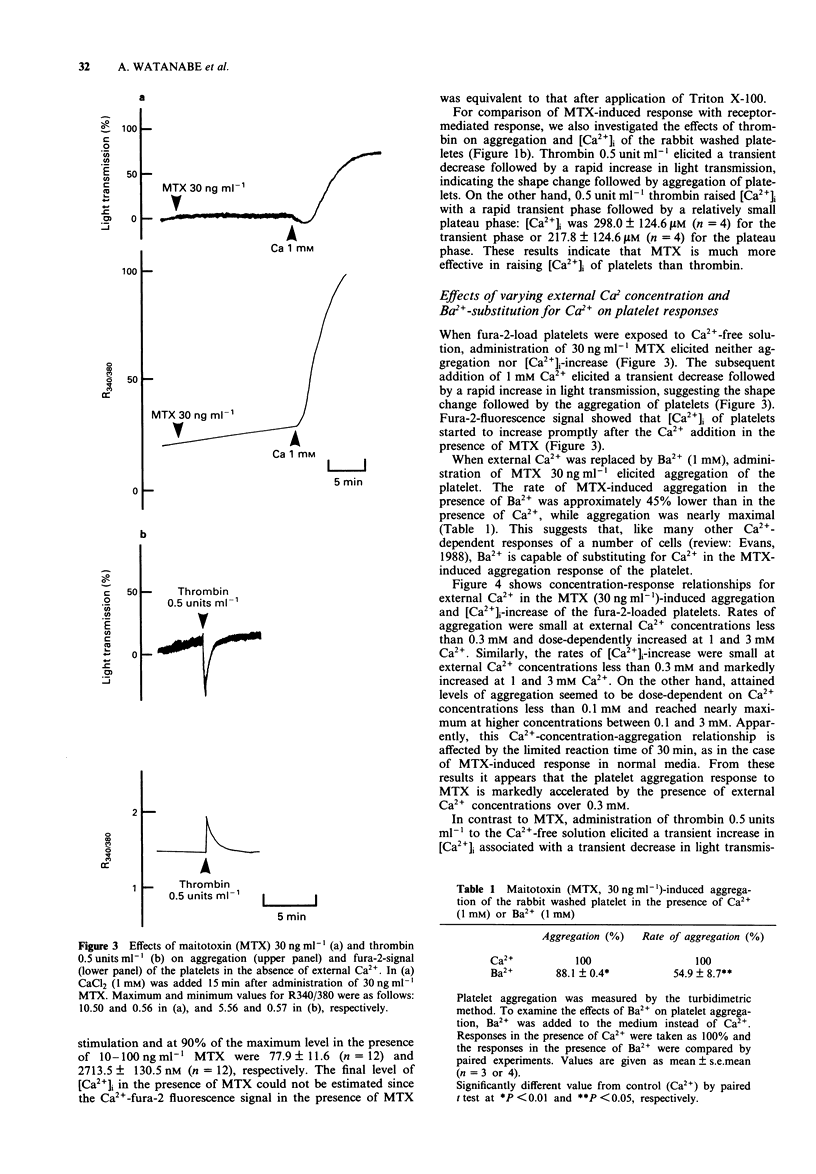
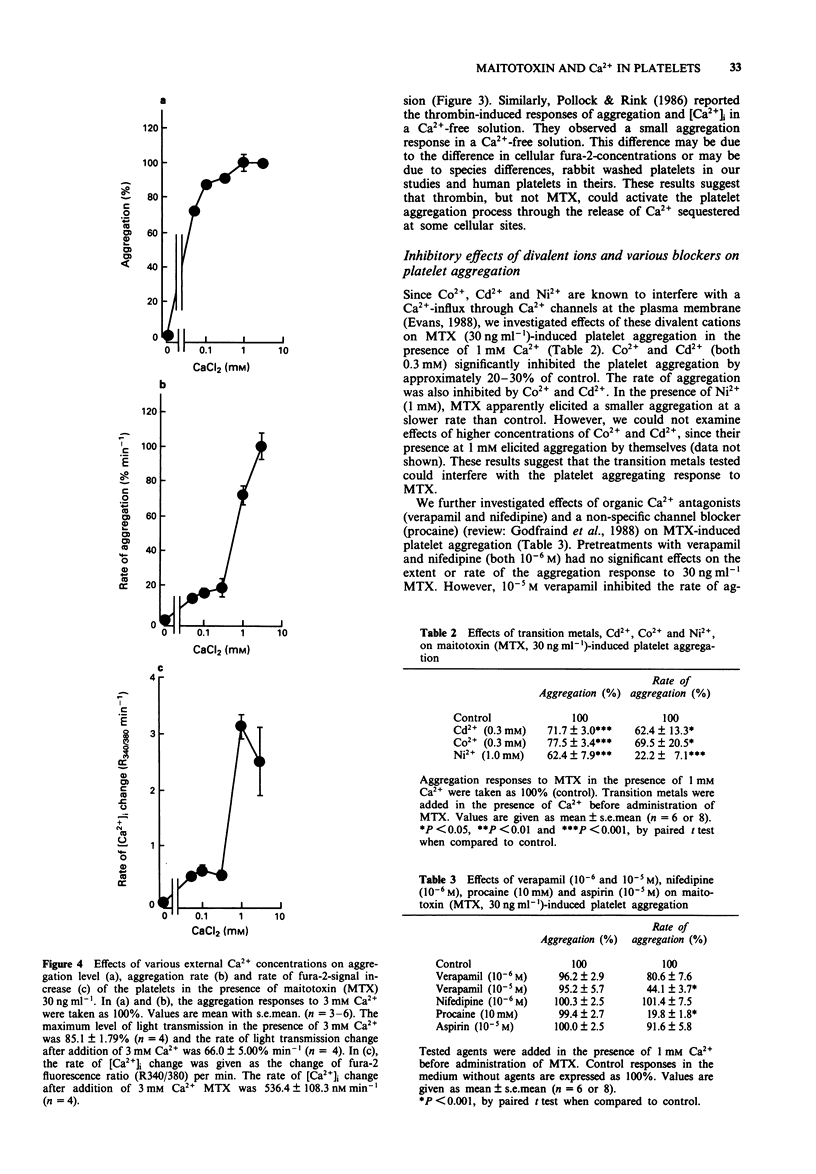
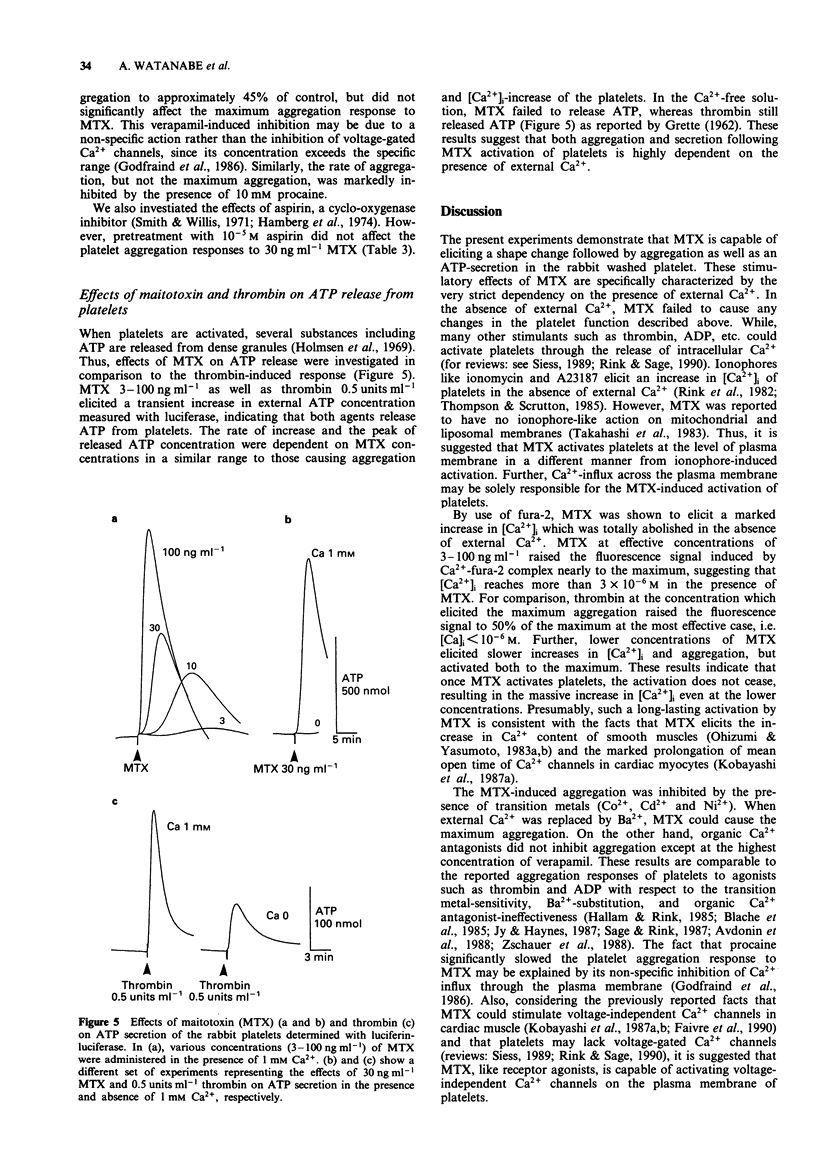
1. Administration of maitotoxin (MTX), a dinoflagellate toxin, caused aggregation of rabbit washed platelets. The cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i), measured by fura-2 fluorescence technique, was also increased by the presence of MTX. Rates of aggregation response and [Ca2+]i-increase were dependent on tested concentrations (3-100 ng ml-1) of the toxin. 2. The MTX-induced platelet aggregation and [Ca2+]i-increase were totally abolished in a Ca(2+)-free solution. The successive administration of Ca2+ in the presence of MTX elicited the aggregation and increase in [Ca2+]i. 3. Ba2+ was capable of substituting for Ca2+ in the MTX-induced platelet aggregation. In the presence of external Ca2+, transition metals, Co2+, Cd2+ and Ni2+, inhibited the aggregation response to MTX. 4. Organic calcium antagonists (verapamil and nifedipine) as well as a cyclo-oxygenase-inhibitor (aspirin) did not apparently inhibit the aggregation response to MTX, except for a high concentration (10(-5) M) of verapamil, while procaine (10 mM) reduced the rate of platelet aggregation. 5. MTX also elicited a release of ATP from platelets, which was abolished in the absence of external Ca2+. 6. In contrast, thrombin 0.5 unit ml-1 could elicit platelet shape change, [Ca2+]i-increase and ATP-release in the absence of external Ca2+. 7. These results suggest that the MTX-induced platelet activation is caused by an enhanced Ca(2+)-influx presumably through voltage-independent Ca2+ channels on the plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avdonin P. V., Men'shikov MYu, Svitina-Ulitina I. V., Tkachuk V. A. Blocking of the receptor-stimulated calcium entry into human platelets by verapamil and nicardipine. Thromb Res. 1988 Dec 15;52(6):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berta P., Phaneuf S., Derancourt J., Casanova J., Durand-Clement M., le Peuch C., Haiech J., Cavadore J. C. The effects of maitotoxin on phosphoinositides and calcium metabolism in a primary culture of aortic smooth muscle cells. Toxicon. 1988;26(2):133–141. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle V. M., Rüegg U. T. Lack of evidence for voltage dependent calcium channels on platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faivre J. F., Deroubaix E., Coulombe A., Legrand A. M., Coraboeuf E. Effect of maitotoxin on calcium current and background inward current in isolated ventricular rat myocytes. Toxicon. 1990;28(8):925–937. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90022-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman S. B., Miller R. J., Miller D. M., Tindall D. R. Interactions of maitotoxin with voltage-sensitive calcium channels in cultured neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4582–4585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfraind T., Miller R., Wibo M. Calcium antagonism and calcium entry blockade. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Dec;38(4):321–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusovsky F., Daly J. W. Maitotoxin: a unique pharmacological tool for research on calcium-dependent mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 1;39(11):1633–1639. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90105-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusovsky F., Yasumoto T., Daly J. W. Maitotoxin, a potent, general activator of phosphoinositide breakdown. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Agonists stimulate divalent cation channels in the plasma membrane of human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80703-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Letter: Mechanism of the anti-aggregating effect of aspirin on human platelets. Lancet. 1974 Jul 27;2(7874):223–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91525-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M., Svensson J., Samuelsson B. Thromboxanes: a new group of biologically active compounds derived from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jy W., Haynes D. H. Thrombin-induced calcium movements in platelet activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 15;929(1):88–102. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Kondo S., Yasumoto T., Ohizumi Y. Cardiotoxic effects of maitotoxin, a principal toxin of seafood poisoning, on guinea pig and rat cardiac muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):1077–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Miyakoda G., Nakamura T., Ohizumi Y. Ca-dependent arrhythmogenic effects of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, on isolated rat cardiac muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 23;111(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ochi R., Ohizumi Y. Maitotoxin-activated single calcium channels in guinea-pig cardiac cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;92(3):665–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. The mechanism of action of maitotoxin in relation to Ca2+ movements in guinea-pig and rat cardiac muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08907.