Abstract
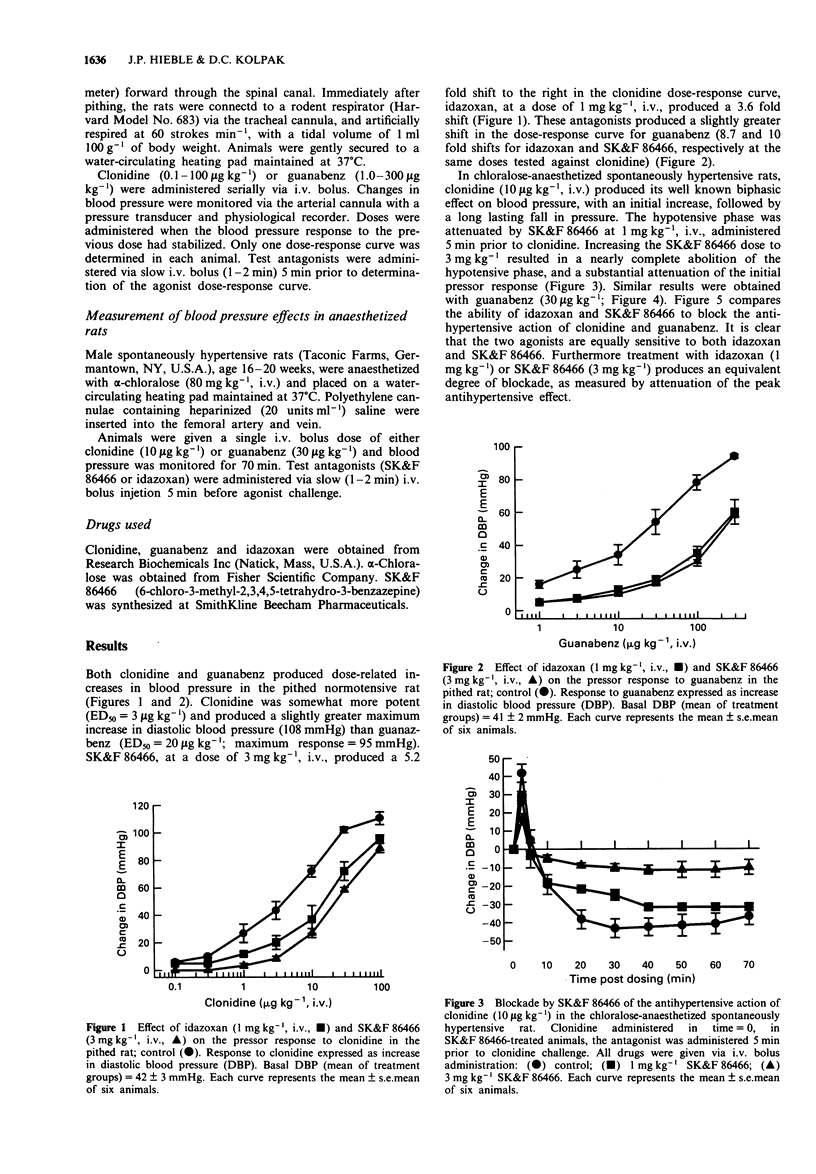
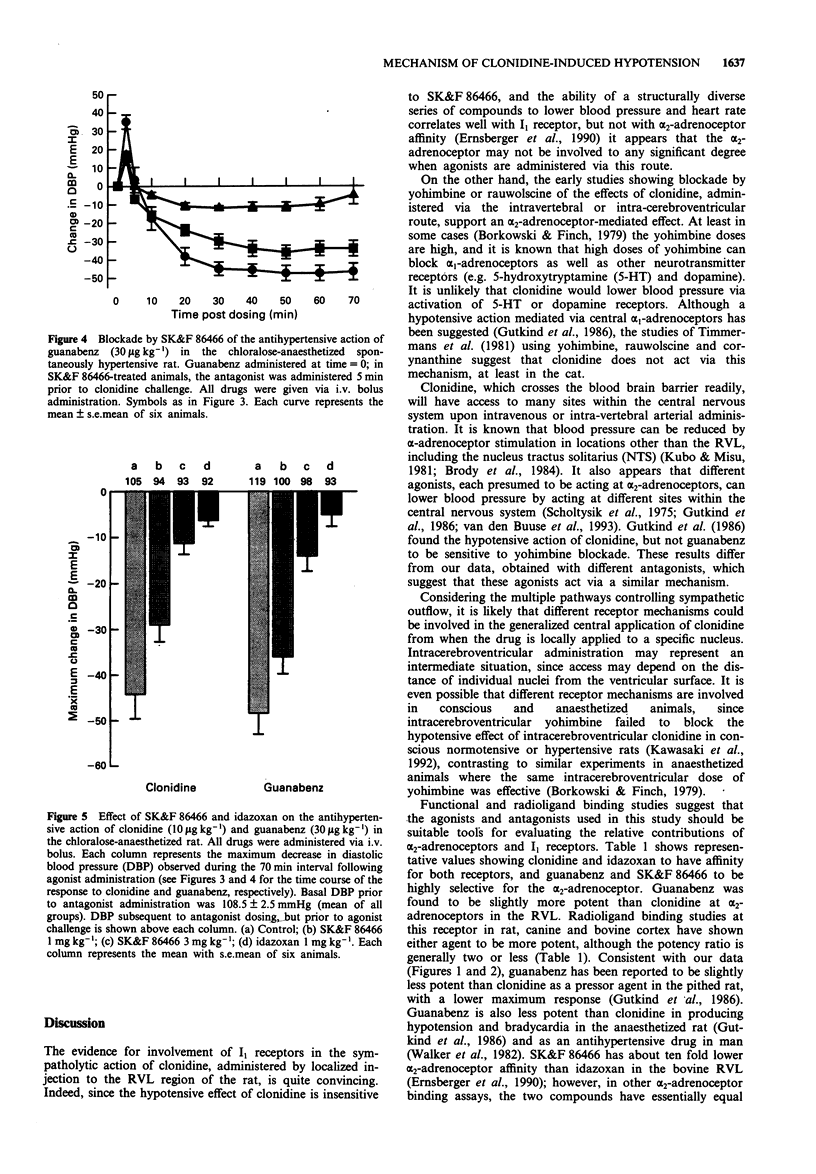
1. During the past few years it has been shown that the sympatholytic effect resulting from localized microinjection of clonidine and other imidazolines into the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVL) results from activation of 'imidazoline' receptors (I1 receptors) rather than from an alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated effect. 2. The relative contributions of these two receptor systems to the hypotensive action of systemically administered clonidine have not been studied. Clonidine has affinity for both I1 and alpha 2-adrenoceptors; guanabenz represents a useful pharmacological tool, since it activates only the alpha 2-adrenoceptor. 3. Antagonists acting at both I1 and alpha 2-adrenoceptors (idazoxan) and at only alpha 2-adrenoceptors (SK&F 86466; 6-chloro-3-methyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-3-benzazepine) are available. Idazoxan (1 mg kg-1, i.v.) and SK&F 86466 (3 mg kg-1, i.v.) produced an equivalent degree of blockade of the pressor response to guanabenz or clonidine in the pithed rat, a response mediated by the alpha 2-adrenoceptor. 4. Guanabenz (30 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) and clonidine (10 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) lowered blood pressure in the chloralose-anaesthetized spontaneously hypertensive rat by 48 +/- 4.6 mmHg and 44 +/- 5.4 mmHg, respectively; this response, for either agonist, was blocked by both idazoxan and SK&F 86466. 5. These data show that the hypotensive effect of intravenously administered clonidine results from activation of central alpha 2-adrenoceptors, with no significant contribution from an I1-mediated effect. Thus clonidine can lower blood pressure by different receptor mechanisms, dependent on the route of administration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaxall H. S., Murphy T. J., Baker J. C., Ray C., Bylund D. B. Characterization of the alpha-2C adrenergic receptor subtype in the opossum kidney and in the OK cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski K. R., Finch L. A comparison of the cardiovascular effects of centrally administered clonidine and adrenaline in the anaesthetized rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;31(1):16–19. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricca G., Dontenwill M., Molines A., Feldman J., Belcourt A., Bousquet P. The imidazoline preferring receptor: binding studies in bovine, rat and human brainstem. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 14;162(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90597-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricca G., Dontenwill M., Molines A., Feldman J., Tibirica E., Belcourt A., Bousquet P. Rilmenidine selectivity for imidazoline receptors in human brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr 25;163(2-3):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody M. J., O'Neill T. P., Porter J. P. Role of central catecholaminergic systems in pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 5):S727–S741. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198400065-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Damon T. H., Graff L. M., Schäfer S. G., Christen M. O. Moxonidine, a centrally acting antihypertensive agent, is a selective ligand for I1-imidazoline sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):172–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Reis D. J. Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):408–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Meeley M. P., Mann J. J., Reis D. J. Clonidine binds to imidazole binding sites as well as alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the ventrolateral medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 28;134(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. E., Ernsberger P., Feinland G., Reis D. J. Rilmenidine lowers arterial pressure via imidazole receptors in brainstem C1 area. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar 26;195(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90534-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Kazanietz M., Enero M. A. Cardiovascular effects of alpha-adrenergic drugs: differences between clonidine and guanabenz. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;332(4):370–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00500089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Hunt A. A., Poyser R. H. Involvement of central alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the mediation of clonidine-induced hypotension in the cat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;32(11):788–789. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb13069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., DeMarinis R. M., Fowler P. J., Matthews W. D. Selective alpha-2 adrenoceptor blockade by SK&F 86466: in vitro characterization of receptor selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jan;236(1):90–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Sulpizio A. C., Nichols A. J., DeMarinis R. M., Pfeiffer F. R., Lavanchy P. G., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Pharmacological differentiation of pre- and post-junctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Dec;4(6):S189–S192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki H., Nakamura S., Takasaki K. Central alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated pressor response to clonidine in conscious, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;59(3):321–331. doi: 10.1254/jjp.59.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. R., Gundlach A. L., Jarrott B., Louis W. J. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor and catecholamine-insensitive binding sites for [3H]rilmenidine in membranes from rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 21;218(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90152-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Misu Y. Pharmacological characterisation of the alpha-adrenoceptors responsible for a decrease of blood pressure in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;317(2):120–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00500066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Paris H., Lafontan M. Binding of [3H]idazoxan and of its methoxy derivative [3H] RX821002 in human fat cells: [3H]idazoxan but not [3H] RX821002 labels additional non-alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):876–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Koenig-Bérard E., Vitou P. The imidazoline-preferring receptor. Life Sci. 1989;45(18):1609–1615. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. G., Rand M. J. Rilmenidine differs from clonidine in that it lacks histamine-like activity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;41(7):464–468. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1989.tb06501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megens A. A., Leysen J. E., Awouters F. H., Niemegeers C. J. Further validation of in vivo and in vitro pharmacological procedures for assessing the alpha 2/alpha 1-selectivity of test compounds: (2). Alpha-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 23;129(1-2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90336-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brodde O. E., Schnepel B., Behrendt J., Tschada R., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. [3H]idazoxan and some other alpha 2-adrenergic drugs also bind with high affinity to a nonadrenergic site. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Ernsberger P. Keeping an eye on the I site: imidazoline-preferring receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parini A., Coupry I., Graham R. M., Uzielli I., Atlas D., Lanier S. M. Characterization of an imidazoline/guanidinium receptive site distinct from the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11874–11878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Fénard S. Action of -adrenergic blocking drugs on the sympathetic centres and their interactions with the central sympatho-inhibitory effect of clonidine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1973 Jan;23(1):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtysik G., Lauener H., Eichenberger E., Bürki H., Salzmann R., Müller-Schweinitzer E., Waite R. Pharmacological actions of the antihypertensive agent N-amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide hydrochloride (BS 100-141). Arzneimittelforschung. 1975 Oct;25(10):1483–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibiriça E., Feldman J., Mermet C., Gonon F., Bousquet P. An imidazoline-specific mechanism for the hypotensive effect of clonidine: a study with yohimbine and idazoxan. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):606–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibiriça E., Feldman J., Mermet C., Monassier L., Gonon F., Bousquet P. Selectivity of rilmenidine for the nucleus reticularis lateralis, a ventrolateral medullary structure containing imidazoline-preferring receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec 17;209(3):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90172-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Schoop A. M., Kwa H. Y., Van Zwieten P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenoceptors participating in the central hypotensive and sedative effects of clonidine using yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 5;70(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Van Zwieten P. A. Postsynaptic alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the circulatory system of the pithed rat: selective stimulation of the alpha 2-type by B-HT 933. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 May 2;63(2-3):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Buuse M., Head G. A., Korner P. I. Differential role of brain ascending noradrenergic bundles in the circulatory effects of alpha-methyldopa and clonidine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;21(1):112–119. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199301000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. R., Hare L. E., Deitch M. W. Comparative antihypertensive effects of guanabenz and clonidine. J Int Med Res. 1982;10(1):6–14. doi: 10.1177/030006058201000102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S. Further characterization of the guinea pig cerebral cortex idazoxan receptor: solubilization, distinction from the imidazole site, and demonstration of cirazoline as an idazoxan receptor-selective drug. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):192–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


