Abstract
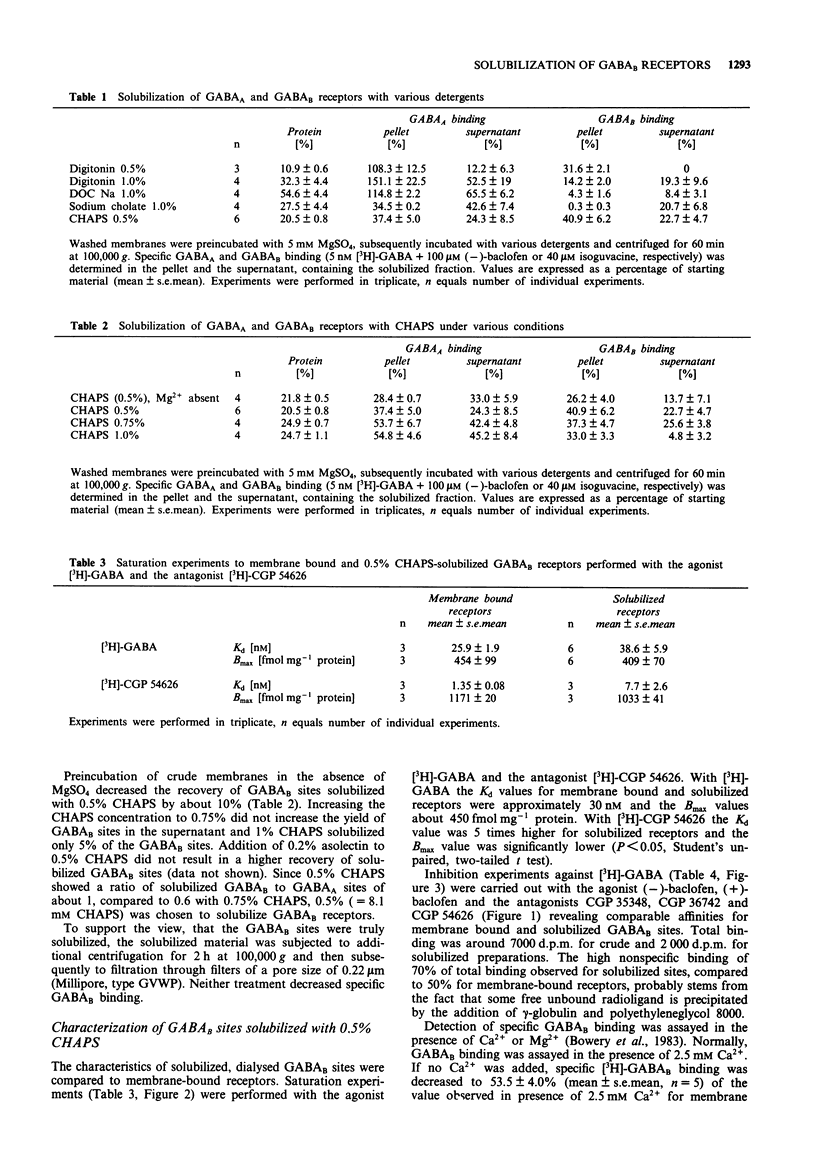
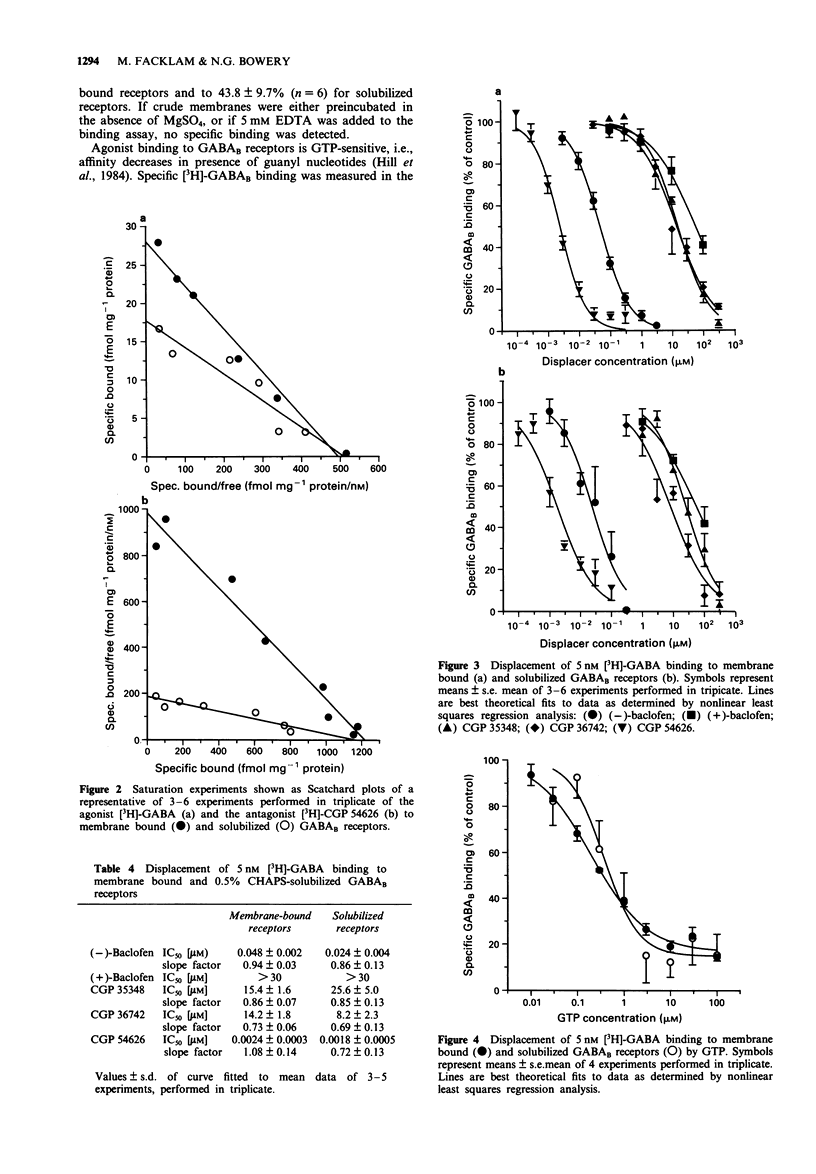
1. The characteristics of membrane bound GABAB receptors in pig brain are similar to those in rat brain as judged by in vitro binding experiments and sensitivity to GTP. The rank order of affinity of GABAB receptor ligands was CGP 54626 > GABA approximately (-)-baclofen >> CGP 35348 = CGP 36742 > (+)-baclofen in membranes from both species. 2. For solubilization of GABAB receptors from pig brain, washed membranes were preincubated with 5 mM MgSO4 and subsequently incubated with various detergents. 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethyl-ammoniol]-1-propane sulphonate (CHAPS) (0.5%) proved to be the most successful, solubilizing 22.7 +/- 4.7% (mean +/- s.e. mean, n = 6) of GABAB receptors. 3. Binding of [3H]-GABA to GABAB receptors solubilized with 0.5% CHAPS exhibited similar characteristics to the binding at membrane bound receptors since, firstly, the Kd and Bmax values (around 30 nM and 450 fmol mg-1 protein, respectively) were comparable; secondly, stereospecific binding for baclofen was obtained in both forms; thirdly, the affinity for the agonists GABA and (-)-baclofen and the antagonists CGP 35348, CGP 36742 and CGP 54626 were the same; fourthly, comparable sensitivity to Ca2+ (2.5 mM) was observed and finally, a similar sensitivity to GTP was apparent. 4. Saturation experiments performed with the GABAB antagonist, [3H]-CGP 54626, indicated a higher Kd value and a lower Bmax value for solubilized (7.7 +/- 2.6 nM and 1033 +/- 41 fmol mg-1 protein, mean +/- s.e. mean, n = 3) than for membrane bound receptors (1.35 +/- 0.08 nM, 1171 +/- 20 fmol mg-1 protein, n = 3).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Ui M., Ogasawara N. Prevention of the agonist binding to gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors by guanine nucleotides and islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in bovine cerebral cortex. Possible coupling of the toxin-sensitive GTP-binding proteins to receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12653–12658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G. GABAB receptor pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:109–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow T., Zukin R. S. Solubilization and preliminary characterization of mu and kappa opiate receptor subtypes from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;24(2):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross J. A., Horton R. W. Are increases in GABAB receptors consistent findings following chronic antidepressant administration? Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guicheney P., Rappaport A., Marcel D. Solubilization of active brain alpha 1-adrenoceptors by a zwitterionic detergent. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):56–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G., Hudson A. L. Inhibition of GABAB receptor binding by guanyl nucleotides. