Abstract
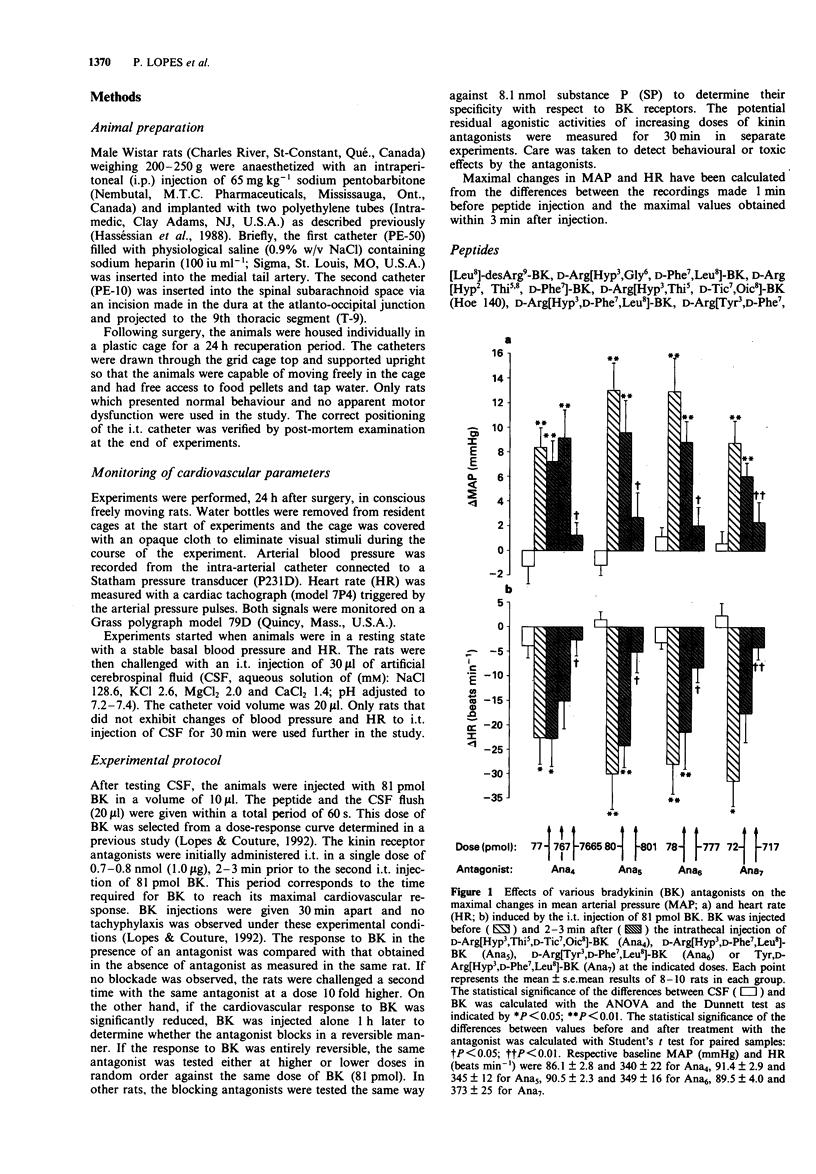
1. The effects of intrathecal (i.t.) pretreatment with selective B1 or B2 kinin receptor antagonists were studied on the cardiovascular response to i.t. injection of bradykinin (BK) in conscious freely moving rats. 2. BK (81 pmol) produced an increase in mean arterial pressure (MAP: 9-13 mmHg) and decrease in heart rate (HR: 20-30 beats min-1) that reached a maximum 2 min after injection. 3. The BK-induced cardiovascular responses were dose-dependently and reversibly reduced by four antagonists with the following rank order of potency: Tyr, D-Arg[Hyp3,D-Phe7,Leu8]-BK = D-Arg[Tyr3,D-Phe7,Leu8]-BK = D- Arg[Hyp3,D-Phe7,Leu8]-BK > D-Arg[Hyp3,Thi5,D-Tic7,Oic8]-BK (Hoe 140). These compounds failed to alter the cardiovascular response to i.t. injection of 8.1 nmol of substance P. 4. Other compounds acting on the B2 receptor, namely D-Arg[Hyp3,Gly6,Leu8]-BK, D-Arg[Hyp3,D-Phe7]-BK, D-Arg[Hyp2,Thi5,8,D-Phe7]-BK and D-Arg[Hyp3,Gly6,D-Phe7,Leu8]-BK or on the B1 receptor, [Leu8]-desArg9-BK, did not influence the cardiovascular responses to BK at doses devoid of intrinsic activity on MAP and HR. 5. None of the kinin receptor antagonists caused motor impairment, respiratory arrest or persisting cardiovascular changes. 6. These results confirm that the cardiovascular effects induced by i.t. BK are mediated by the activation of a B2 receptor in the rat spinal cord. However, the rank order of potency of antagonists does not conform to the classical B2 functional site characterized in peripheral tissues.
