Abstract
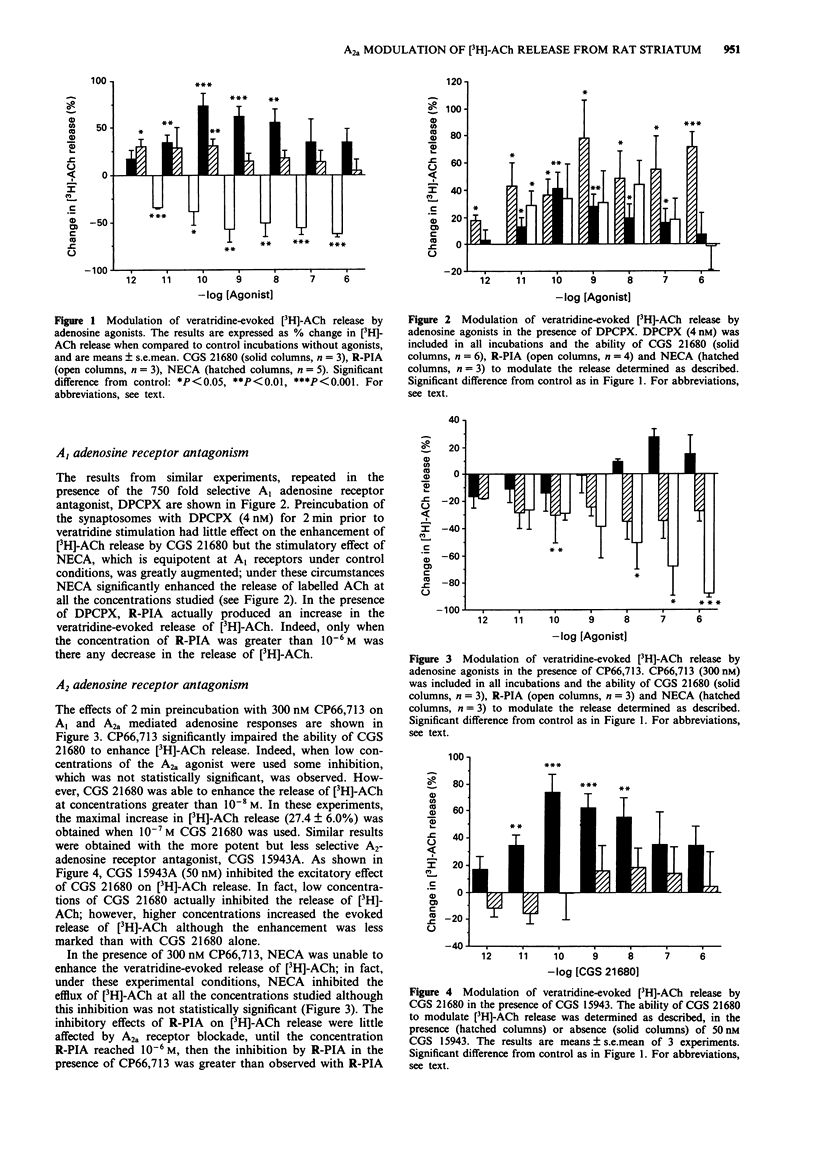
1. The effects of A1 and A2a adenosine receptor agonists on the veratridine-evoked release of [3H]-acetylcholine ([3H]-ACh) from rat striatal synaptosomes was investigated by use of the A1-selective agonist, R-PIA and the 185 fold selective A2a agonist, CGS 21680. The effects of NECA, which is equipotent at both receptor subtypes, were also studied. 2. The evoked release of [3H]-ACh was significantly enhanced by the A2a agonist CGS 21680 but decreased by the A1 agonist, R-PIA. The effects of NECA were dependent on the concentration used, with high concentrations inhibiting and low concentrations enhancing the evoked release of [3H]-ACh. In the absence of any antagonists, the rank order of potency for these three drugs on increasing [3H]-ACh release was CGS 21680 > NECA > R-PIA. 3. The stimulatory effects of CGS 21680 and low NECA concentrations on evoked [3H]-ACh release were antagonized by the A2a receptor antagonists, CP66,713 (300 nM) and CGS 15943A (50 nM) whilst the inhibitory effects of R-PIA were reversed by the selective A1 antagonist, DPCPX (4 nM). In the presence of DPCPX, NECA greatly enhanced the evoked release of [3H]-ACh at all concentrations studied when, during such A1 receptor blockade, the rank order of potency was NECA >> CGS 21680 > R-PIA. 4. These results demonstrate that both A1 and A2a adenosine receptors modulate the veratridine-evoked release of [3H]-ACh from rat striatal synaptosomes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barraco R. A., Phillis J. W. Subtypes of adenosine receptors in the brainstem mediate opposite blood pressure responses. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Apr;30(4):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90067-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., James S., Reddington M., Richardson P. J. Both A1 and A2a purine receptors regulate striatal acetylcholine release. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correia-de-Sá P., Sebastião A. M., Ribeiro J. A. Inhibitory and excitatory effects of adenosine receptor agonists on evoked transmitter release from phrenic nerve ending of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1614–1620. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T. V. The physiological role of adenosine in the central nervous system. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1985;27:63–139. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. S., Weaver D. R., Rivkees S. A., Peterfreund R. A., Pollack A. E., Adler E. M., Reppert S. M. Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: selective co-expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jul;14(3):186–195. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Dunwiddie T. V. How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G., WHITTAKER V. P. The isolation of nerve endings from brain: an electron-microscopic study of cell fragments derived by homogenization and centrifugation. J Anat. 1962 Jan;96:79–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide I., Padgett W. L., Jacobson K. A., Daly J. W. A2A adenosine receptors from rat striatum and rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells: characterization with radioligand binding and by activation of adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):352–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison A. J., Webb R. L., Oei H. H., Ghai G. R., Zimmerman M. B., Williams M. CGS 21680C, an A2 selective adenosine receptor agonist with preferential hypotensive activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):47–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S., Richardson P. J. The subcellular distribution of [3H]-CGS 21680 binding sites in the rat striatum: copurification with cholinergic nerve terminals. Neurochem Int. 1993 Aug;23(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90088-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S., Xuereb J. H., Askalan R., Richardson P. J. Adenosine receptors in post-mortem human brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):238–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden J. Adenosine deaminase for removing adenosine: how much is enough? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jul;10(7):260–262. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupica C. R., Cass W. A., Zahniser N. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Effects of the selective adenosine A2 receptor agonist CGS 21680 on in vitro electrophysiology, cAMP formation and dopamine release in rat hippocampus and striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1134–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Mir M. I., Probst A., Palacios J. M. Adenosine A2 receptors: selective localization in the human basal ganglia and alterations with disease. Neuroscience. 