Abstract
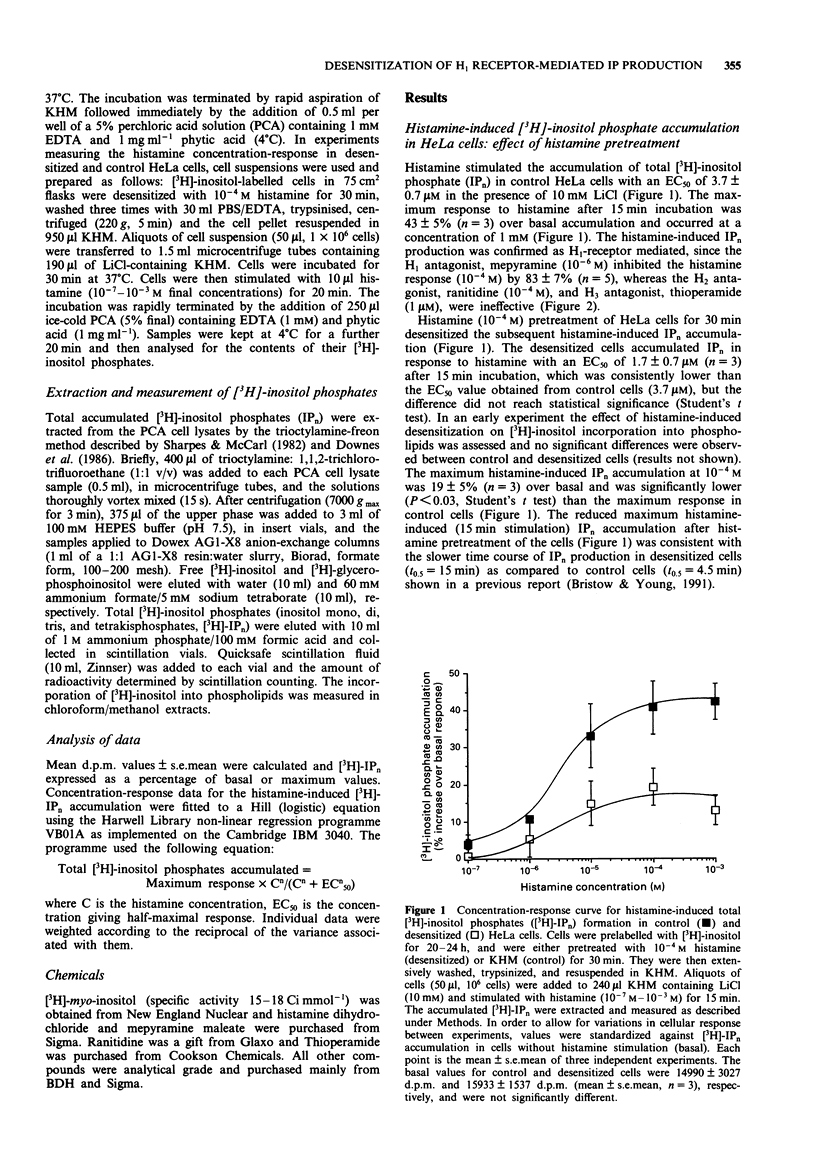
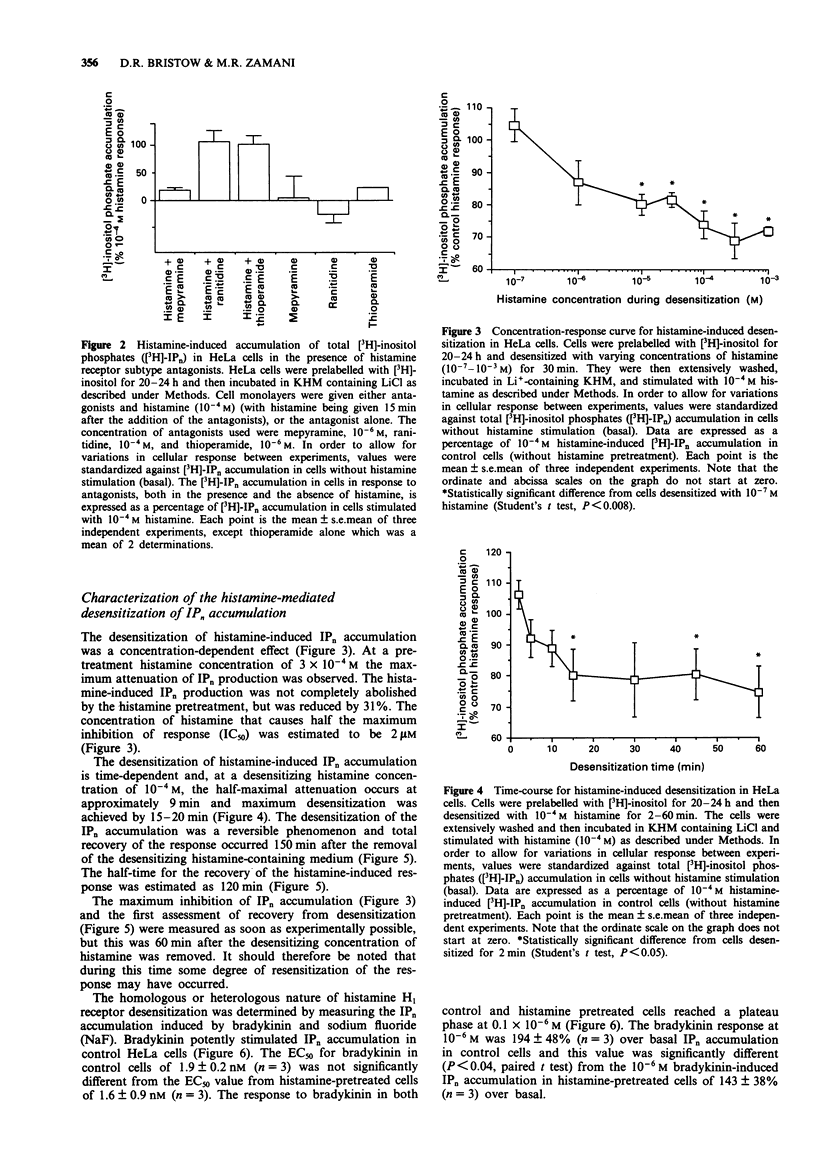
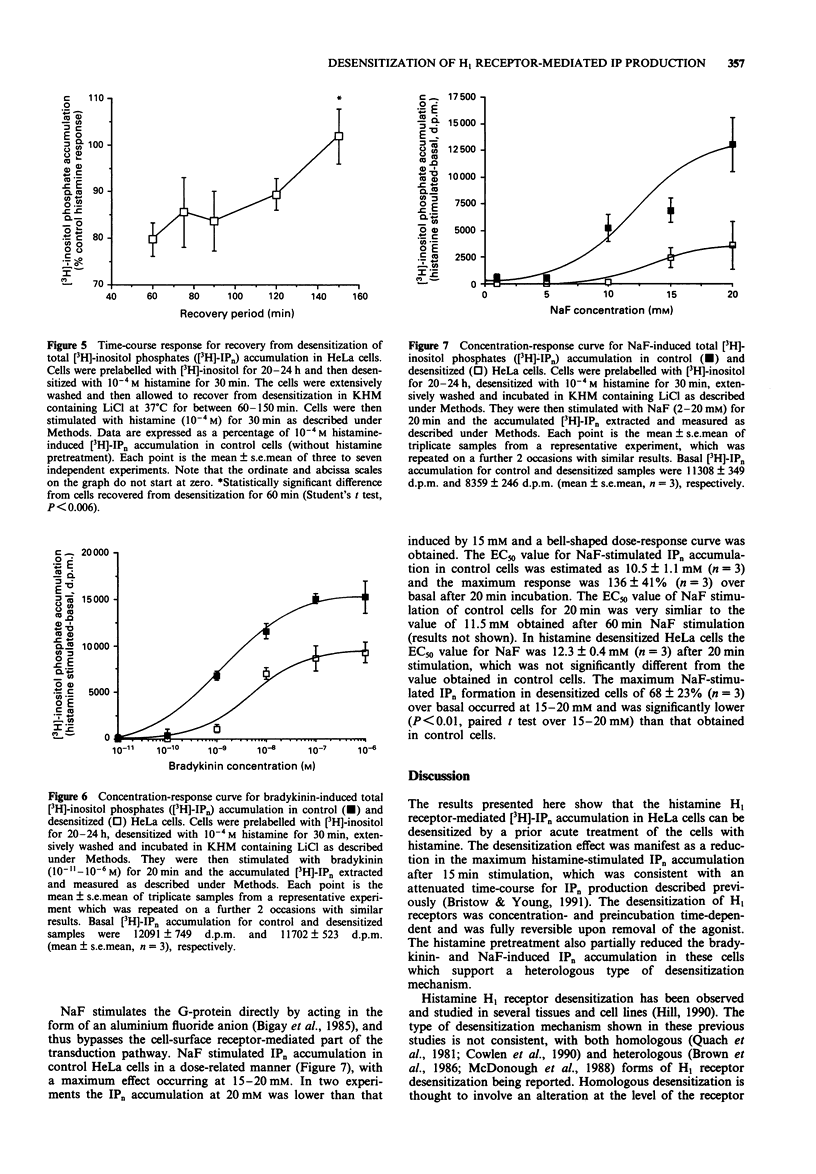
1. Histamine stimulated the accumulation of total [3H]-inositol phosphates (IPn) in control HeLa cells with an EC50 of 3.7 +/- 0.7 microM in the presence of 10 mM LiCl. The maximum response to histamine after 15 min incubation was 43 +/- 5% over basal accumulation and occurred at a concentration of 1 mM histamine. 2. The histamine-induced IPn production in HeLa cells was confirmed as H1 receptor-mediated, since the H1 antagonist mepyramine (10(-6) M) inhibited the histamine response (10(-4) M) by 83 +/- 7%, whereas the H2 antagonist, ranitidine (10(-4) M), and H3 antagonist, thioperamide (10(-6) M), were ineffective. 3. Histamine (10(-4) M) pretreatment of HeLa cells for 30 min desensitized the subsequent histamine-induced IPn accumulation. The desensitized cells accumulated IPn in response to histamine with an EC50 of 1.7 +/- 0.7 microM after 15 min incubation. The maximum histamine-induced IPn accumulation at 10(-4) M was 19 +/- 5% over basal and was significantly lower (P < 0.03) than the maximum response in control cells. 4. The desensitization of histamine-induced IPn accumulation was time-dependent and, at a desensitizing histamine concentration of 10(-4) M, the half-maximal attenuation occurred after approximately 9 min and maximum desensitization was achieved by 15-20 min. The desensitization of the IPn accumulation was a reversible phenomenon and full recovery of the response occurred 150 min after the removal of the desensitizing histamine-containing medium. The half-time for the recovery of the histamine-induced response was estimated at 120 min.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., DeBlasi A., Stone W. C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: primary structure delineates a multigene family. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):235–240. doi: 10.1126/science.2552582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootman M. D., Berridge M. J., Taylor C. W. All-or-nothing Ca2+ mobilization from the intracellular stores of single histamine-stimulated HeLa cells. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:163–178. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. II. Effects of agonist occupancy on phosphorylation of alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors by protein kinase C and the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3106–3113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow D. R., Arias-Montaño J. A., Young J. M. Histamine-induced inositol phosphate accumulation in HeLa cells: lithium sensitivity. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):677–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow D. R., Young J. M. Characteristics of histamine-induced inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in HeLa cells. Agents Actions Suppl. 1991;33:387–392. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7309-3_28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Prendiville P., Cain C. Alpha 1-adrenergic and H1-histamine receptor control of intracellular Ca2+ in a muscle cell line: the influence of prior agonist exposure on receptor responsiveness. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;29(6):531–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowlen M. S., Barnes M. R., Toews M. L. Regulation of histamine H1 receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis by histamine and phorbol esters in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 13;188(2-3):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90045-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon-Carter O., Chuang D. M. Homologous desensitization of muscarinic cholinergic, histaminergic, adrenergic, and serotonergic receptors coupled to phospholipase C in cerebellar granule cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):598–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driver A. G., Kukoly C. A., Bennett T. E. Expression of histamine H1 receptors on cultured histiocytic lymphoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 15;38(18):3083–3091. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga K., Haga T., Ichiyama A. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1639–1644. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazama A., Yada T., Okada Y. HeLa cells have histamine H1-receptors which mediate activation of the K+ conductance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 30;845(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J. Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Mar;42(1):45–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Regulation of neurotransmitter receptor desensitization by protein phosphorylation. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90211-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of chick heart muscarinic cholinergic receptors by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4543–4547. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai W. S., Rogers T. B., el-Fakahany E. E. Protein kinase C is involved in desensitization of muscarinic receptors induced by phorbol esters but not by receptor agonists. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):23–29. doi: 10.1042/bj2670023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., DeBlasi A., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of adrenergic receptor function by phosphorylation. I. Agonist-promoted desensitization and phosphorylation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors coupled to inositol phospholipid metabolism in DDT1 MF-2 smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3098–3105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G. Role of phosphorylation in desensitization of the beta-adrenoceptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90113-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E. G., Santell L. Thrombin- and histamine-induced signal transduction in human endothelial cells. Stimulation and agonist-dependent desensitization of protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):174–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Agonist-induced desensitization of a P2Y-purinergic receptor-regulated phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19535–19539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough P. M., Eubanks J. H., Brown J. H. Desensitization and recovery of muscarinic and histaminergic Ca2+ mobilization in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):135–141. doi: 10.1042/bj2490135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi M., Payan D. G. Phorbol ester-mediated desensitization of histamine H1 receptors on a cultured smooth muscle cell line. Life Sci. 1988;43(18):1433–1440. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Duchemin A. M., Rose C., Schwartz J. C. Specific desensitization of histamine H1 receptor-mediated [3H]glycogen hydrolysis in brain slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. R., Albers F. J., Middleton J. P., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Obeid L. M., Dennis V. W. 5-HT1A and histamine H1 receptors in HeLa cells stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and phosphate uptake via distinct G protein pools. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):372–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharps E. S., McCarl R. L. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure 32P incorporation into phosphorylated metabolites in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Daniel K., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor regulates its functional coupling to adenylate cyclase and subcellular distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9408–9412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Bayerdörffer E., Haase W., Irvine R. F., Schulz I. Effect of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate on isolated subcellular fractions of rat pancreas. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):241–253. doi: 10.1007/BF01868717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Berridge M. J., Brown K. D., Cooke A. M., Potter B. V. DL-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphorothioate mobilizes intracellular calcium in Swiss 3T3 cells and Xenopus oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):626–632. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90438-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. E., Richelson E. Desensitization of histamine H1 receptor-mediated cyclic GMP formation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):462–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., Tertoolen L. G., Lambrechts A. C., Remorie R., de Laat S. W., Moolenaar W. H. Histamine-H1-receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Ca2+ signalling and membrane-potential oscillations in human HeLa carcinoma cells. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):235–243. doi: 10.1042/bj2660235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Berlin R. D. Intracellular elevations of free calcium induced by activation of histamine H1 receptors in interphase and mitotic HeLa cells: hormone signal transduction is altered during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2533–2539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita M., Fukui H., Sugama K., Horio Y., Ito S., Mizuguchi H., Wada H. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding the bovine histamine H1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11515–11519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



