Abstract
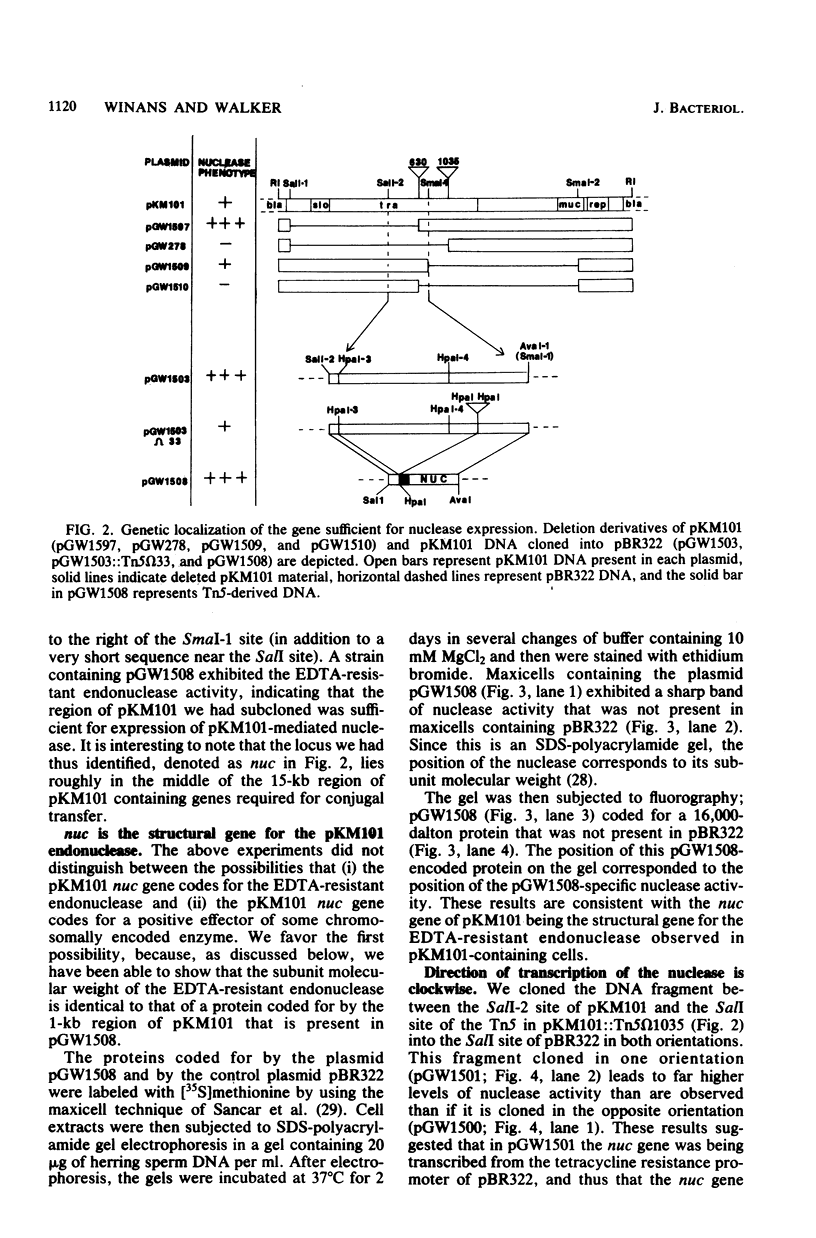
The genetic and biochemical properties of an endonuclease mediated by the mutagenesis-enhancing plasmid pKM101 have been investigated. Taking advantage of the observation that this endonuclease, unlike host-coded DNases, is active in the presence of EDTA, we have developed an assay with nondenaturing acrylamide gels containing DNA. We have localized the plasmid DNA sufficient for nuclease expression to a 0.8-kilobase sequence that is near regions of DNA necessary for conjugal transfer, and we have determined that this gene is transcribed clockwise on the pKM101 map. The pKM101 gene mediating this activity codes for a 16,000-dalton protein, which is the same molecular mass as the nuclease monomer, leading us to conclude that this gene codes for the nuclease itself rather than for an activator of some host-coded enzyme. Cellular fractionation experiments have shown that the enzyme is localized in the periplasm. We have not been able to demonstrate any physiological role for the enzyme, but we have ruled out a direct involvement of the nuclease in any of the following known plasmid-associated phenotypes: (i) mutagenesis enhancement, (ii) conjugal transfer, (iii) entry exclusion, (iv) fertility inhibition of coresident P-group plasmids, (v) killing of Klebsiella pneumoniae used as conjugal recipients, and (vi) plasmid curing induced by treatment of cells with fluorodeoxyuridine. In addition, we have shown that the enzyme does not restrict bacteriophage or affect the ability of the host to utilize DNA as a source of thymine. Finally, we have shown that 11 of the 26 other plasmids tested also elaborated EDTA-resistant DNases.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achtman M., Kennedy N., Skurray R. Cell--cell interactions in conjugating Escherichia coli: role of traT protein in surface exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5104–5108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Morphology of pili determined by the N incompatibility group plasmid N3 and interaction with bacteriophages PR4 and IKe. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):632–636. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Rutherford E. L. Basic characterization of a lipid-containing bacteriophage specific for plasmids of the P, N, and W compatibility groups. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;21(2):152–163. doi: 10.1139/m75-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Willetts N. S. A physical and genetic map of the IncN plasmid R46. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):188–201. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Walker G. C. Proteins required for ultraviolet light and chemical mutagenesis. Identification of the products of the umuC locus of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):175–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatoon H., Iyer R. V., Iyer V. N. A new filamentous bacteriophage with sex-factor specificity. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Botstein D. Secretion of beta-lactamase requires the carboxy end of the protein. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):749–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackey D., Walker G. C., Keng T., Linn S. Characterization of an endonuclease associated with the drug resistance plasmid pKM101. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.583-588.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. J., Shanabruch W. G., Walker G. C. Functional organization of plasmid pKM101. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1310–1316. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1310-1316.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. J., Walker G. C. Restriction endonuclease cleavage map of pKM101: relationship to parental plasmid R46. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00269669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto H., Kamio Y., Kobayashi R., Terawaki Y. R plasmic Rtsl-mediated production of extracellular deoxyribonuclease in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):387–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.387-389.