1991;42(3):697–706. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90038-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson F. E., Fredholm B. B. Autoradiographic evidence for G-protein coupled A2-receptors in rat neostriatum using [3H]-CGS 21680 as a ligand. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;342(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00178977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittel Z., Heldman E., Rubinstein R., Cohen S. Distinct muscarinic receptor subtypes differentially modulate acetylcholine release from corticocerebral synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1990 Aug;55(2):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter N. M., Radulovacki M., Green R. D. Desensitization of adenosine and dopamine receptors in rat brain after treatment with adenosine analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jan;244(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Olah M. E., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Distinct pathways of desensitization of A1- and A2-adenosine receptors in DDT1 MF-2 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):639–647. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to A1 adenosine receptors by guanine nucleotides is mediated via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1194–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. J. Choline uptake and metabolism in affinity-purified cholinergic nerve terminals from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1986 Apr;46(4):1251–1255. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. J. Quantitation of cholinergic synaptosomes from guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):258–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. J., Siddle K., Luzio J. P. Immunoaffinity purification of intact, metabolically active, cholinergic nerve terminals from mammalian brain. Biochem J. 1984 Apr 15;219(2):647–654. doi: 10.1042/bj2190647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarges R., Howard H. R., Browne R. G., Lebel L. A., Seymour P. A., Koe B. K. 4-Amino[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalines. A novel class of potent adenosine receptor antagonists and potential rapid-onset antidepressants. J Med Chem. 1990 Aug;33(8):2240–2254. doi: 10.1021/jm00170a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Jacobs O., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Striatal restricted adenosine A2 receptor (RDC8) is expressed by enkephalin but not by substance P neurons: an in situ hybridization histochemistry study. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):1062–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Libert F., Vassart G., Dumont J. E., Vanderhaeghen J. J. A cloned G protein-coupled protein with a distribution restricted to striatal medium-sized neurons. Possible relationship with D1 dopamine receptor. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 11;519(1-2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90097-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Libert F., Vassart G., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Distribution of adenosine A2 receptor mRNA in the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Sep 16;130(2):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastião A. M., Ribeiro J. A. Evidence for the presence of excitatory A2 adenosine receptors in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Apr 13;138(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90467-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. E., O'Regan M. H., Perkins L. M., Phillis J. W. Excitatory transmitter amino acid release from the ischemic rat cerebral cortex: effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1683–1690. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Adenosine as a neuromodulator. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:103–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan W., Sutherland G. R., Geiger J. D. Binding of the adenosine A2 receptor ligand [3H]CGS 21680 to human and rat brain: evidence for multiple affinity sites. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1763–1771. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Q. Y., Li C., Olah M. E., Johnson R. A., Stiles G. L., Civelli O. Molecular cloning and characterization of an adenosine receptor: the A3 adenosine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7432–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


