Abstract
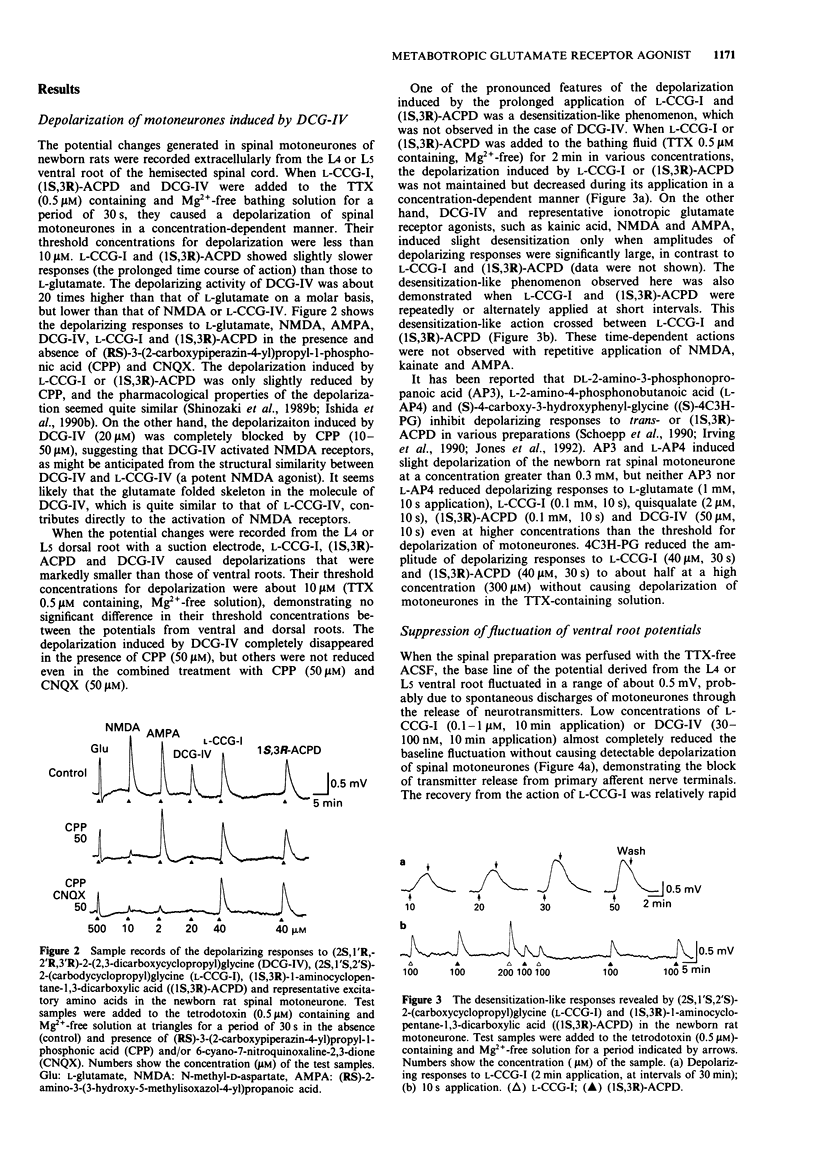
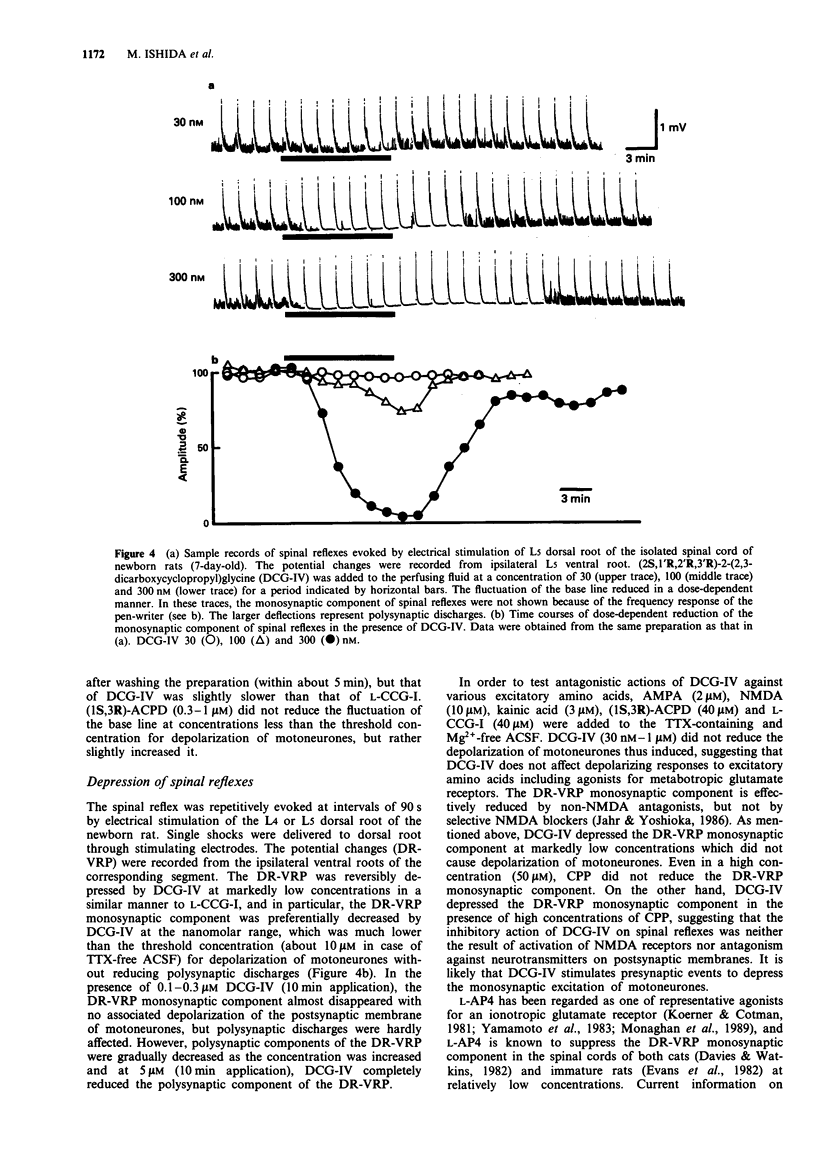
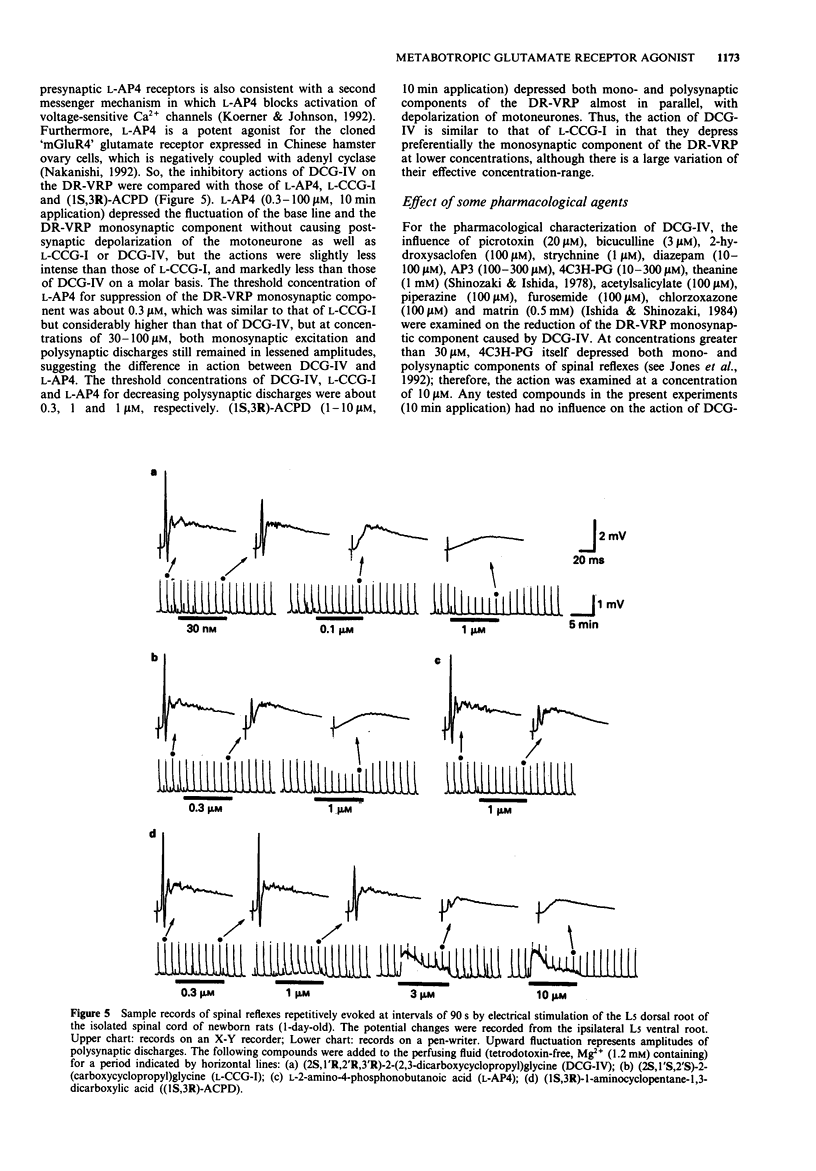
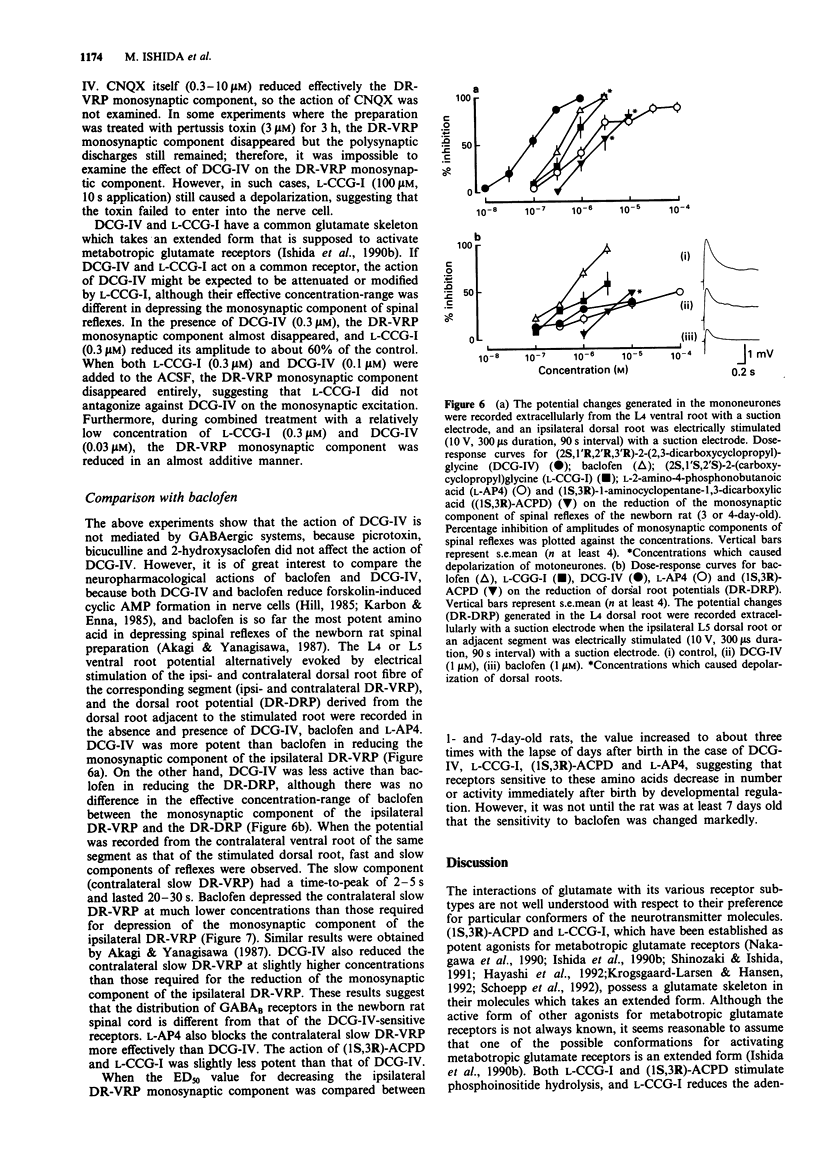
1. Neuropharmacological actions of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, (2S,1'R,2'R,3'R)-2(2,3-dicarboxycyclopropyl)glycine (DCG-IV), were examined in the isolated spinal cord of the newborn rat, and compared with those of the established agonists of (2S,1'S,2'S)-2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (L-CCG-I) or (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid ((1S,3R)-ACPD). 2. At concentrations higher than 10 microM, DCG-IV caused a depolarization which was completely blocked by selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists. The depolarization was pharmacologically quite different from that caused by L-CCG-I and (1S,3R)-ACPD. 3. DCG-IV reduced the monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones rather than polysynaptic discharges in the nanomolar range without causing postsynaptic depolarization of motoneurones. DCG-IV was more effective than L-CCG-I, (1S,3R)-ACPD or L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (L-AP4) in reducing the monosynaptic excitation of motoneurones. 4. DCG-IV (30 nM-1 microM) did not depress the depolarization induced by known excitatory amino acids in the newborn rat motoneurones, but depressed the baseline fluctuation of the potential derived from ventral roots. Therefore, DCG-IV seems to reduce preferentially transmitter release from primary afferent nerve terminals. 5. Depression of monosynaptic excitation caused by DCG-IV was not affected by any known pharmacological agents, including 2-amino-3-phosphonopropanoic acid (AP3), diazepam, 2-hydroxysaclofen, picrotoxin and strychnine. 6. DCG-IV has the potential of providing further useful information on the physiological function of metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagi H., Yanagisawa M. GABAergic modulation of a substance P-mediated reflex of slow time course in the isolated rat spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):189–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss V., Desai M. A., Smith T. S., Conn P. J. Trans-ACPD-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis and modulation of hippocampal pyramidal cell excitability do not undergo parallel developmental regulation. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 30;594(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Watkins J. C. Actions of D and L forms of 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate and 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate in the cat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 11;235(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai M. A., Conn P. J. Excitatory effects of ACPD receptor activation in the hippocampus are mediated by direct effects on pyramidal cells and blockade of synaptic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;66(1):40–52. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Tanabe Y., Aramori I., Masu M., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y., Nakanishi S. Agonist analysis of 2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine isomers for cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R. GABAB receptor modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in rat brain slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):249–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving A. J., Schofield J. G., Watkins J. C., Sunter D. C., Collingridge G. L. 1S,3R-ACPD stimulates and L-AP3 blocks Ca2+ mobilization in rat cerebellar neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90462-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida M., Akagi H., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y., Shinozaki H. A potent metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist: electrophysiological actions of a conformationally restricted glutamate analogue in the rat spinal cord and Xenopus oocytes. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 24;537(1-2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90375-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida M., Ohfune Y., Shimada Y., Shimamoto K., Shinozaki H. Changes in preference for receptor subtypes of configurational variants of a glutamate analog: conversion from the NMDA-type to the non-NMDA type. Brain Res. 1991 May 31;550(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90420-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida M., Shinozaki H. Glutamate inhibitory action of matrine at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;82(2):523–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10789.