Abstract
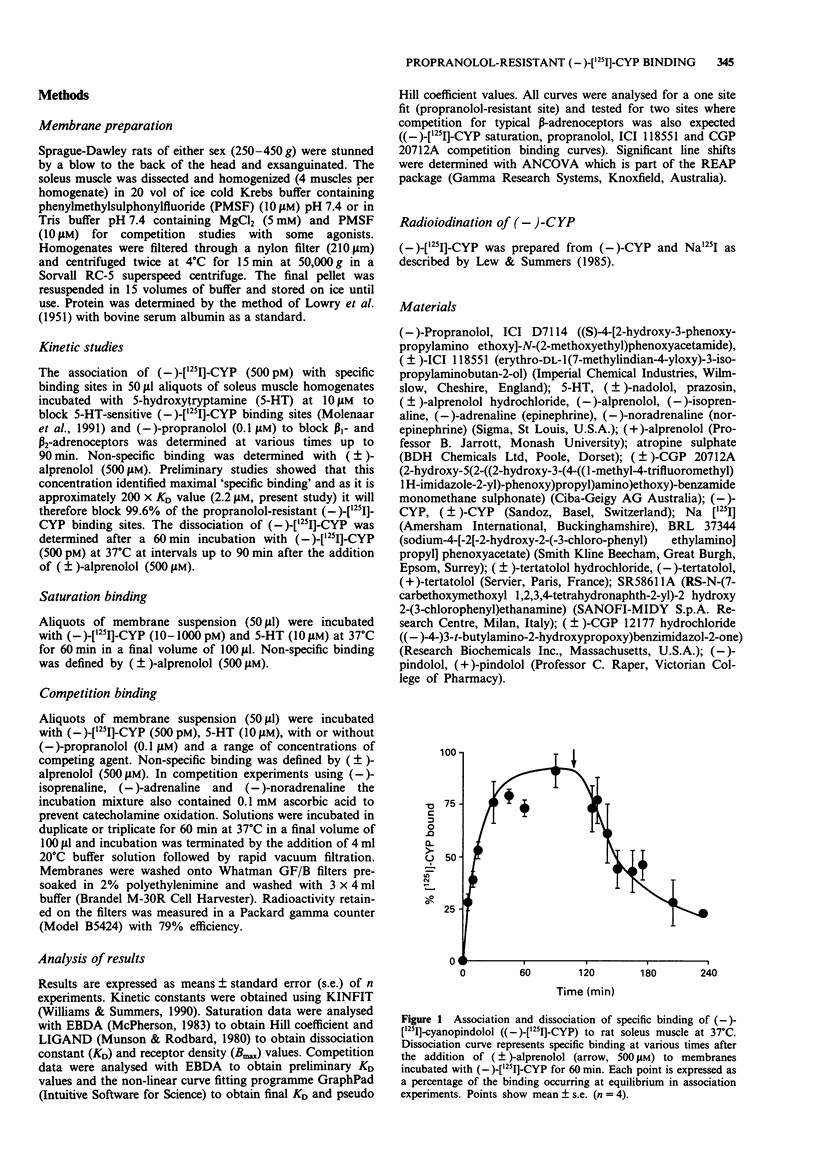
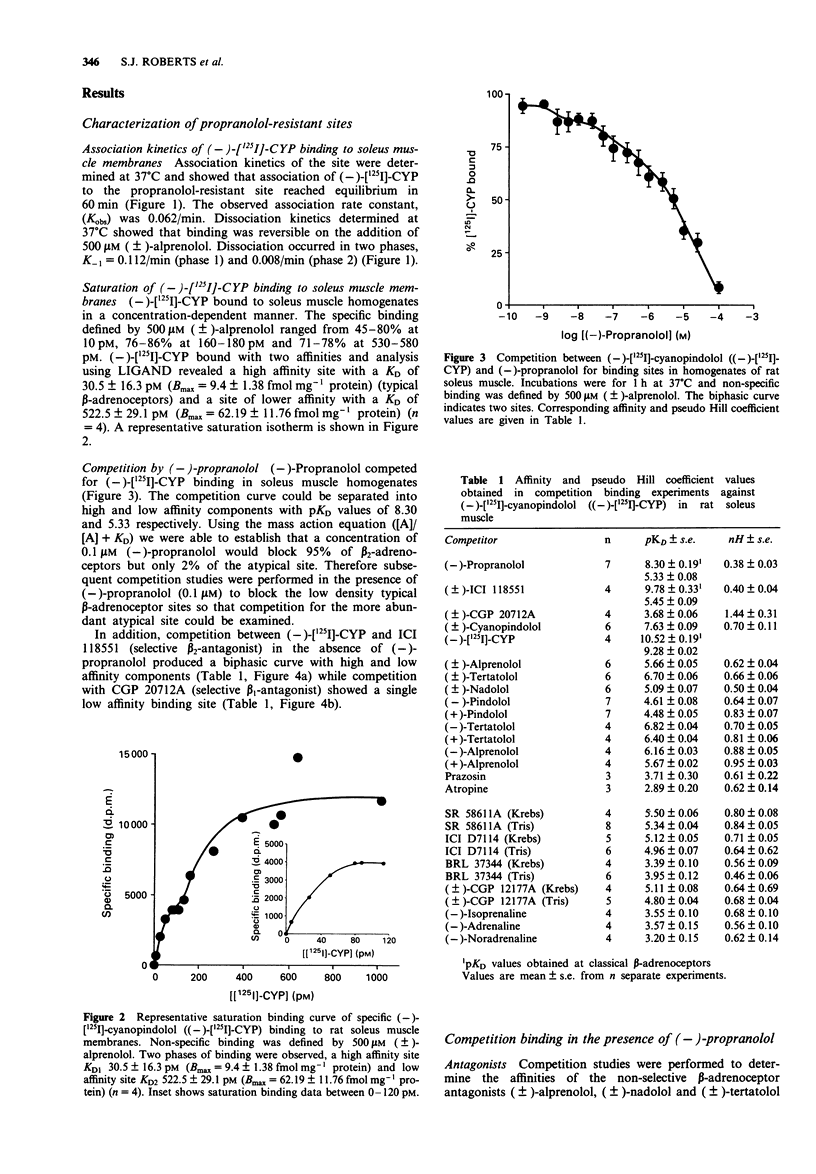
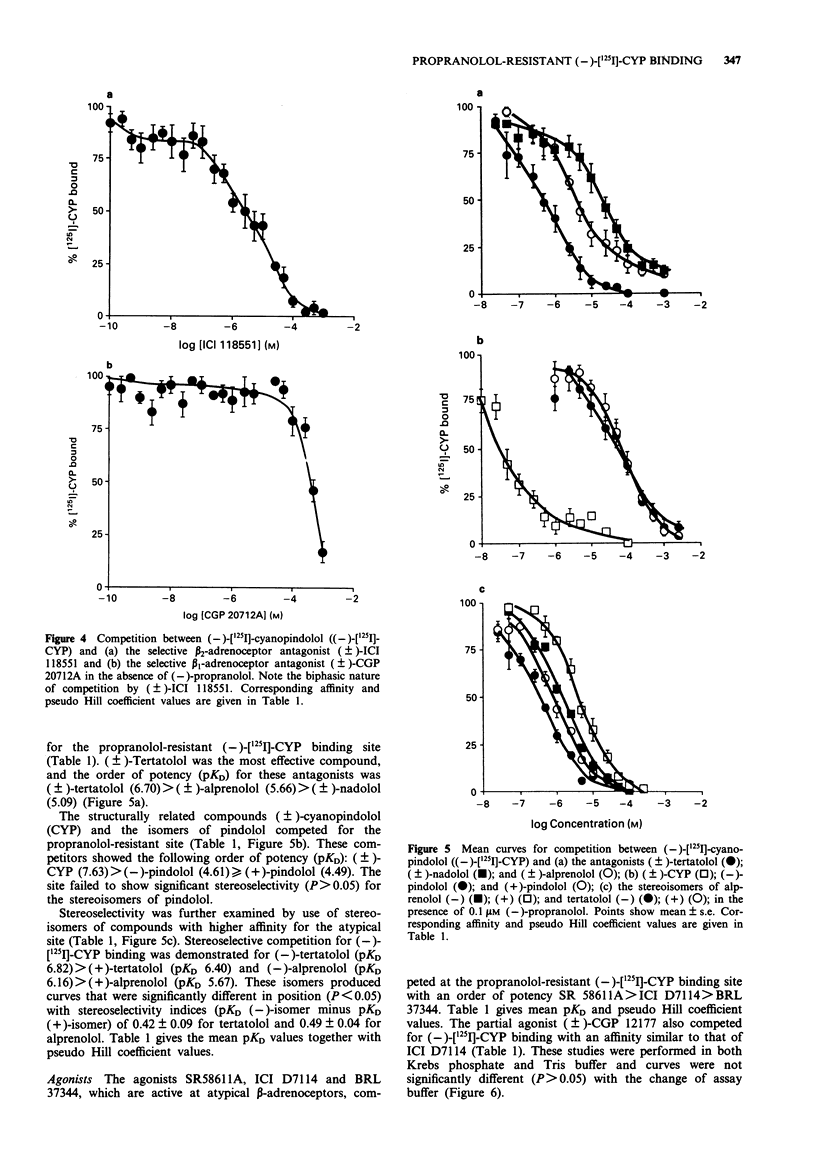
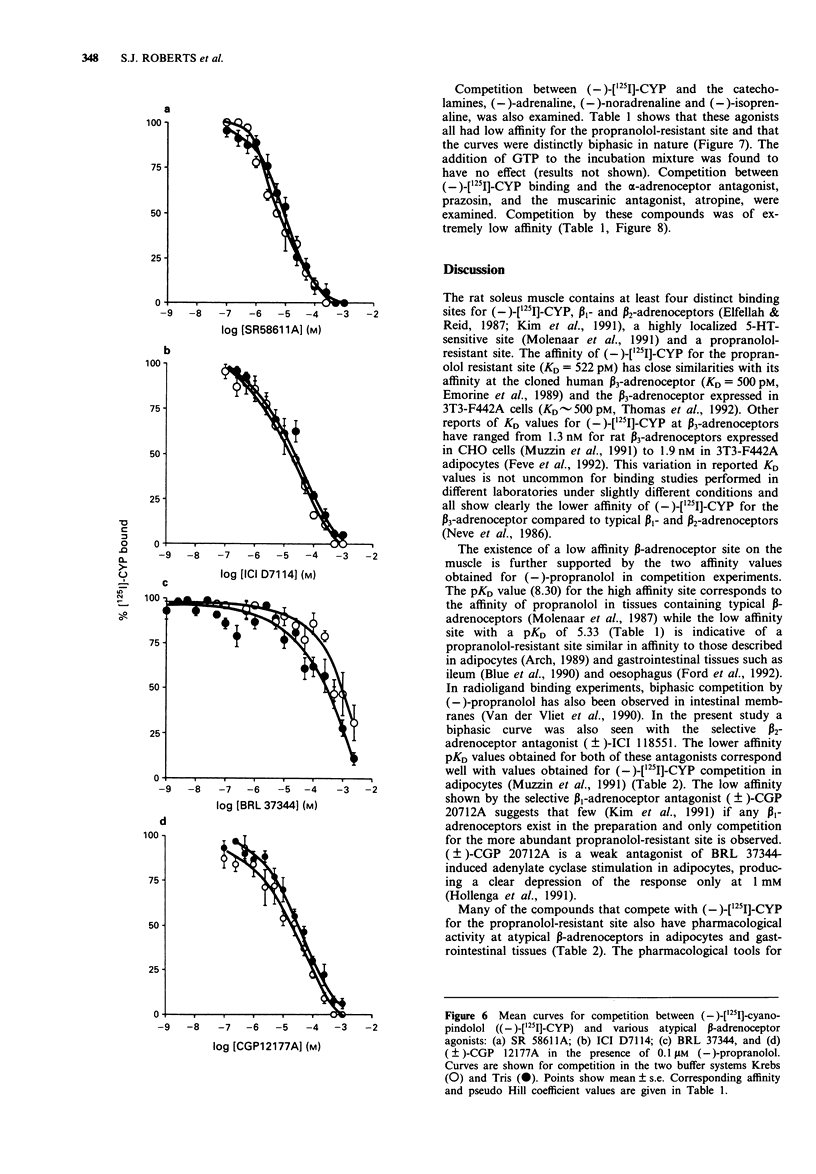
1. The characteristics of a propranolol-resistant (-)-[125I]-cyanopindolol (CYP) binding site in rat soleus muscle were determined. 2. Saturation studies performed on homogenates of rat soleus muscle showed two phases of (-)-[125I]-CYP binding, a high affinity site (KD1 30.5 +/- 16.3 pM, Bmax 9.4 +/- 1.38 fmol mg-1 protein) and a lower affinity site (KD2 522.5 +/- 29.1 pM, Bmax 62.19 +/- 11.76 fmol mg-1 protein, n = 4). 3. In rat soleus muscle homogenates labelled with (-)-[125I]-CYP (500 pM), (-)-propranolol competition curves were biphasic with pKD values of 8.30 +/- 0.19, and 5.33 +/- 0.08, n = 7. 4. Competition between (-)-[125I]-CYP (500 pM) and (+/-)-tertatolol, (+/-)-nadolol, (+/-)-alprenolol, (+/-)-CYP, and (-) and (+)-pindolol showed that these compounds competed for binding at the propranolol-resistant site with affinities lower than those displayed at typical beta-adrenoceptors. The atypical beta-adrenoceptor agonists BRL 37344, SR58611A and ICI D7114 and the partial agonist (+/-)-CGP 12177 also competed for (-)-[125I]-CYP binding. 5. Stereoselectivity was demonstrated for the stereoisomers of alprenolol and tertalolol. The (-)-isomers of alprenolol and tertalolol had higher affinity than their corresponding (+)-isomers (3.1 and 2.6 fold respectively). These low stereoselectivity values are a characteristic of atypical beta-adrenoceptors. 6. The beta-adrenoceptor agonists, (-)-adrenaline, (-)-isoprenaline and (-)-noradrenaline, all showed lower affinity than the atypical beta-adrenoceptor agonists and competition curves appeared biphasic in nature.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
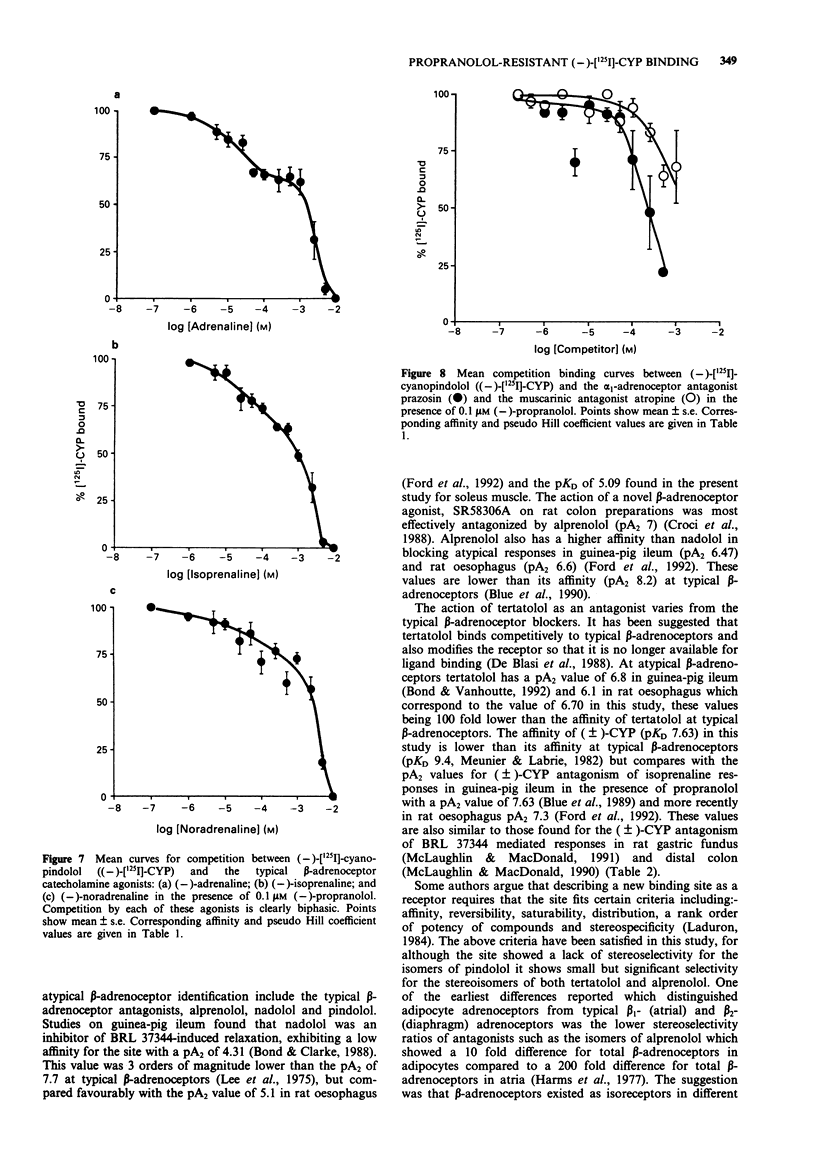
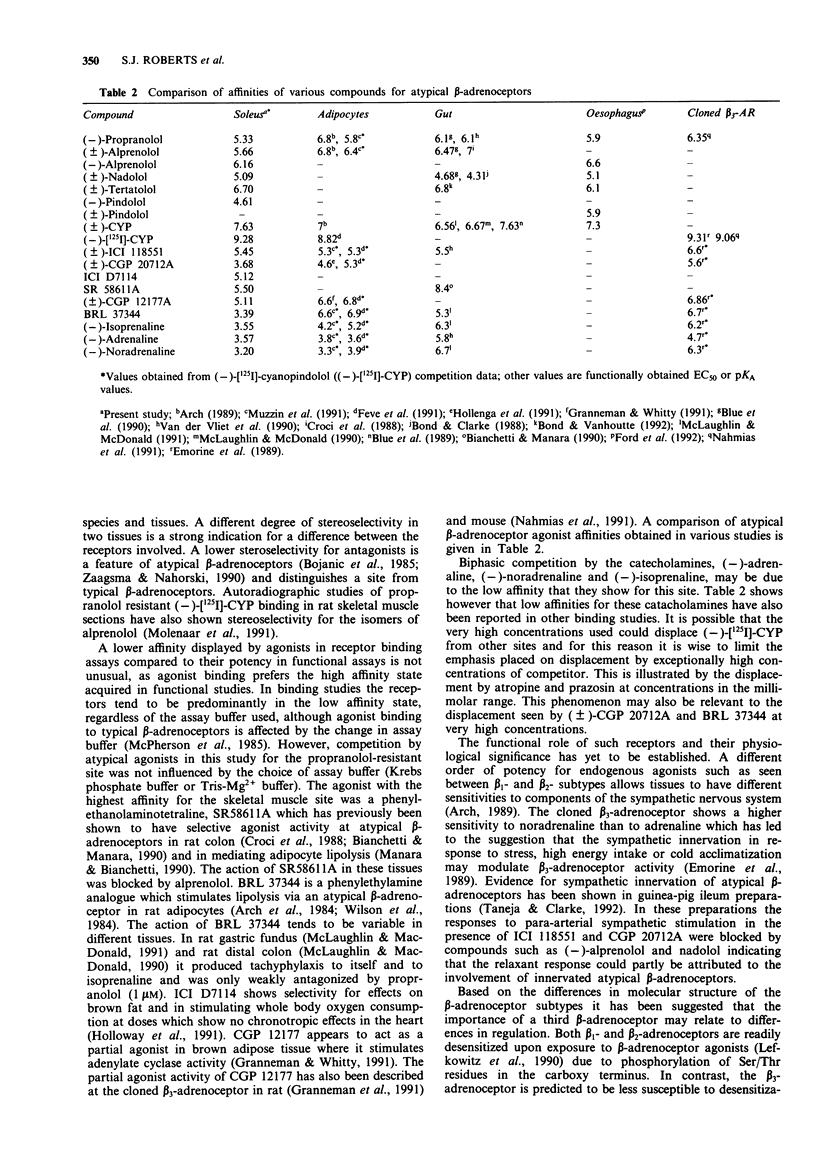


