Abstract
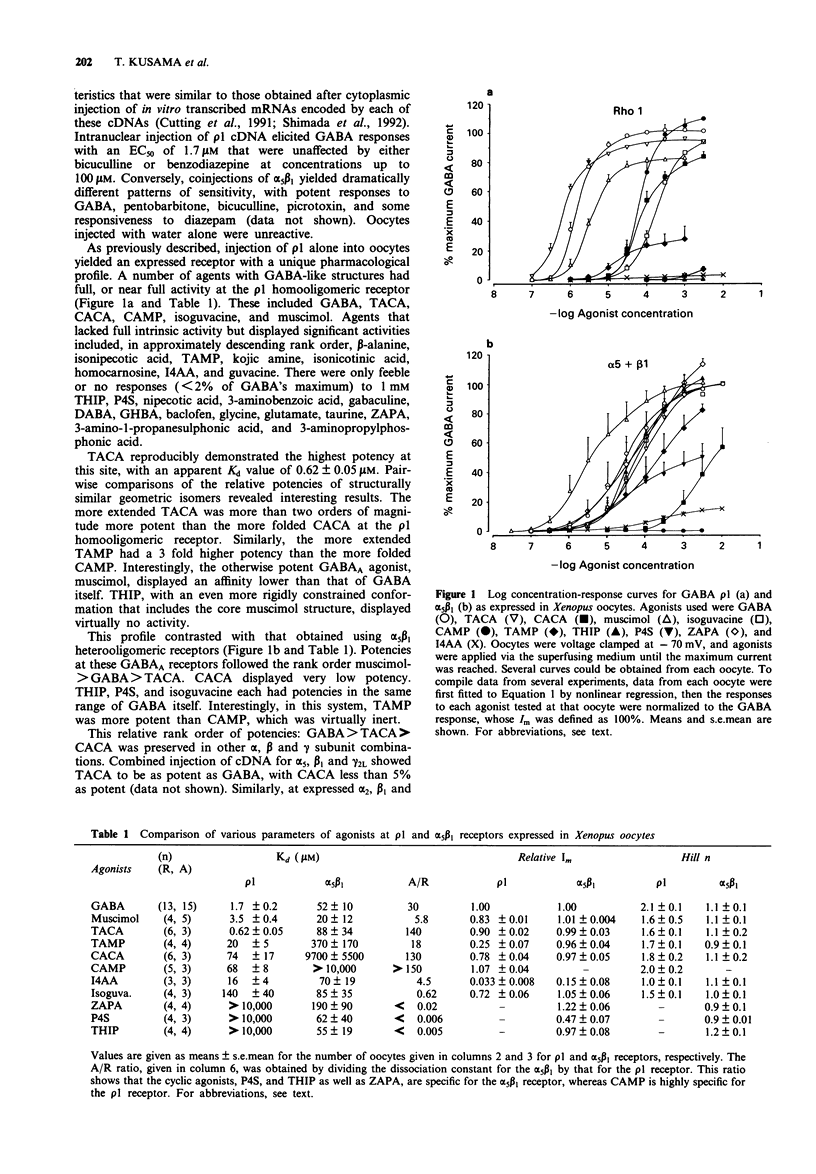
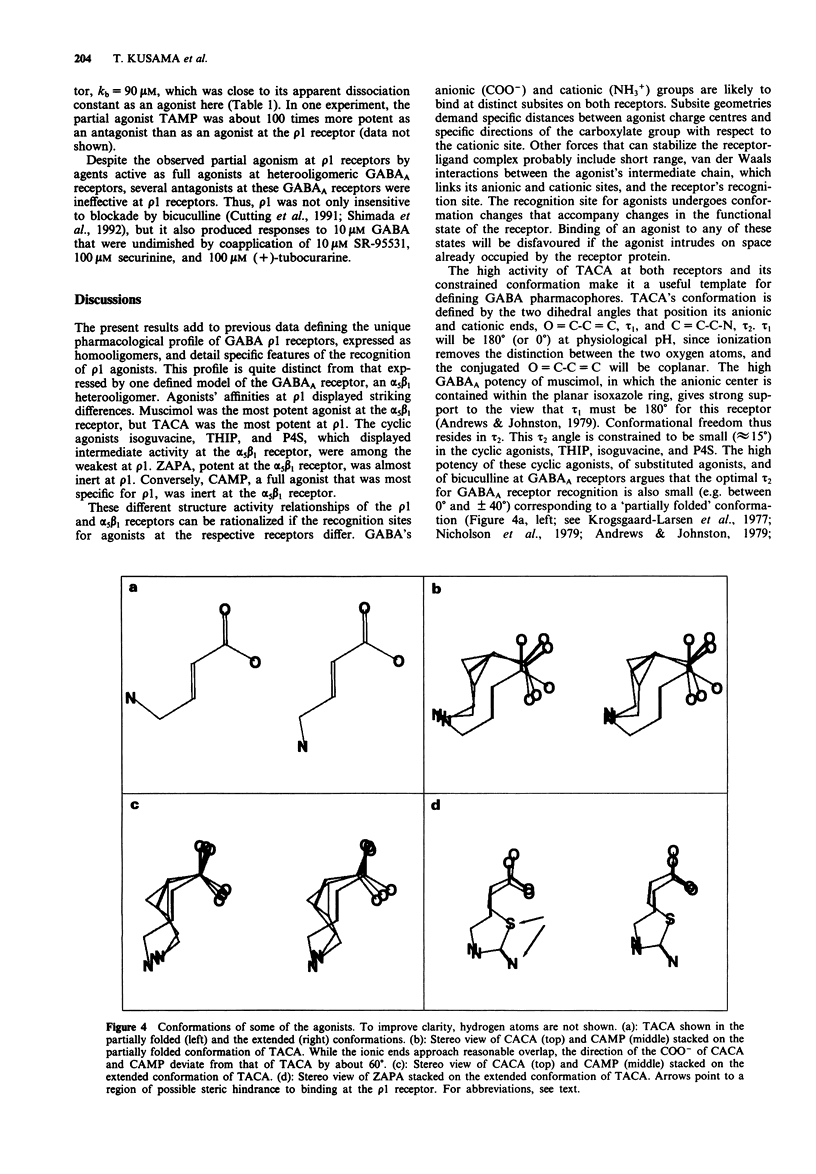
1. The rho 1 protein, which we previously cloned from retina, assembles as a homooligomer that transduces the binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) into robust chloride currents. However, its insensitivity to bicuculline, pentobarbitone and benzodiazepines, all potent agents at typical GABAA receptors, suggested that it may react atypically to other GABA agonists and antagonists. 2. cDNAs for the rho 1 and the alpha 5 beta 1 receptors for GABA were expressed as homo- and heterooligomers, respectively, in Xenopus oocytes. The selectivities of the respective receptors for various agonists were investigated using concentration-response experiments in voltage clamped cells. 3. The most potent agonists at the rho 1 receptor were trans-4-aminocrotonic acid (TACA) > GABA > muscimol; at the alpha 5 beta 1 receptor the rank order was muscimol > GABA > 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazole[4,5-c]pyridine-3-ol (THIP). The most specific agonists were cis-(2-(aminomethyl)-cyclopropyl-carboxylic acid (CAMP) and THIP for the rho 1 and the alpha 5 beta 1 receptors, respectively. 4. Comparing GABA, TACA and cis-aminocrotonic acid (CACA) at rho 1 receptors expressed in COS cells gave results almost indistinguishable from those found at oocytes; the pharmacology of rho 1 seems independent of the expression system. 5. Agonists THIP, piperidine-4-sulphonic acid (P4S), and isoguvacine, whose C-C-C-N chains are constrained by rings into a folded conformation and were potent at the alpha 5 beta 1 receptor, were among the weakest at the rho 1 receptor.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

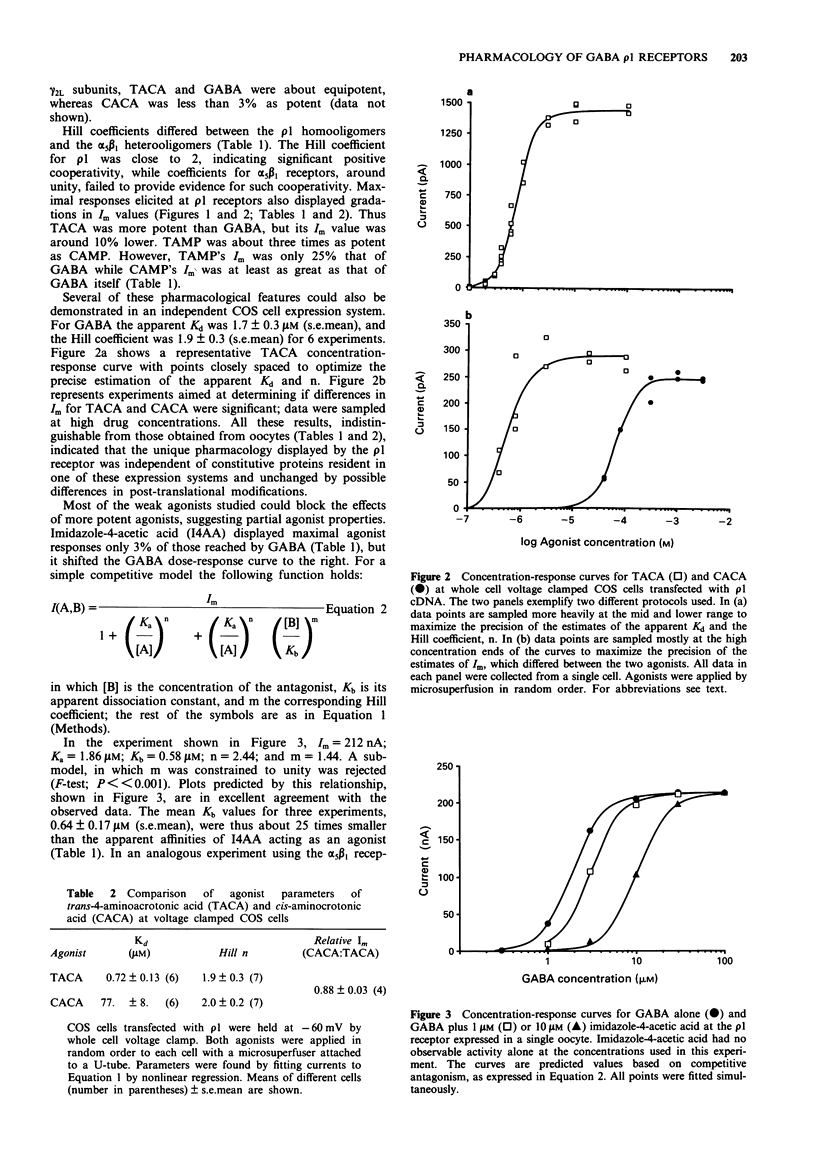


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan R. D., Curtis D. R., Headley P. M., Johnston G. A., Lodge D., Twitchin B. The synthesis and activity of cis- and trans-2-(aminomethyl) cyclopropanecarboxylic acid as conformationally restricted analogues of GABA. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):652–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11193.