Abstract
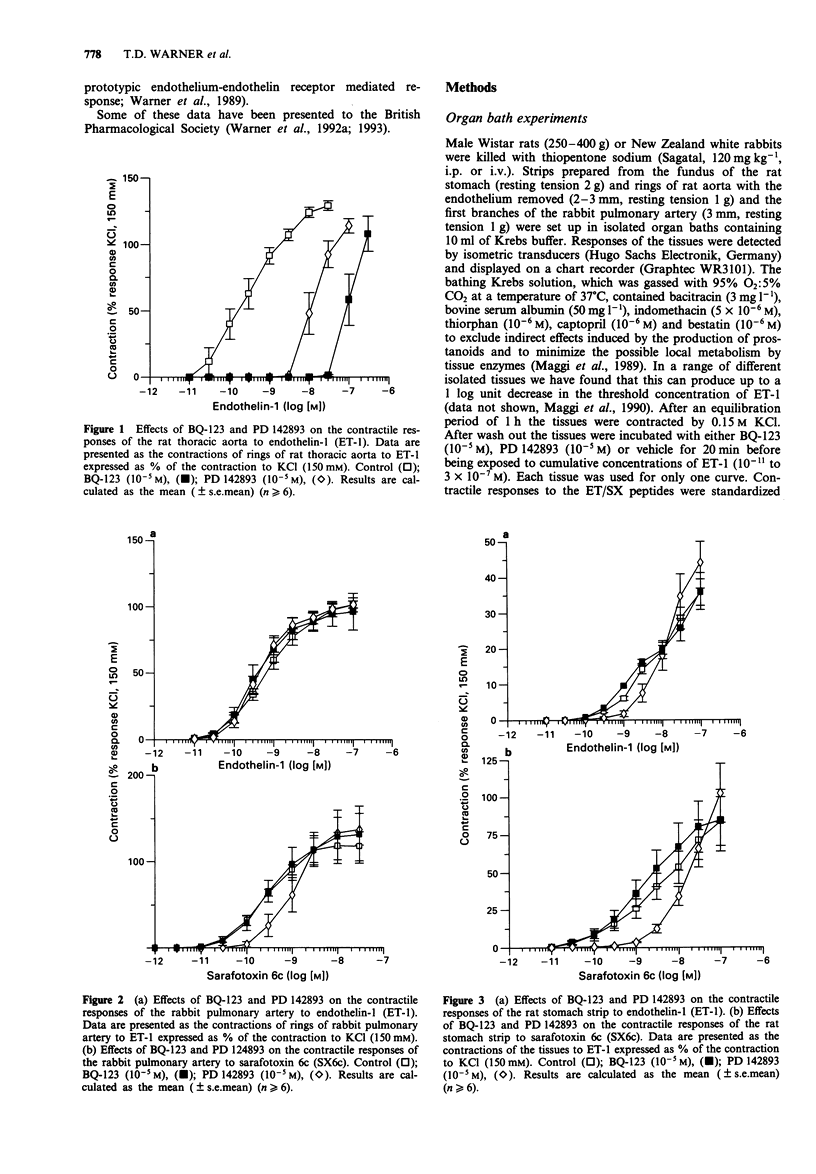
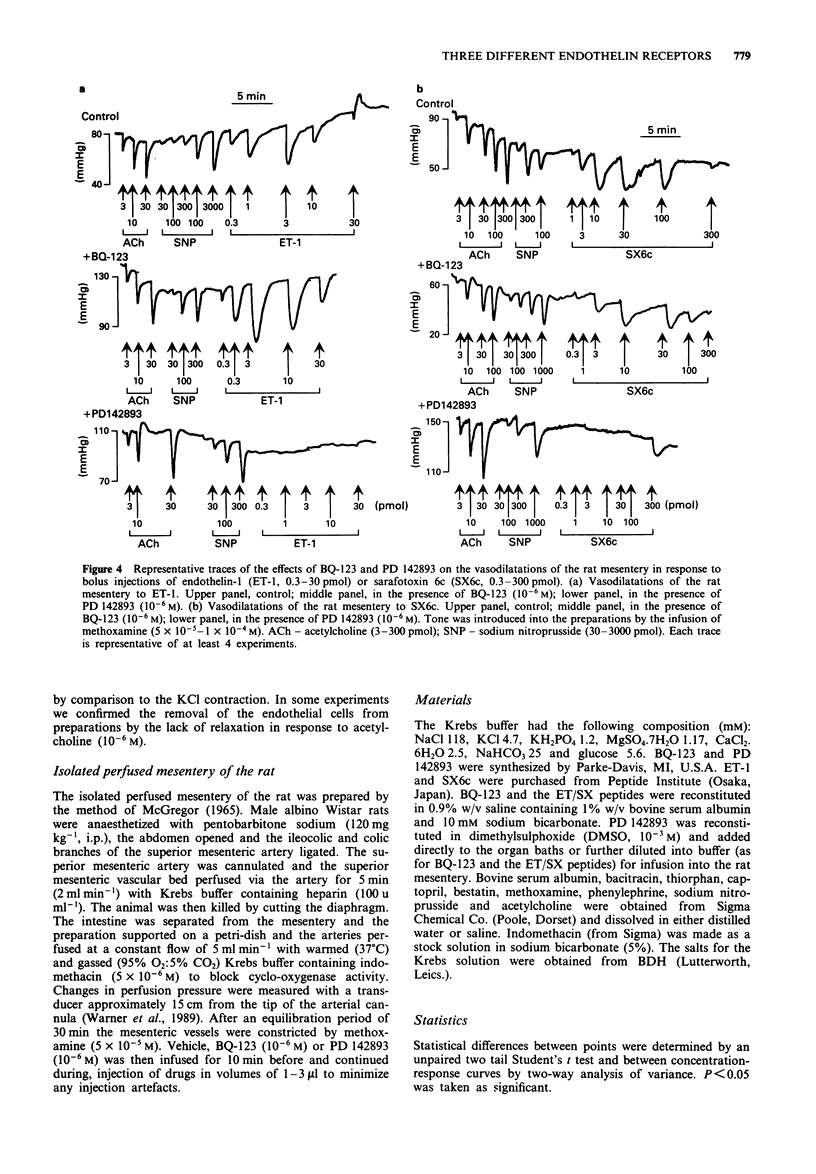
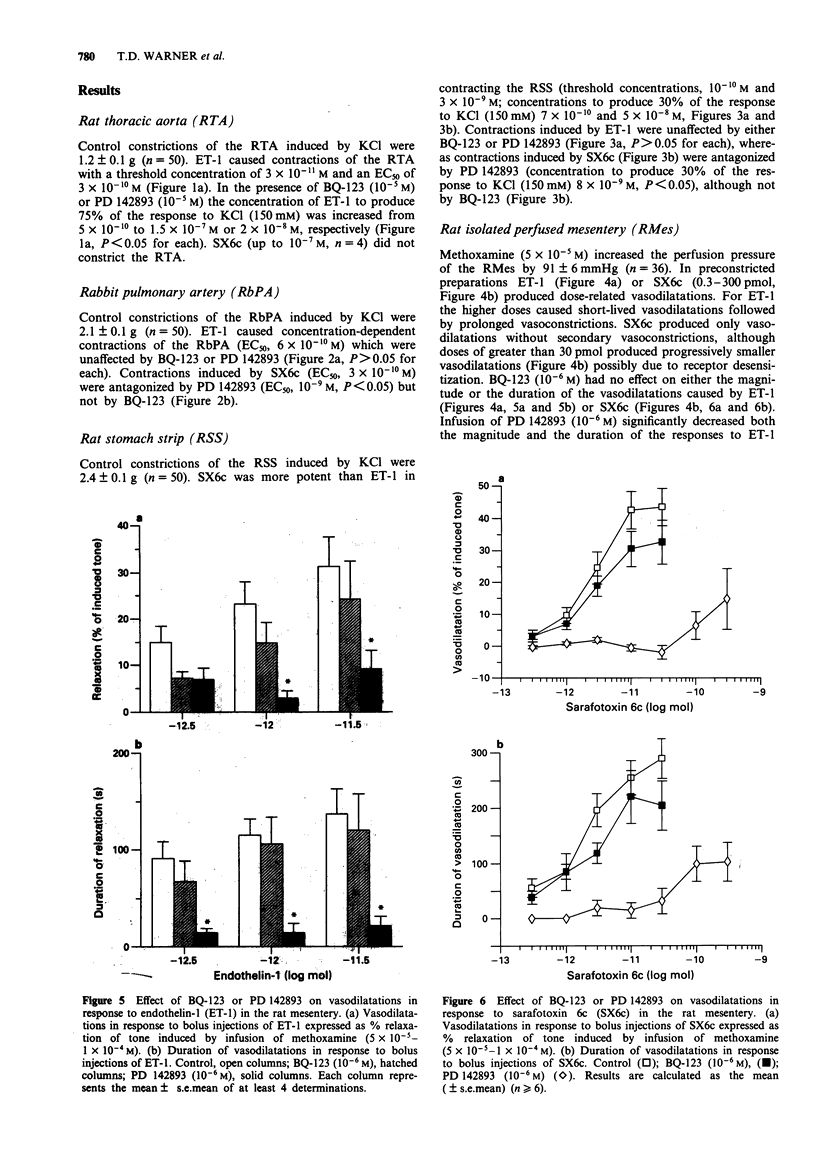
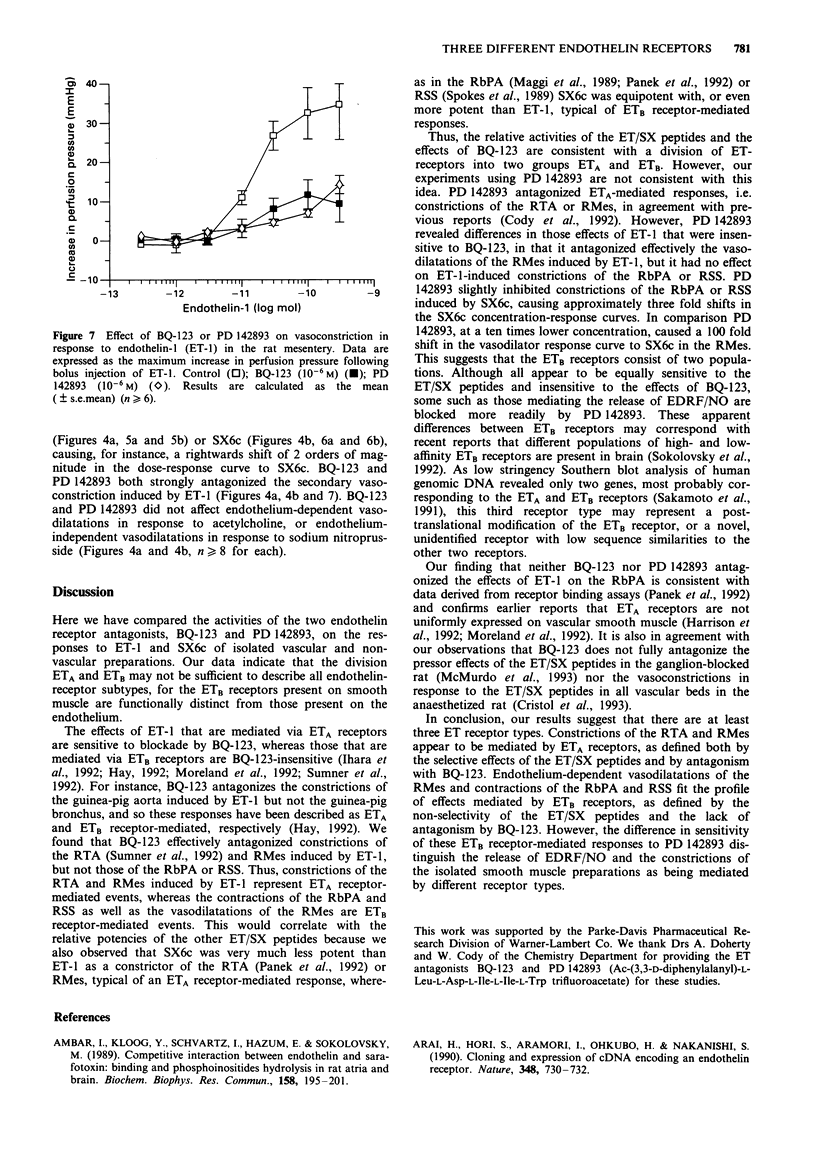
1. We have compared the receptors mediating the contractions of rings of rat thoracic aorta or rabbit pulmonary artery and rat stomach strips in response to the endothelin/sarafotoxin (ET/SX) family of peptides and to those mediating endothelium-dependent vasodilations within the isolated perfused mesentery of the rat. To discriminate ETA receptors from ETB receptors we have used the criteria that ET-1 is more active than SX6c on ETA receptors, and that the ET/SX peptides are equiactive on ETB receptors. We have also assessed the effects of the ETA receptor-selective antagonist BQ-123, and the non-selective ET receptor antagonist PD 142893 on the responses of each preparation to the ET/SX peptides. 2. ET-1-induced constrictions of the rat thoracic aorta (EC50 3 x 10(-10) M), a prototypic ETA receptor-mediated response, or isolated perfused mesentery of the rat were antagonized by BQ-123 (10(-5) M) or PD 142893 (10(-5) M). SX6c did not constrict either the rat isolated perfused mesentery or the rat thoracic aorta. Thus, ETA receptors mediate these constrictions. 3. ET-1 and SX6c were approximately equipotent in constricting rabbit pulmonary artery rings (EC50S 3-6 x 10(-10) M). Neither BQ-123 (10(-5) M) nor PD 142893 antagonized the contractions induced by ET-1. These effects suggest mediation by ETB receptors but PD 142893 (10(-5) M) did give a 3 fold antagonism of constrictions induced by SX6c. 4. SX6c was more potent than ET-1 in contracting the rat stomach strip (threshold concentrations 10(-10) and 3 x 10(-10) M).