Full text
PDF
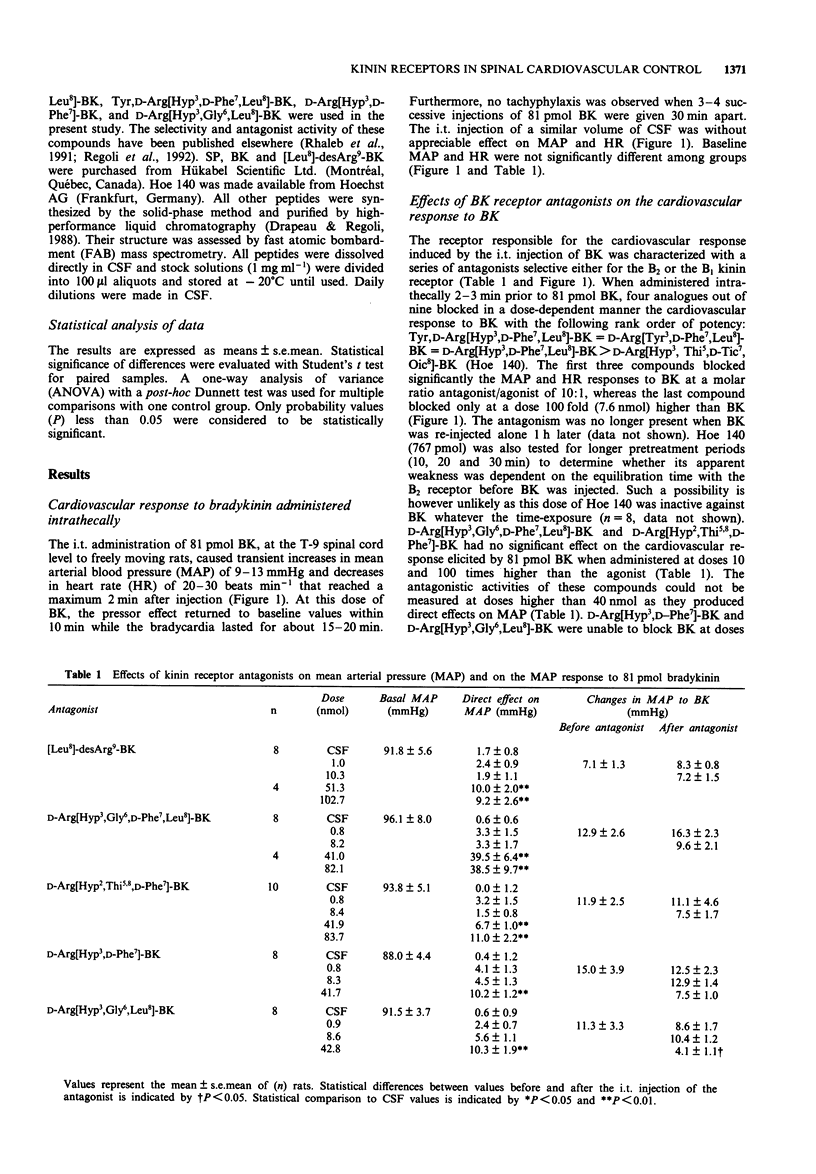



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bathon J. M., Proud D. Bradykinin antagonists. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1991;31:129–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.31.040191.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braas K. M., Manning D. C., Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin analogues: differential agonist and antagonist activities suggesting multiple receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa F. M., Innis R. B., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin-like immunoreactive neuronal systems localized histochemically in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1489–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diz D. I. Bradykinin and related peptides in central control of the cardiovascular system. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., Regoli D. Synthesis of bradykinin analogs. Methods Enzymol. 1988;163:263–272. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)63025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Mantione C. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Yamamura H. I. Characterization of [3H]bradykinin binding sites in guinea-pig central nervous system: possible existence of B2 subtypes. Life Sci. 1989;44(22):1645–1653. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90481-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasséssian H., Drapeau G., Couture R. Spinal action of neurokinins producing cardiovascular responses in the conscious freely moving rat: evidence for a NK-1 receptor mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;338(6):649–654. doi: 10.1007/BF00165629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann K., Schaechtelin G., Marin-Grez M. Kinins in cerebrospinal fluid: reduced concentration in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Experientia. 1986 Dec 1;42(11-12):1238–1239. doi: 10.1007/BF01946402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock F. J., Wirth K., Albus U., Linz W., Gerhards H. J., Wiemer G., Henke S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vitro studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):769–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):739–768. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya K., Yamauchi A., Sasaki T. Regional distribution and characterization of kinin in the CNS of the rat. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1892–1897. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Griesbacher T., Eckhardt M., Henke S., Breipohl G., Knolle J. New, long-acting, potent bradykinin antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey C. J., Nakaie C. R., Martins D. T. Central nervous system kinin receptors and the hypertensive response mediated by bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):763–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llona I., Vavrek R., Stewart J., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Identification of pre- and postsynaptic bradykinin receptor sites in the vas deferens: evidence for different structural prerequisites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):608–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes P., Couture R. Cardiovascular responses elicited by intrathecal kinins in the conscious rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;210(2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90664-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes P., Kar S., Tousignant C., Regoli D., Quirion R., Couture R. Autoradiographic localization of [125I-Tyr8]-bradykinin receptor binding sites in the guinea pig spinal cord. Synapse. 1993 Sep;15(1):48–57. doi: 10.1002/syn.890150106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A. The pharmacology of the efferent function of sensory nerves. J Auton Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;11(3):173–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1991.tb00317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., Regoli D., Giroud J. P. Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(2):209–229. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEachern A. E., Shelton E. R., Bhakta S., Obernolte R., Bach C., Zuppan P., Fujisaki J., Aldrich R. W., Jarnagin K. Expression cloning of a rat B2 bradykinin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7724–7728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry D. C., Snyder S. H. Identification of bradykinin in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1984 Oct;43(4):1072–1080. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham T. M., Couture R. Inhibitory action of (+/-)CP-96,345 on the cardiovascular responses to intrathecal substance P and neuropeptide K in the conscious freely moving rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;347(1):34–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00168769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Owen P. J. Multiple B2 kinin receptors in mammalian tissues. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Nov;9(11):387–389. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90059-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Barabé J. Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev. 1980 Mar;32(1):1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Jukic D., Tousignant C., Rhaleb N. E. Kinin receptor classification. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992;38(Pt 1):475–486. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7321-5_60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D. Neurohumoral regulation of precapillary vessels: the kallikrein-kinin system. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1984;6 (Suppl 2):S401–S412. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198406002-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhaleb N. E., Télémaque S., Rouissi N., Dion S., Jukic D., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Structure-activity studies of bradykinin and related peptides. B2-receptor antagonists. Hypertension. 1991 Jan;17(1):107–115. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifo J., Pourrat M., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Huidobro-Toro J. P. Bradykinin receptor antagonists used to characterize the heterogeneity of bradykinin-induced responses in rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 13;142(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Forbes G., Nolly H., Dujovny M., Carretero O. A. Kallikrein-kinins in the central nervous system. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1984;6(10-11):1731–1738. doi: 10.3109/10641968409046068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguin L., Widdowson P. S., Giesen-Crouse E. Existence of three subtypes of bradykinin B2 receptors in guinea pig. J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):2125–2133. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., Manning D. C., DeHaas C. J., Ferkany J. W., Borosky S. A., Connor J. R., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Bradykinin as a pain mediator: receptors are localized to sensory neurons, and antagonists have analgesic actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3245–3249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. M., Vavrek R. J. Kinin antagonists: design and activities. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 6):S69–S74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth K., Hock F. J., Albus U., Linz W., Alpermann H. G., Anagnostopoulos H., Henk S., Breipohl G., König W., Knolle J. Hoe 140 a new potent and long acting bradykinin-antagonist: in vivo studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):774–777. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Hsu C. Y., Junker H., Chao S., Hogan E. L., Chao J. Kininogen and kinin in experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):975–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBlois D., Bouthillier J., Marceau F. Pharmacological modulation of the up-regulated responses to des-Arg9-bradykinin in vivo and in vitro. Immunopharmacology. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):187–198. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(89)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