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W. Analytical isoelectric focusing of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):713–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.713-718.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann J., Spingarn N. E., Kobori J., Ames B. N. Detection of carcinogens as mutagens: bacterial tester strains with R factor plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):979–983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortelmans K. E., Stocker B. A. Ultraviolet light protection, enhancement of ultraviolet light mutagenesis, and mutator effect of plasmid R46 in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):271–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.271-282.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Margolin W., Krueger J. H., Walker G. C. Mutations affecting regulation of methionine biosynthetic genes isolated by use of met-lac fusions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.609-619.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEU H. C., HEPPEL L. A. THE RELEASE OF RIBONUCLEASE INTO THE MEDIUM WHEN ESCHERICHIA COLI CELLS ARE CONVERTED TO SPEROPLASTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3893–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. L. RP1 properties and fertility inhibition among P, N, W, and X incompatibility group plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):28–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.28-35.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Walker G. C. Identification of plasmid (pKM101)-coded proteins involved in mutagenesis and UV resistance. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):278–281. doi: 10.1038/300278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney R. J., Bremer K., Smith J. T. R factor elimination by inhibitors of thymidylate synthetase (fluorodeoxyuridine and showdomycin) and the occurrence of single strand breaks in plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00264837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney R. J., Smith J. T. R-factor elimination by thymine starvation. Genet Res. 1971 Oct;18(2):173–177. doi: 10.1017/s001667230001257x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A., Hogness D. S. Translation of Drosophila melanogaster sequences in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Iyer V. N. Killing of Klebsiella pneumoniae mediated by conjugation with bacteria carrying antibiotic-resistance plasmids of the group N. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. L., Lacks S. A. Nuclease detection in SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 15;80(1):76–90. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90627-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORTMAN K., LEHMAN I. R. THE DEOXYRIBONUCLEASES OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. VI. CHANGES IN ENZYME LEVELS IN RESPONSE TO ALTERATIONS IN PHYSIOLOGICAL STATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2964–2974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Wharton R. P., Seltzer S., Kacinski B. M., Clarke N. D., Rupp W. D. Identification of the uvrA gene product. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 5;148(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90234-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanabruch W. G., Walker G. C. Localization of the plasmid (pKM101) gene(s) involved in recA+lexA+-dependent mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(2):289–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00425456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweats D. J., Pinney R. J., Smith J. T. R-factor-mediated nuclease activity involved in thymineless elimination. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):790–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.790-795.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C., Dobson P. P. Mutagenesis and repair deficiencies of Escherichia coli umuC mutants are suppressed by the plasmid pKM101. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Apr 17;172(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00276210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