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):652–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme E. C., Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S. Two populations of binding sites for muscarinic antagonists in the rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. F., Caron M. G. Agonist binding promotes a guanine nucleotide reversible increase in the apparent size of the bovine anterior pituitary dopamine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13528–13534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott C., Maguire J. J., Moratalla R., Bowery N. G. Regional effects of pertussis toxin in vivo and in vitro on GABAB receptor binding in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1993 Jan;52(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90183-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Saijoh K., Tanaka C. Solubilization of D2 dopamine receptor coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory protein from bovine striatum. J Neurochem. 1983 Sep;41(3):841–847. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Asakura M., Tsukamoto T., Imafuku J., Ino M., Saitoh N., Miyamura S., Hasegawa K. Solubilization and characterization of rat brain alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Neurochem. 1985 May;44(5):1625–1632. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori Y., Hirouchi M., Taguchi J., Kuriyama K. Functional coupling of the gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor with calcium ion channel and GTP-binding protein and its alteration following solubilization of the gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):80–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori Y., Kuriyama K. Solubilization and partial purification of GABAB receptor from bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Oct 15;172(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramkumar V., Stiles G. L. Reciprocal modulation of agonist and antagonist binding to A1 adenosine receptors by guanine nucleotides is mediated via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1194–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz W., Freissmuth M. Reverse intrinsic activity of antagonists on G protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):376–380. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90116-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Koski G., Streaty R. A., Hjelmeland L. M., Klee W. A. Solubilization of active opiate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4623–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Bockaert J., Rouot B. Solubilization of brain alpha-2 adrenoceptor with a zwitterionic detergent: preservation of agonist binding and its sensitivity to GTP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 30;119(3):1116–1121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90890-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. K., Limbird L. E. Solubilization of human platelet alpha-adrenergic receptors: evidence that agonist occupancy of the receptor stabilizes receptor--effector interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szekely A. M., Barbaccia M. L., Costa E. Effect of a protracted antidepressant treatment on signal transduction and [3H](-)-baclofen binding at GABAB receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):155–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