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R. The brown adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Jul;48(2):215–223. doi: 10.1079/pns19890032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti A., Manara L. In vitro inhibition of intestinal motility by phenylethanolaminotetralines: evidence of atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):831–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue D. R., Bond R. A., Adham N., Delmendo R., Michel A. D., Eglen R. M., Whiting R. L., Clarke D. E. Antagonist characterization of atypical beta adrenoceptors in guinea pig ileum: blockade by alprenolol and dihydroalprenolol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1034–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanic D., Jansen J. D., Nahorski S. R., Zaagsma J. Atypical characteristics of the beta-adrenoceptor mediating cyclic AMP generation and lipolysis in the rat adipocyte. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):131–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Charlton K. G., Clarke D. E. Responses to norepinephrine resistant to inhibition by alpha and beta adrenoceptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Vanhoutte P. M. Interaction of tertatolol at the "atypical" or beta 3-adrenoceptor in guinea-pig ileum. Gen Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;23(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(92)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow M., Sherrod T. R., Green R. D. Analysis of beta receptor drug interactions in isolated rabbit atrium, aorta, stomach and trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jan;171(1):52–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckner C. K., Christopherson R. C. Adrenergic receptors of rat esophageal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 May;189(2):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Leighton B., Wilson S., Thurlby P. L., Arch J. R. An investigation of the beta-adrenoceptor that mediates metabolic responses to the novel agonist BRL28410 in rat soleus muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croci T., Cecchi R., Tarantino A., Aureggi G., Bianchetti A., Boigegrain R., Manara L. Inhibition of rat colon motility by stimulation of atypical beta-adrenoceptors with new gut-specific agents. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1988 Feb;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(88)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Blasi A., Fratelli M., Marasco O. Certain beta-blockers can decrease beta-adrenergic receptor number: I. Acute reduction in receptor number by tertatolol and bopindolol. Circ Res. 1988 Aug;63(2):273–278. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfellah M. S., Reid J. L. Identification and characterisation of beta-adrenoceptors in guinea-pig skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Feve B., Pairault J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg D. A. Structural basis for functional diversity of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenergic receptors. 1991 Mar 15-Apr 1Biochem Pharmacol. 41(6-7):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90188-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Baude B., Krief S., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J., Emorine L. J. Inhibition by dexamethasone of beta 3-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Evidence for a transcriptional mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15909–15915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fève B., Emorine L. J., Lasnier F., Blin N., Baude B., Nahmias C., Strosberg A. D., Pairault J. Atypical beta-adrenergic receptor in 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Pharmacological and molecular relationship with the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20329–20336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Whitty C. J. CGP 12177A modulates brown fat adenylate cyclase activity by interacting with two distinct receptor sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivegnée A. R., Fontaine J., Reuse J. Effect of dopamine on dog distal colon in-vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;36(7):454–457. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Zaagsma J., de Vente J. Differentiation of beta-adrenoceptors in right atrium, diaphragm and adipose tissue of the rat, using stereoisomers of propranolol, alprenolol, nifenalol and practolol. Life Sci. 1977 Jul 1;21(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. Relationship between lipolysis and cyclic AMP generation mediated by atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):577–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. R., Howe R., Rao B. S., Stribling D., Mayers R. M., Briscoe M. G., Jackson J. M. ICI D7114 a novel selective beta-adrenoceptor agonist selectively stimulates brown fat and increases whole-body oxygen consumption. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J. Is there a third heart beta-adrenoceptor? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Aug;10(8):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Sainz R. D., Molenaar P., Summers R. J. Characterization of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors in rat skeletal muscles. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 9;42(9):1783–1789. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P. M. Criteria for receptor sites in binding studies. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):833–839. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. J., Evans D. B., Baky S. H., Laffan R. J. Pharmacology of nadolol (SQ 11725), a beta-adrenergic antagonist lacking direct myocardial depression. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep-Oct;33(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G. Role of phosphorylation in desensitization of the beta-adrenoceptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 May;11(5):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90113-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R., Summers R. J. Autoradiographic localization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in guinea-pig kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;85(2):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maltin C. A., Hay S. M., Delday M. I., Reeds P. J., Palmer R. M. Evidence that the hypertrophic action of clenbuterol on denervated rat muscle is not propranolol-sensitive. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;96(4):817–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11889.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manara L., Bianchetti A. Further heterogeneity of the beta-adrenoceptor. The phenylethanolaminotetralines: new selective agonists for atypical beta-adrenoceptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jun;11(6):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Characterization of catecholamine-mediated relaxations in rat isolated gastric fundus: evidence for an atypical beta-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1351–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Evidence for the existence of 'atypical' beta-adrenoceptors (beta 3-adrenoceptors) mediating relaxation in the rat distal colon in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Molenaar P., Malta E., Raper C. Influence of assay buffer on dissociation constants of drugs at beta-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 10;119(1-2):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier H., Labrie F. Specificity of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor stimulating cyclic AMP accumulation in the intermediate lobe of rat pituitary gland. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 16;81(3):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P., Canale E., Summers R. J. Autoradiographic localization of beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptors in guinea pig atrium and regions of the conducting system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):1048–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P., Roberts S. J., Kim Y. S., Pak H. S., Sainz R. D., Summers R. J. Localization and characterization of two propranolol resistant (-) [125I]cyanopindolol binding sites in rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 17;209(3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90179-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Fraser C. M., Giacobino J. P. Radioligand binding studies of the atypical beta 3-adrenergic receptor in rat brown adipose tissue using [3H]CGP 12177. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80046-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Kuhne F., Gocayne J. D., McCombie W. R., Venter J. C., Giacobino J. P., Fraser C. M. An adipose tissue-specific beta-adrenergic receptor. Molecular cloning and down-regulation in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24053–24058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias C., Blin N., Elalouf J. M., Mattei M. G., Strosberg A. D., Emorine L. J. Molecular characterization of the mouse beta 3-adrenergic receptor: relationship with the atypical receptor of adipocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3721–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve K. A., McGonigle P., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of the selectivity of radioligands for subtypes of beta adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jul;238(1):46–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman B. J., Leathard H. L. Evidence that an atypical beta-adrenoceptor mediates the inhibition of spontaneous rhythmical contractions of rabbit isolated jejunum induced by ritodrine and salbutamol. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):27–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12083.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneja D. T., Clarke D. E. Evidence for a noradrenergic innervation to "atypical" beta adrenoceptors (or putative beta-3 adrenoceptors) in the ileum of guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate K. M., Briend-Sutren M. M., Emorine L. J., Delavier-Klutchko C., Marullo S., Strosberg A. D. Expression of three human beta-adrenergic-receptor subtypes in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. F., Holt B. D., Schwinn D. A., Liggett S. B. Long-term agonist exposure induces upregulation of beta 3-adrenergic receptor expression via multiple cAMP response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4490–4494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Localization of adrenergic receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit jejunum to cholinergic neurons and to smooth muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Feb;99(2):190–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wilson S., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Arch J. R. The rat lipolytic beta-adrenoceptor: studies using novel beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 4;100(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. T., McElligott M. A. Multiple actions of beta-adrenergic agonists on skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2610001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaagsma J., Nahorski S. R. Is the adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor a prototype for the recently cloned atypical 'beta 3-adrenoceptor'? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):3–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet A., Rademaker B., Bast A. A beta adrenoceptor with atypical characteristics is involved in the relaxation of the rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):218–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