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand A. M., Bagnis R. Effects of highly purified maitotoxin extracted from dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus on action potential of isolated rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1984 Jul;16(7):663–666. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(84)80630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Login I. S., Judd A. M., MacLeod R. M. Activation of calcium channels by maitotoxin. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:63–79. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton J. G., Frojmovic M. M. Turbidometric evaluations of platelet activation: relative contributions of measured shape change, volume, and early aggregation. J Pharmacol Methods. 1983 Apr;9(2):101–115. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(83)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto T., Ohizumi Y., Washio H., Yasumoto Y. Potent excitatory effect of maitotoxin on Ca channels in the insect skeletal muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):439–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00587546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Kajiwara A., Yasumoto T. Excitatory effect of the most potent marine toxin, maitotoxin, on the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):199–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Contractile response of the rabbit aorta to maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:711–721. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Contraction and increase in tissue calcium content induced by maitotoxin, the most potent known marine toxin, in intestinal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J., Irvine R. F. Liberation of [3H]arachidonic acid and changes in cytosolic free calcium in fura-2-loaded human platelets stimulated by ionomycin and collagen. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):869–877. doi: 10.1042/bj2350869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock W. K., Rink T. J. Thrombin and ionomycin can raise platelet cytosolic Ca2+ to micromolar levels by discharge of internal Ca2+ stores: studies using fura-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):308–314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Calcium signaling in human platelets. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:431–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Smith S. W., Tsien R. Y. Cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human platelets: Ca2+ thresholds and Ca-independent activation for shape-change and secretion. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 1;148(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage S. O., Rink T. J. The kinetics of changes in intracellular calcium concentration in fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16364–16369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):58–178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Schmidt B. H., Alonso R., Vian L., Tep A., Yasumoto T., Cory R. N., Bockaert J. New insights into maitotoxin action. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):663–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Maitotoxin, a Ca2+ channel activator candidate. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7287–7289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Tatsumi M., Ohizumi Y., Yasumoto T. Ca2+ channel activating function of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin known, in clonal rat pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10944–10949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. T., Scrutton M. C. Intracellular calcium fluxes in human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Mar 1;147(2):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Tamura S., Fukushima N., Takagi H. Pertussis toxin (IAP) enhances maitotoxin (a putative Ca2+ channel agonist)-induced Ca2+ entry into synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 2;122(3):379–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90421-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Tamura S., Harada H., Yasumoto T., Takagi H. The maitotoxin-evoked Ca2+ entry into synaptosomes is enhanced by cholera toxin. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 18;67(2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama A., Murata M., Oshima Y., Iwashita T., Yasumoto T. Some chemical properties of maitotoxin, a putative calcium channel agonist isolated from a marine dinoflagellate. J Biochem. 1988 Aug;104(2):184–187. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii M., Tsunoo A., Kuroda Y., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Maitotoxin-induced membrane current in neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 20;424(1):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschauer A., van Breemen C., Bühler F. R., Nelson M. T. Calcium channels in thrombin-activated human platelet membrane. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):703–705. doi: 10.1038/334703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