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Yoshioka K. Ia afferent excitation of motoneurones in the in vitro new-born rat spinal cord is selectively antagonized by kynurenate. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:515–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karbon E. W., Enna S. J. Characterization of the relationship between gamma-aminobutyric acid B agonists and transmitter-coupled cyclic nucleotide-generating systems in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):53–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Horikawa Y., Ishihara T., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y. 2-(Carboxycyclopropyl)glycines: binding, neurotoxicity and induction of intracellular free Ca2+ increase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90529-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner J. F., Cotman C. W. Micromolar L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid selectively inhibits perforant path synapses from lateral entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1981 Jul 6;216(1):192–198. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo Y., Akita K., Ishida M., Shinozaki H. A significant increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration induced by (2S,3R,4S)-2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine, a new potent NMDA agonist, in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 20;567(2):342–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90817-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovinger D. M. Trans-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid (t-ACPD) decreases synaptic excitation in rat striatal slices through a presynaptic action. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Aug 5;129(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90710-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. J. Metabotropic excitatory amino acid receptors reveal their true colors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Oct;12(10):365–367. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90604-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Bridges R. J., Cotman C. W. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:365–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Saitoh K., Ishihara T., Ishida M., Shinozaki H. (2S,3S,4S) alpha-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine is a novel agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 2;184(1):205–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90686-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):597–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1329206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawy S., Jahr C. E. Suppression by glutamate of cGMP-activated conductance in retinal bipolar cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):269–271. doi: 10.1038/346269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti F., Iadarola M. J., Wroblewski J. T., Costa E. Excitatory amino acid recognition sites coupled with inositol phospholipid metabolism: developmental changes and interaction with alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1931–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Trans-ACPD, a selective agonist of the phosphoinositide-coupled excitatory amino acid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):585–587. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter R. H., Roberts P. J., Jane D. E., Watkins J. C. (S)-homoquisqualate: a potent agonist at the glutamate metabotropic receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):509–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Johnson B. G., Monn J. A. Inhibition of cyclic AMP formation by a selective metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist. J Neurochem. 1992 Mar;58(3):1184–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D., Bockaert J., Sladeczek F. Pharmacological and functional characteristics of metabotropic excitatory amino acid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):508–515. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90052-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiells R. A., Falk G. Glutamate receptors of rod bipolar cells are linked to a cyclic GMP cascade via a G-protein. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Nov 22;242(1304):91–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ishida M. A metabotropic L-glutamate receptor agonist: pharmacological difference between rat central neurones and crayfish neuromuscular junctions. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1992 Sep;103(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(92)90220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ishida M. Excitatory amino acids: physiological and pharmacological probes for neuroscience research. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1993;53(1):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ishida M., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y. A conformationally restricted analogue of L-glutamate, the (2S,3R,4S) isomer of L-alpha-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine, activates the NMDA-type receptor more markedly than NMDA in the isolated rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 20;480(1-2):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ishida M., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y. Potent NMDA-like actions and potentiation of glutamate responses by conformational variants of a glutamate analogue in the rat spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1213–1224. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki H., Ishida M. Theanine as a glutamate antagonist at a crayfish neuromuscular junction. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 28;151(1):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90967-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Hirono C. A new type of glutamate receptor linked to inositol phospholipid metabolism. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):531–533. doi: 10.1038/325531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Ito I., Watanabe M. Glutamate receptor subtypes may be classified into two major categories: a study on Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):129–132. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90118-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., Sawada S., Takada S. Suppressing action of 2-amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid on mossy fiber-induced excitation in the guinea pig hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1983;51(1):128–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00236810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