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan R. D., Dickenson H. W., Hiern B. P., Johnston G. A., Kazlauskas R. Isothiouronium compounds as gamma-aminobutyric acid agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):379–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. R., Johnston G. A. GABA agonists and antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;28(18):2697–2702. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90549-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger T., Vercauteren D. P., Durant F., Andre J. M. 3- and 5-isoxazolol zwitterions: an ab initio molecular orbital study relating to GABA agonism and antagonism. J Theor Biol. 1987 Aug 21;127(4):479–489. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(87)80144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Jones G. P. A comparison of gamma-aminobutyric acid and the semi-rigid analogues 4-aminotetrolic acid, 4-aminocrotonic acid and imidazole-4-acetic acid on the isolated superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;56(3):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Kamatchi G. L. GABAA receptor subtypes: from pharmacology to molecular biology. FASEB J. 1991 Nov;5(14):2916–2923. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.14.1661244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting G. R., Lu L., O'Hara B. F., Kasch L. M., Montrose-Rafizadeh C., Donovan D. M., Shimada S., Antonarakis S. E., Guggino W. B., Uhl G. R. Cloning of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) rho 1 cDNA: a GABA receptor subunit highly expressed in the retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew C. A., Johnston G. A., Weatherby R. P. Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors: studies on the binding of (-)-baclofen to rat cerebellar membranes. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Dec 21;52(3):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P. GABA synaptic mechanisms: stereochemical and conformational requirements. Med Res Rev. 1988 Jan-Mar;8(1):27–56. doi: 10.1002/med.2610080103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen P., Johnston G. A., Lodge D., Curtis D. R. A new class of GABA agonist. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):53–55. doi: 10.1038/268053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Ryu P. D., Randic M. Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids and peptide-induced responses in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Aug 14;103(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson S. H., Suckling C. J., Iversen L. L. GABA analogues: conformational analysis of effects on [3H]GABA binding to postsynaptic receptors in human cerebellum. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):249–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Tobin A. J. Molecular biology of GABAA receptors. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1469–1480. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2155149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polenzani L., Woodward R. M., Miledi R. Expression of mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors with distinct pharmacology in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4318–4322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer J. C., Lin C. L., Kitayama S., Uhl G. R. Ligand autoradiographic receptor screening. II. Expression of receptor cDNA in transfected COS cells grown on polyester disks and its recovery. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Feb;9(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90012-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Cutting G., Uhl G. R. gamma-Aminobutyric acid A or C receptor? gamma-Aminobutyric acid rho 1 receptor RNA induces bicuculline-, barbiturate-, and benzodiazepine-insensitive gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):683–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada S., Spivak C., Uhl G. Endothelin receptor: a profoundly desensitizing receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 25;193(1):123–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Trube G., Möhler H., Malherbe P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., O'Hara B., Shimada S., Zaczek R., DiGiorgianni J., Nishimori T. Dopamine transporter: expression in Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90126-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


