Abstract
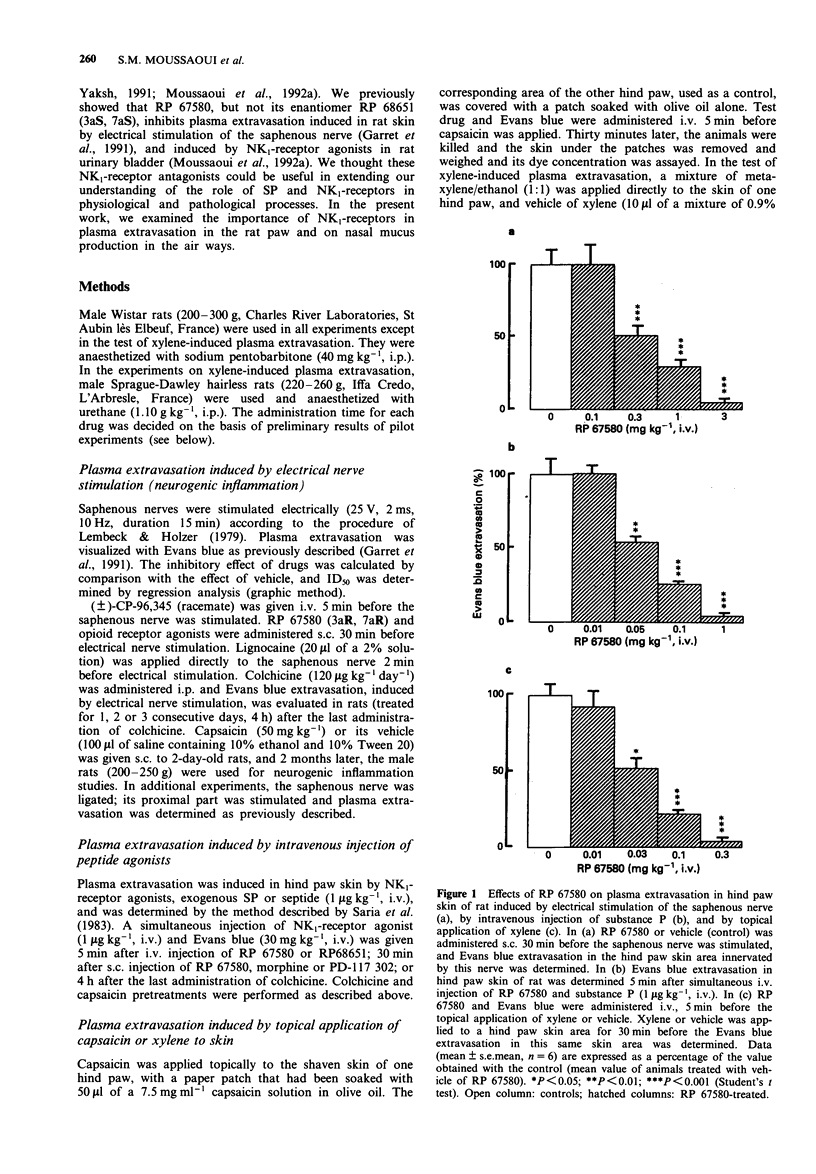
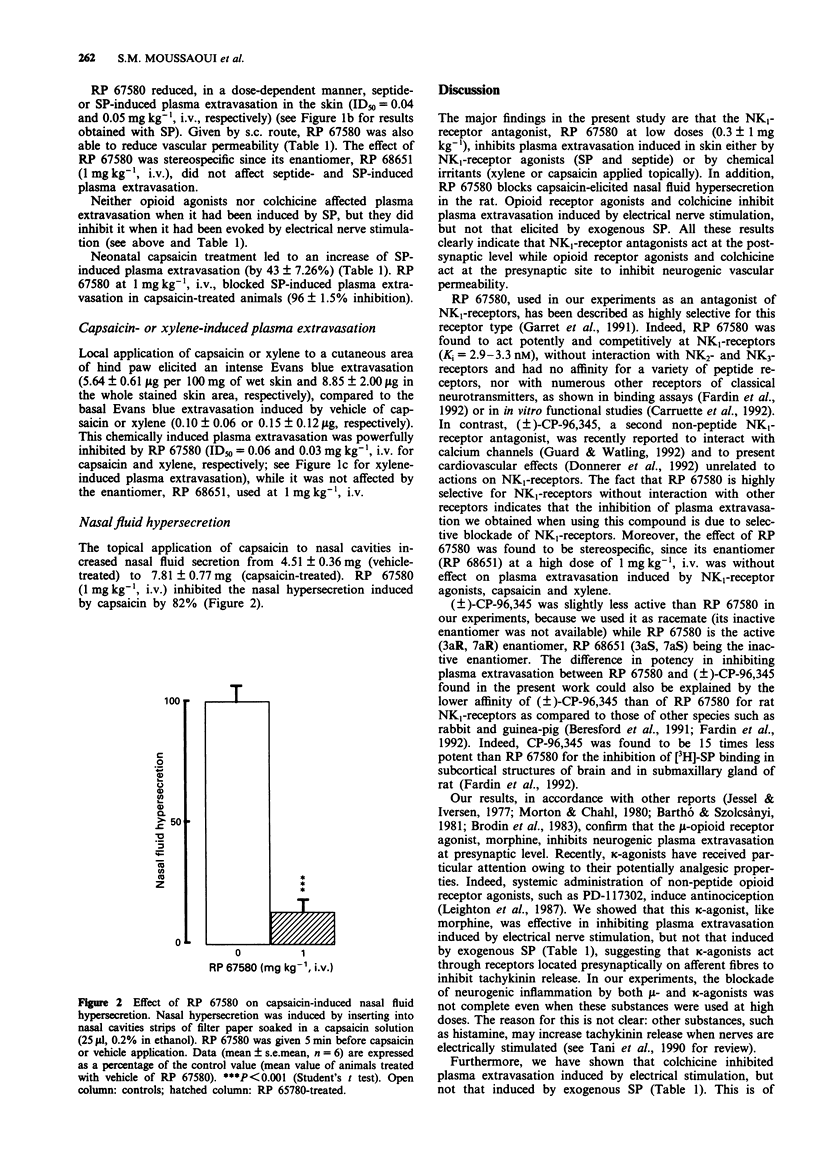
1. The non-peptide neurokinin NK1-receptor antagonist, RP 67580 (3aR, 7aR), a perhydroisoindolone derivative, powerfully reduced plasma extravasation in rat hind paw skin induced by local application of xylene (ID50 = 0.03 mg kg-1, i.v.) or capsaicin (ID50 = 0.06 mg kg-1, i.v.), or by i.v. injection of exogenous substance P (SP) or septide ([pGlu6,Pro9]SP(6-11)) (ID50 = 0.04-0.05 mg kg-1, i.v.). RP 67580 (1 mg kg-1, i.v.) also abolished capsaicin-induced nasal fluid hypersecretion (by 82 +/- 5%). These effects were found to be stereospecific, the enantiomer, RP 68651 (3aS, 7aS), being inactive at 1 mg kg-1, i.v. 2. In rats neonatally treated with capsaicin (50 mg kg-1, s.c.), plasma extravasation induced by SP was significantly increased (by 43 +/- 7%). RP 67580 (1 mg kg-1, i.v.) completely inhibited the SP-induced plasma extravasation in capsaicin neonatally treated-animals, as it did in control animals. This result suggests that RP 67580 acts at the postsynaptic level for the inhibition of plasma extravasation. 3. Opioid receptor agonists, mu-(morphine) and kappa-(PD-117302) at 10 mg kg-1, s.c., in contrast to NK1-receptor antagonists, did not inhibit plasma extravasation induced by exogenous SP. They were, however, partially effective against plasma extravasation induced by electrical nerve stimulation (74 +/- 4% and 48 +/- 9% inhibition at 10 mg kg-1, s.c. of morphine and PD-117302, respectively, compared to 90 +/- 3% inhibition obtained with RP 67580, 3 mg kg-1, s.c.).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelli L., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Del Bianco E., Regoli D., Drapeau G., Giachetti A. Effect of synthetic tachykinin analogues on airway microvascular leakage in rats and guinea-pigs: evidence for the involvement of NK-1 receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;11(4):267–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. V., Helme R. D., Thomas K. L. NK-1 receptor mediation of neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat skin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1232–1238. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Szolcsányi J. Opiate agonists inhibit neurogenic plasma extravasation in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresford I. J., Birch P. J., Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J. Investigation into species variants in tachykinin NK1 receptors by use of the non-peptide antagonist, CP-96,345. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):292–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bill A., Stjernschantz J., Mandahl A., Brodin E., Nilsson G. Substance P: release on trigeminal nerve stimulation, effects in the eye. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Jul;106(3):371–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodin E., Gazelius B., Panopoulos P., Olgart L. Morphine inhibits substance P release from peripheral sensory nerve endings. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Apr;117(4):567–570. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahl L. A., Ladd R. J. Local oedema and general excitation of cutaneous sensory receptors produced by electrical stimulation of the saphenous nerve in the rat. Pain. 1976 Mar;2(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(76)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Haegerstrand A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Hökfelt T. Neurokinin A-like immunoreactivity in rat primary sensory neurons; coexistence with substance P. Histochemistry. 1985;83(1):37–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00495297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C. Peptides and neurogenic inflammation. Br Med Bull. 1987 Apr;43(2):386–400. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C. The skin as an organ for the study of the pharmacology of neuropeptides. Skin Pharmacol. 1988;1(2):77–83. doi: 10.1159/000210752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamse R., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;68(2):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartschuh W., Weihe E., Reinecke M. Peptidergic (neurotensin, VIP, substance P) nerve fibres in the skin. Immunohistochemical evidence of an involvement of neuropeptides in nociception, pruritus and inflammation. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Jul;109 (Suppl 25):14–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb06811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helme R. D., White D. M., Andrews P. V. Neurogenic inflammation in skin blisters. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(2):382–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00230918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hägermark O., Hökfelt T., Pernow B. Flare and itch induced by substance P in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Oct;71(4):233–235. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12515092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Kellerth J. O., Nilsson G., Pernow B. Experimental immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of substance P in cat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 19;100(2):235–252. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jancsó N., Jancsó-Gábor A., Szolcsányi J. Direct evidence for neurogenic inflammation and its prevention by denervation and by pretreatment with capsaicin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):138–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessell T. M., Iversen L. L. Opiate analgesics inhibit substance P release from rat trigeminal nucleus. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):549–551. doi: 10.1038/268549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. T., Marfurt C. F. Peptidergic and serotoninergic innervation of the rat dura mater. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Jul 22;309(4):515–534. doi: 10.1002/cne.903090408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMBECK F. Zur Frage der zentralen Ubertragung afferenter Impulse. III. Das Vorkommen und die Bedeutung der Substanz P in den dorsalen Wurzeln des Rückenmarks. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;219(3):197–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam F. Y., Ferrell W. R. Specific neurokinin receptors mediate plasma extravasation in the rat knee joint. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1263–1267. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. [pGlu6,Pro9]SP6-11, a selective agonist for the substance P P-receptor subtype. J Med Chem. 1986 Jul;29(7):1284–1288. doi: 10.1021/jm00157a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton G. E., Johnson M. A., Meecham K. G., Hill R. G., Hughes J. Pharmacological profile of PD 117302, a selective kappa-opioid agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;92(4):915–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Donnerer J., Tsuchiya M., Nagahisa A. The non-peptide tachykinin antagonist, CP-96,345, is a potent inhibitor of neurogenic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):527–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Holzer P. Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00500282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Lundblad L., Saria A., Anggård A. Inhibition of cigarette smoke-induced oedema in the nasal mucosa by capsaicin pretreatment and a substance P antagonist. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;326(2):181–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00517317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Martling C. R., Saria A., Folkers K., Rosell S. Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema due to activation of capsaicin-sensitive vagal afferents and substance P release. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1361–1368. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn B., Shakhanbeh J. Substance P content of the skin, neurogenic inflammation and numbers of C-fibres following capsaicin application to a cutaneous nerve in the rabbit. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):769–775. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton C. R., Chahl L. A. Pharmacology of the neurogenic oedema response to electrical stimulation of the saphenous nerve in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;314(3):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00498549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. A., Reinhard J. F., Jr, Romero J., Melamed E., Pettibone D. J. Neurotransmitters and the fifth cranial nerve: is there a relation to the headache phase of migraine? Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):883–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92692-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moussaoui S. M., Le Prado N., Bonici B., Faucher D. C., Cuiné F., Laduron P. M., Garret C. Distribution of neurokinin B in rat spinal cord and peripheral tissues: comparison with neurokinin A and substance P and effects of neonatal capsaicin treatment. Neuroscience. 1992 Jun;48(4):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90285-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. I., Iversen L. L., Goedert M., Chapman D., Hunt S. P. Dose-dependent effects of capsaicin on primary sensory neurons in the neonatal rat. J Neurosci. 1983 Feb;3(2):399–406. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-02-00399.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen-Bjergaard U., Nielsen L. B., Jensen K., Edvinsson L., Jansen I., Olesen J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide, neurokinin A and substance P: effects on nociception and neurogenic inflammation in human skin and temporal muscle. Peptides. 1991 Mar-Apr;12(2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(91)90022-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow B. Role of tachykinins in neurogenic inflammation. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):812s–815s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersson G., Malm L., Ekman R., Håkanson R. Capsaicin evokes secretion of nasal fluid and depletes substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide from the nasal mucosa in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):930–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14623.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Lundberg J. M., Skofitsch G., Lembeck F. Vascular protein linkage in various tissue induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;324(3):212–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00503897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani E., Senba E., Kokumai S., Masuyama K., Ishikawa T., Tohyama M. Histamine application to the nasal mucosa induces release of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P from peripheral terminals of trigeminal ganglion: a morphological study in the guinea pig. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Apr 20;112(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90312-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yaksh T. L. Stereospecific effects of a nonpeptidic NK1 selective antagonist, CP-96,345: antinociception in the absence of motor dysfunction. Life Sci. 1991;49(26):1955–1963. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90637-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemer D., Livneh A., Danon Y. L., Pras M., Sohar E. Long-term colchicine treatment in children with familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):973–977. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


