Abstract
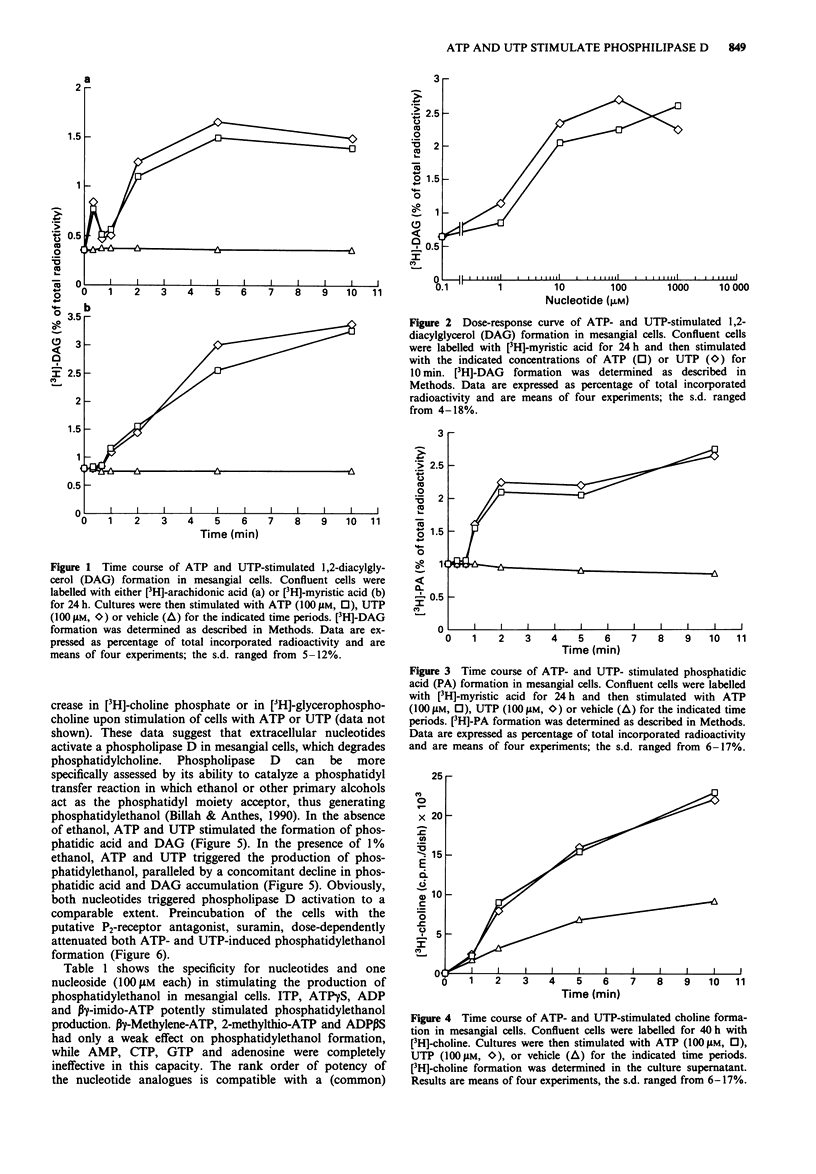
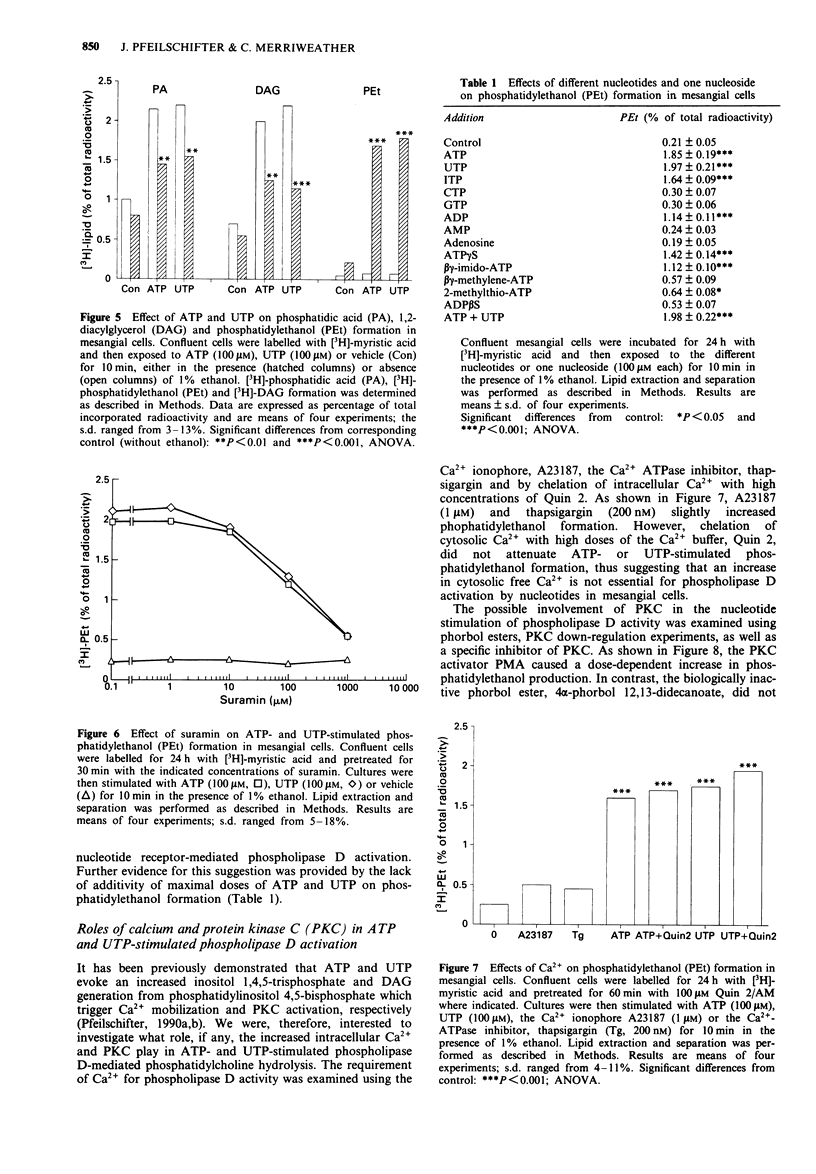
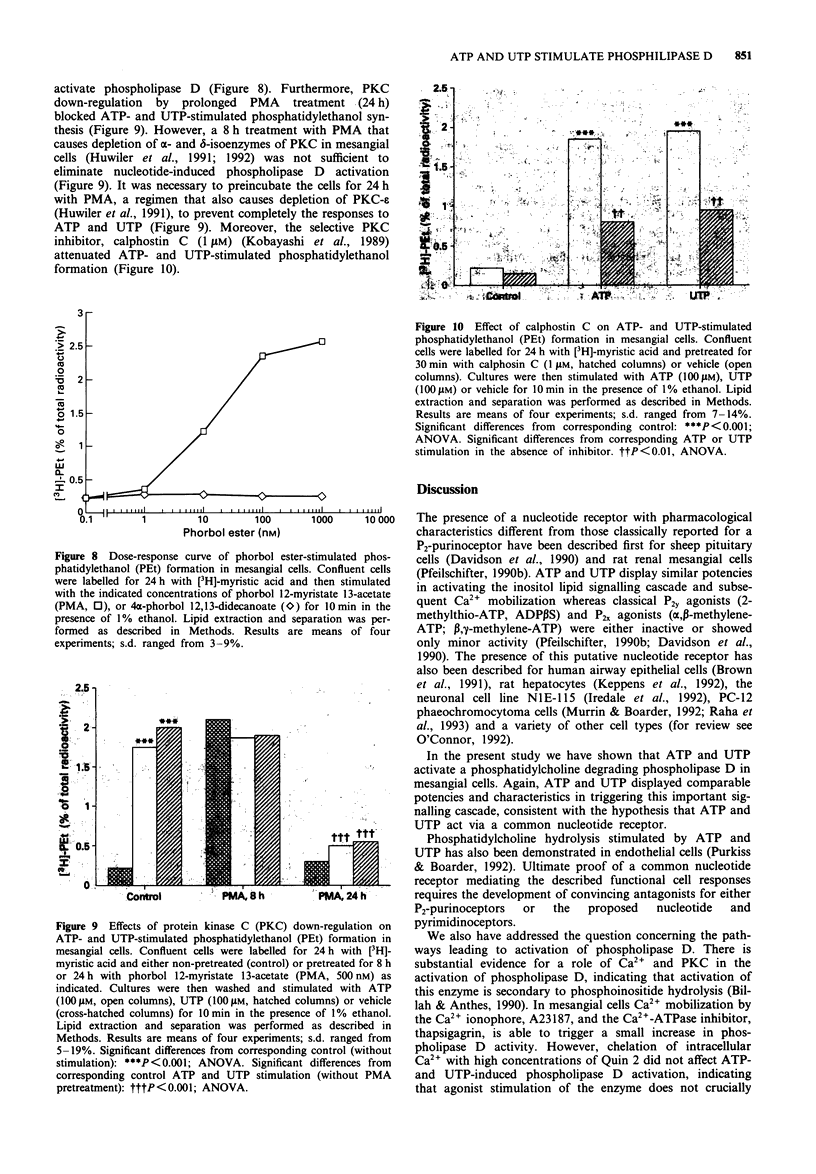
1. We have studied whether a nucleotide receptor mediates the effects of extracellular ATP and UTP on phosphatidylcholine metabolism in rat cultured glomerular mesangial cells. 2. ATP and UTP stimulated a biphasic 1,2-diacylglycerol (DAG) formation in [3H]-arachidonic acid-labelled mesangial cells. In contrast, in cells labelled with [3H]-myristic acid, a tracer that preferentially marks phosphatidylcholine, both nucleotides induced a delayed monophasic production of DAG with a concomitant increase in phosphatidic acid and choline formation. 3. A phospholipase D-mediated phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis was further suggested by the observation that ATP and UTP stimulate the accumulation of phosphatidylethanol, when ethanol was added to mesangial cells. 4. The rank order of potency of a series of nucleotide analogues for stimulation of phosphatidylethanol formation was UTP = ATP > ITP > ATP gamma S > beta gamma-imido-ATP = ADP > 2-methylthio-ATP = beta gamma-methylene-ATP = ADP beta S, while AMP, adenosine, CTP and GTP were inactive, indicating the presence of a nucleotide receptor. 5. Elevation of cytosolic free Ca2+ by the calcium ionophore A23187 (1 microM) or the Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, thapsigargin (200 nM) slightly increased phosphatidylethanol formation. However, chelation of cytosolic Ca2+ with high concentrations of Quin 2 did not attenuate ATP- and UTP-induced phosphatidylethanol production, thus suggesting that Ca2+ is not crucially involved in agonist-stimulated phospholipase D activation. 6. The protein kinase C (PKC) activator, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), but not the biologically inactive 4 alpha-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate, increased phospholipase D activity in mesangial cells, suggesting that PKC may mediate nucleotide-induced phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Anthes J. C. The regulation and cellular functions of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):281–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2690281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. A., Lazarowski E. R., Boucher R. C., Harden T. K. Evidence that UTP and ATP regulate phospholipase C through a common extracellular 5'-nucleotide receptor in human airway epithelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):648–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. ATP stimulates secretion in human neutrophils and HL60 cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein coupled to phospholipase C. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):25–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. S., Wakefield I. K., Sohnius U., van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P. A novel extracellular nucleotide receptor coupled to phosphoinositidase-C in pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Jan;126(1):80–87. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez I., Diaz-Meco M. T., Municio M. M., Berra E., García de Herreros A., Cornet M. E., Sanz L., Moscat J. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C zeta subspecies in maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3776–3783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwendt M., Leibersperger H., Marks F. Differentiative action of K252a on protein kinase C and a calcium-unresponsive, phorbol ester/phospholipid-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):974–982. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91765-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Fabbro D., Pfeilschifter J. Possible regulatory functions of protein kinase C-alpha and -epsilon isoenzymes in rat renal mesangial cells. Stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis and feedback inhibition of angiotensin II-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):441–445. doi: 10.1042/bj2790441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Fabbro D., Stabel S., Pfeilschifter J. Immunocharacterization of delta- and zeta-isoenzymes of protein kinase C in rat renal mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 6;300(3):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80858-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huwiler A., Schulze-Lohoff E., Fabbro D., Pfeilschifter J. Immunocharacterization of protein kinase C isoenzymes in rat kidney glomeruli, and cultured glomerular epithelial and mesangial cells. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Jan-Feb;1(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Stehle T., Gerok W. Actions of extracellular UTP and ATP in perfused rat liver. A comparative study. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iredale P. A., Martin K. F., Alexander S. P., Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation and calcium mobilisation via activation of an atypical P2 receptor in the neuronal cell line, N1E-115. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1083–1087. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keppens S., Vandekerckhove A., De Wulf H. Extracellular ATP and UTP exert similar effects on rat isolated hepatocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;105(2):475–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester M., Simonson M. S., McDermott R. G., Baldi E., Dunn M. J. Endothelin stimulates phosphatidic acid formation in cultured rat mesangial cells: role of a protein kinase C-regulated phospholipase D. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Mar;150(3):578–585. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041500319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlynn E., Liebetanz J., Reutener S., Wood J., Lydon N. B., Hofstetter H., Vanek M., Meyer T., Fabbro D. Expression and partial characterization of rat protein kinase C-delta and protein kinase C-zeta in insect cells using recombinant baculovirus. J Cell Biochem. 1992 Jul;49(3):239–250. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240490306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrin R. J., Boarder M. R. Neuronal "nucleotide" receptor linked to phospholipase C and phospholipase D? Stimulation of PC12 cells by ATP analogues and UTP. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E. Recent developments in the classification and functional significance of receptors for ATP and UTP, evidence for nucleotide receptors. Life Sci. 1992;50(22):1657–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90420-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Dobek E. A., Bishop W. R. Endothelin-1 activates phospholipase D and thymidine incorporation in fibroblasts overexpressing protein kinase C beta 1. Cell Regul. 1991 Nov;2(11):897–903. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.11.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Pachter J. A., Weinstein I. B., Bishop W. R. Overexpression of protein kinase C beta 1 enhances phospholipase D activity and diacylglycerol formation in phorbol ester-stimulated rat fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):598–602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulmichl M., Pfeilschifter J., Wöll E., Lang F. Cellular mechanisms of ATP-induced hyperpolarization in renal epitheloid MDCK-cells. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Apr;147(1):68–75. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavenstädt H., Späth M., Schlunck G., Nauck M., Fischer R., Wanner C., Schollmeyer P. Effect of nucleotides on the cytosolic free calcium activity and inositol phosphate formation in human glomerular epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;107(1):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer L. M., Strulovici B., Saltiel A. R. Interferon-alpha selectively activates the beta isoform of protein kinase C through phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6537–6541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Angiotensin II B-type receptor mediates phosphoinositide hydrolysis in mesangial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 2;184(1):201–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Comparison of extracellular ATP and UTP signalling in rat renal mesangial cells. No indications for the involvement of separate purino- and pyrimidino-ceptors. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):469–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2720469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J. Extracellular ATP stimulates polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis and prostaglandin synthesis in rat renal mesangial cells. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide binding protein and feedback inhibition by protein kinase C. Cell Signal. 1990;2(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Hosang M. Effects of homo- and heterodimeric isoforms of PDGF on signalling events in rat renal mesangial cells. Cell Signal. 1991;3(5):413–424. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(91)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Huwiler A., Merriweather C., Briner V. A. Angiotensin II stimulation of phospholipase D in rat renal mesangial cells is mediated by the AT1 receptor subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;225(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Kurtz A., Bauer C. Activation of phospholipase C and prostaglandin synthesis by [arginine]vasopressin in cultures. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 1;223(3):855–859. doi: 10.1042/bj2230855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Thüring B., Festa F. Extracellular ATP stimulates poly(inositol phospholipid) hydrolysis and eicosanoid synthesis in mouse peritoneal macrophages in culture. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 22;186(3):509–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirotton S., Raspe E., Demolle D., Erneux C., Boeynaems J. M. Involvement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium in the action of adenine nucleotides on aortic endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17461–17466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard P. H., Vance D. E. Choline metabolism and phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 15;196(1):261–267. doi: 10.1042/bj1960261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkiss J. R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of phosphatidate synthesis in endothelial cells in response to P2-receptor activation. Evidence for phospholipase C and phospholipase D involvement, phosphatidate and diacylglycerol interconversion and the role of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1992 Oct 1;287(Pt 1):31–36. doi: 10.1042/bj2870031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raha S., de Souza L. R., Reed J. K. Intracellular signalling by nucleotide receptors in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1993 Mar;154(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lohoff E., Zanner S., Ogilvie A., Sterzel R. B. Extracellular ATP stimulates proliferation of cultured mesangial cells via P2-purinergic receptors. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):F374–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.3.F374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R., Schultz G. Involvement of pyrimidinoceptors in the regulation of cell functions by uridine and by uracil nucleotides. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travo P., Weber K., Osborn M. Co-existence of vimentin and desmin type intermediate filaments in a subpopulation of adult rat vascular smooth muscle cells growing in primary culture. Exp Cell Res. 1982 May;139(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troyer D. A., Gonzalez O. F., Padilla R. M., Kreisberg J. I. Vasopressin and phorbol ester-stimulated phosphatidylcholine metabolism in mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F185–F191. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Moatassim C., Dornand J., Mani J. C. Extracellular ATP and cell signalling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 19;1134(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Häussinger D., Starke K. Evidence for a vasoconstriction-mediating receptor for UTP, distinct from the P2 purinoceptor, in rabbit ear artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):556–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00169313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


