Abstract
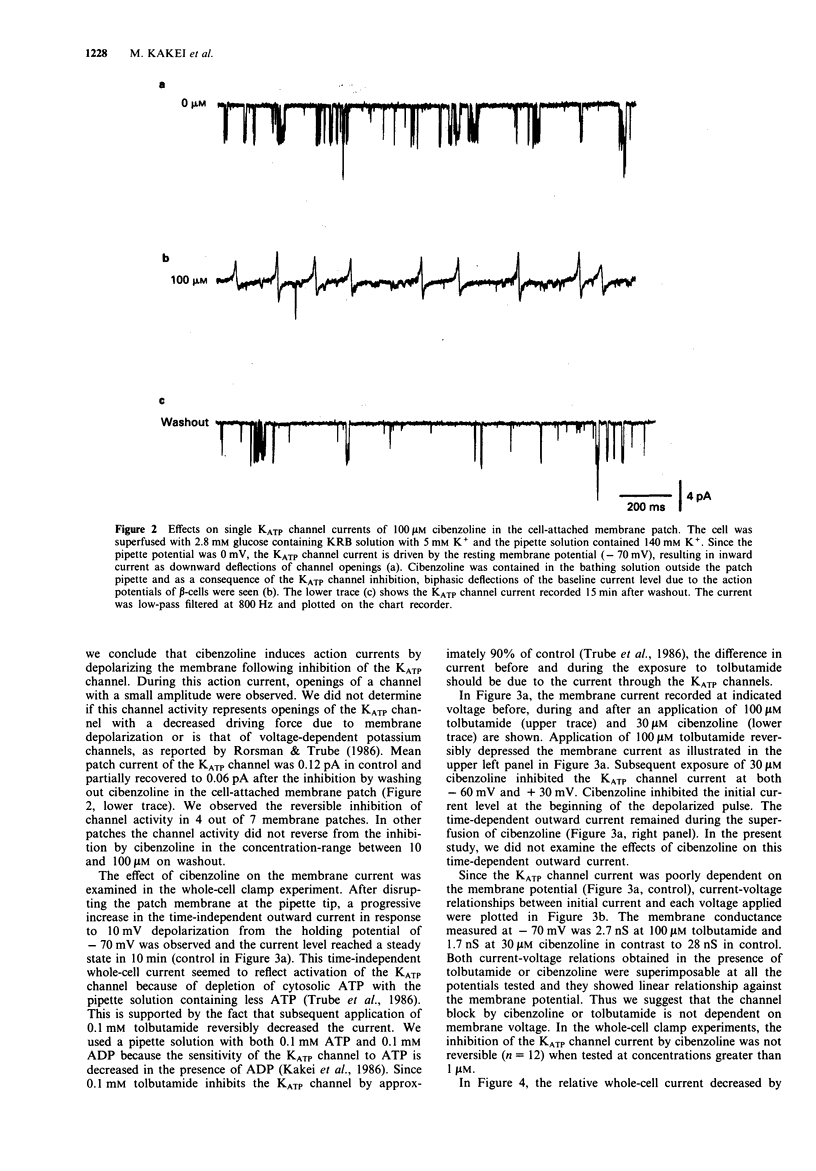
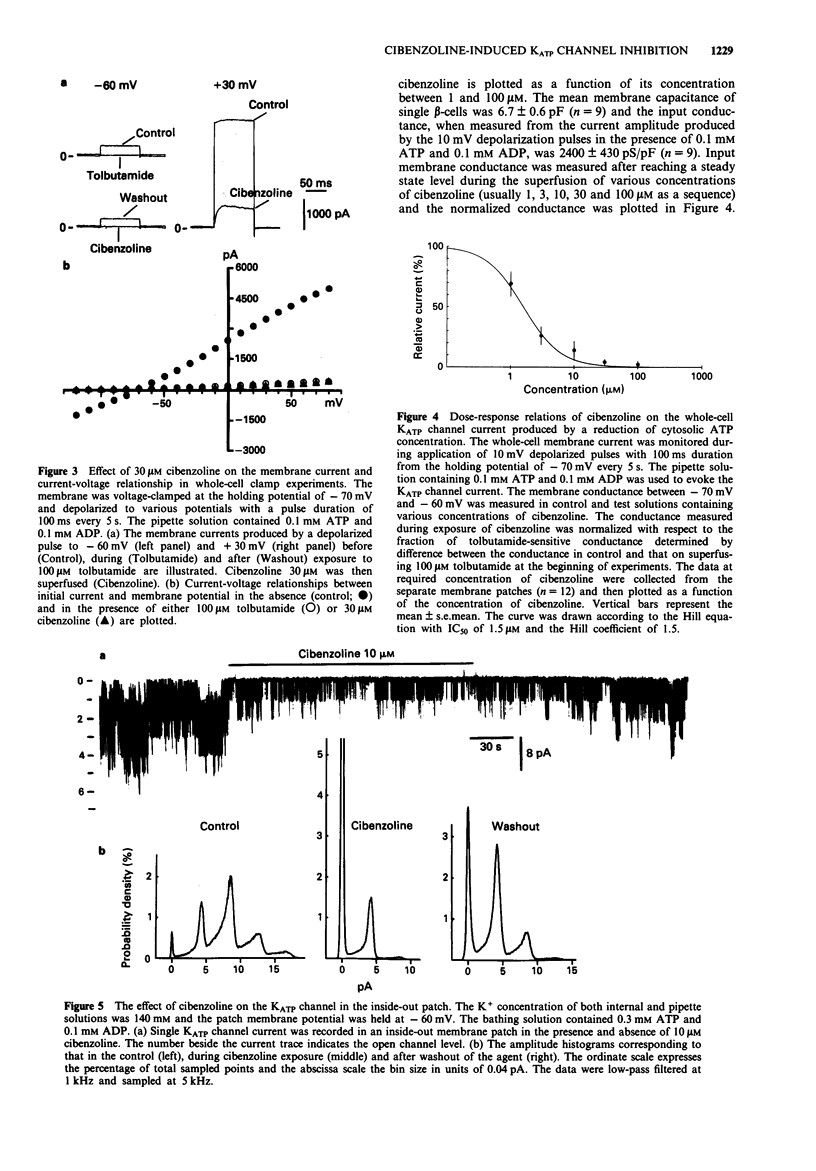
1. Cibenzoline, a class I antiarrhythmic agent, was investigated for its effect on the ATP-sensitive K+ channel of pancreatic beta-cells by the patch clamp technique. 2. In perforated patch clamp experiments, cibenzoline depolarized the membrane of single beta-cells and thereafter, caused firing of action potentials in the presence of 2.8 mM glucose. 3. Cibenzoline inhibited the activity of the ATP-sensitive K+ channel in cell-attached recordings in the presence of 2.8 mM glucose and evoked repetitive fluctuations of the baseline current, apparently reflecting the action potentials of the beta-cell. 4. In whole-cell clamp experiments, time-independent outward current was induced by depleting cytoplasmic ATP with 0.1 mM ATP and 0.1 mM ADP in the solution contained in the pipette. The outward current was inhibited by cibenzoline in a dose-dependent manner in the concentration range of 1 microM to 100 microM and half maximum inhibition occurred at 1.5 microM. 5. Cibenzoline blocked substantially the ATP-sensitive K+ channel current when applied at the inner side of the membrane in isolated inside-out membrane patches. 6. It is concluded that cibenzoline blocks the ATP-sensitive K+ channel of pancreatic beta-cells and, thereby, stimulates insulin secretion at sub-stimulatory levels of glucose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronoff G., Brier M., Mayer M. L., Barbalas M., Aogaichi K., Sloan R., Brazzell R., Massarella J. Bioavailability and kinetics of cibenzoline in patients with normal and impaired renal function. J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;31(1):38–44. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1991.tb01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Harrison D. E., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):446–448. doi: 10.1038/312446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Kerr A. J., Gibson J. S., Williams B. A. Amantadine and sparteine inhibit ATP-regulated K-currents in the insulin-secreting beta-cell line, HIT-T15. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Rorsman P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1989;54(2):87–143. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(89)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand G., Gross R., Petit P., Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Ribes G. Evidence for a direct stimulatory effect of cibenzoline on insulin secretion in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 22;214(2-3):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90113-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Hales C. N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):271–273. doi: 10.1038/311271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachot B. A., Bezier M., Cherrier J. F., Daubeze J. Cibenzoline and hypoglycaemia. Lancet. 1988 Jul 30;2(8605):280–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92570-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Significance of ionic fluxes and changes in membrane potential for stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic B-cells. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1043–1052. doi: 10.1007/BF01971450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman D. E., Mohiuddin S. M., Ahmed I. S., Dahl J. M. Cibenzoline-induced hypoglycemia. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987 Jan;21(1 Pt 1):38–40. doi: 10.1177/10600280870211p104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holck M., Osterrieder W. Inhibition of the myocardial Ca2+ inward current by the class 1 antiarrhythmic agent, cibenzoline. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):705–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdent C., Noblet C., Vandoren C., Levesque H., Morin C., Moore N., Courtois H., Wolf L. M. Hypoglycémie induite par la cibenzoline chez le sujet âgé. Rev Med Interne. 1991 Mar-Apr;12(2):143–145. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(05)81379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeandel C., Preiss M. A., Pierson H., Penin F., Cuny G., Bannwarth B., Netter P. Hypoglycaemia induced by cibenzoline. Lancet. 1988 May 28;1(8596):1232–1233. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakei M., Kelly R. P., Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. The ATP-sensitivity of K+ channels in rat pancreatic B-cells is modulated by ADP. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81533-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Y., Benowitz N. L. Poisoning due to class IA antiarrhythmic drugs. Quinidine, procainamide and disopyramide. Drug Saf. 1990 Nov-Dec;5(6):393–420. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199005060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefort G., Haissaguerre M., Floro J., Beauffigeau P., Warin J. F., Latapie J. L. Hypoglycémies au cours de surdosages par un nouvel antiarythmique: la cibenzoline. Trois observations. Presse Med. 1988 Apr 16;17(14):687–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massarella J. W., Khoo K. C., Szuna A. J., Sandor D. A., Morganroth J., Aogaichi K. Pharmacokinetics of cibenzoline after single and repetitive dosing in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;26(2):125–130. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1986.tb02920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka S., Nawada T., Hisatome I., Miyamoto J., Hasegawa J., Kotake H., Mashiba H. Comparison of Ca2+ channel inhibitory effects of cibenzoline with verapamil on guinea-pig heart. Gen Pharmacol. 1991;22(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(91)90314-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panisko D. M., Keystone J. S. Treatment of malaria--1990. Drugs. 1990 Feb;39(2):160–189. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Ashford M. L., Cook D. L., Hales C. N. The sulphonylurea receptor may be an ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Lancet. 1985 Aug 31;2(8453):474–475. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Peters M., McShane P., Gray D. W., Morris P. J. Isolation of rat pancreatic islets by ductal injection of collagenase. Transplantation. 1986 Dec;42(6):689–691. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198612000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Undrovinas A. I., Burnashev N., Eroshenko D., Fleidervish I., Starmer C. F., Makielski J. C., Rosenshtraukh L. V. Quinidine blocks adenosine 5'-triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in heart. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):H1609–H1612. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.5.H1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yada T., Kakei M., Tanaka H. Single pancreatic beta-cells from normal rats exhibit an initial decrease and subsequent increase in cytosolic free Ca2+ in response to glucose. Cell Calcium. 1992 Jan;13(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(92)90031-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


