Abstract
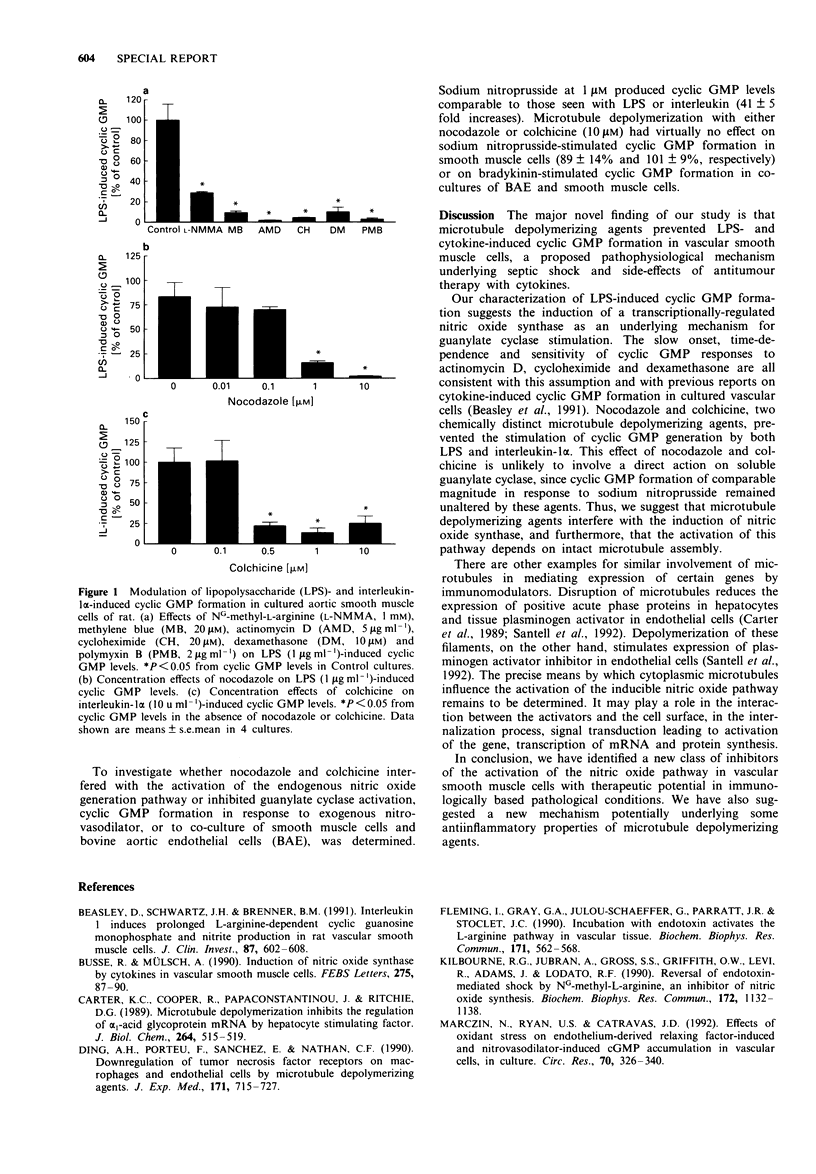
We investigated the role of microtubules in the induction of nitric oxide synthase in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. We found that like interleukin-1 alpha, lipopolysaccharide elicited a time and concentration-dependent accumulation of cyclic GMP via induction of nitric oxide synthase. Nocodazole and colchicine, two chemically distinct microtubule depolymerizing agents, completely prevented lipopolysaccharide- and interleukin-induced (and nitric oxide-mediated) cyclic GMP generation. In contrast to lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 alpha, cyclic GMP accumulation in response to sodium nitroprusside, an exogenous nitrovasodilator, was not altered by either nocodazole or colchicine. Our findings demonstrate that microtubule depolymerizing agents inhibit nitric oxide synthase induction and suggest a prominent role for microtubules in mediating the activation of the inducible nitric oxide pathway in smooth muscle cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley D., Schwartz J. H., Brenner B. M. Interleukin 1 induces prolonged L-arginine-dependent cyclic guanosine monophosphate and nitrite production in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):602–608. doi: 10.1172/JCI115036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter K. C., Cooper R., Papaconstantinou J., Ritchie D. G. Microtubule depolymerization inhibits the regulation of alpha 1-acid glycoprotein mRNA by hepatocyte stimulating factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Porteu F., Sanchez E., Nathan C. F. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptors on macrophages and endothelial cells by microtubule depolymerizing agents. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):715–727. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming I., Gray G. A., Julou-Schaeffer G., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Incubation with endotoxin activates the L-arginine pathway in vascular tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):562–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91183-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Jubran A., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Adams J., Lodato R. F. Reversal of endotoxin-mediated shock by NG-methyl-L-arginine, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1132–1138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91565-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczin N., Ryan U. S., Catravas J. D. Effects of oxidant stress on endothelium-derived relaxing factor-induced and nitrovasodilator-induced cGMP accumulation in vascular cells in culture. Circ Res. 1992 Feb;70(2):326–340. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santell L., Marotti K., Bartfeld N. S., Baynham P., Levin E. G. Disruption of microtubules inhibits the stimulation of tissue plasminogen activator expression and promotes plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 expression in human endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Aug;201(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90284-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