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambar I., Kloog Y., Schvartz I., Hazum E., Sokolovsky M. Competitive interaction between endothelin and sarafotoxin: Binding and phosphoinositides hydrolysis in rat atria and brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bdolah A., Wollberg Z., Fleminger G., Kochva E. SRTX-d, a new native peptide of the endothelin/sarafotoxin family. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 9;256(1-2):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81706-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clozel M., Gray G. A., Breu V., Löffler B. M., Osterwalder R. The endothelin ETB receptor mediates both vasodilation and vasoconstriction in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 31;186(2):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90826-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody W. L., Doherty A. M., He J. X., DePue P. L., Rapundalo S. T., Hingorani G. A., Major T. C., Panek R. L., Dudley D. T., Haleen S. J. Design of a functional hexapeptide antagonist of endothelin. J Med Chem. 1992 Aug 21;35(17):3301–3303. doi: 10.1021/jm00095a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristol J. P., Warner T. D., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Mediation via different receptors of the vasoconstrictor effects of endothelins and sarafotoxins in the systemic circulation and renal vasculature of the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):776–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori T., Hirata Y., Marumo F. Specific receptors for endothelin-3 in cultured bovine endothelial cells and its cellular mechanism of action. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 24;263(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison V. J., Randriantsoa A., Schoeffter P. Heterogeneity of endothelin-sarafotoxin receptors mediating contraction of pig coronary artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):511–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W. Pharmacological evidence for distinct endothelin receptors in guinea-pig bronchus and aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):759–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Warner T. D., Sheng H., Murad F. Endothelin increases cyclic GMP levels in LLC-PK1 porcine kidney epithelial cells via formation of an endothelium-derived relaxing factor-like substance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1102–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloog Y., Ambar I., Sokolovsky M., Kochva E., Wollberg Z., Bdolah A. Sarafotoxin, a novel vasoconstrictor peptide: phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat heart and brain. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):268–270. doi: 10.1126/science.2845579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGREGOR D. D. THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION OF VASOCONSTRICTOR RESPONSES IN PERFUSED MESENTERIC BLOOD VESSELS OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A., Meli A. The activity of peptides of the endothelin family in various mammalian smooth muscle preparations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90869-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Giachetti A., Meli A. Further studies on the response of the guinea-pig isolated bronchus to endothelins and sarafotoxin S6b. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90126-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurdo L., Corder R., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Incomplete inhibition of the pressor effects of endothelin-1 and related peptides in the anaesthetized rat with BQ-123 provides evidence for more than one vasoconstrictor receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):557–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12840.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland S., McMullen D. M., Delaney C. L., Lee V. G., Hunt J. T. Venous smooth muscle contains vasoconstrictor ETB-like receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek R. L., Major T. C., Hingorani G. P., Doherty A. M., Taylor D. G., Rapundalo S. T. Endothelin and structurally related analogs distinguish between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90519-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki T., Ihara M., Fukuroda T., Yamagiwa M., Yano M. [Ala1,3,11,15]endothelin-1 analogs with ETB agonistic activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 30;179(1):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91367-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saida K., Mitsui Y., Ishida N. A novel peptide, vasoactive intestinal contractor, of a new (endothelin) peptide family. Molecular cloning, expression, and biological activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14613–14616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Yanagisawa M., Sakurai T., Takuwa Y., Yanagisawa H., Masaki T. Cloning and functional expression of human cDNA for the ETB endothelin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Jul 31;178(2):656–663. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M., Ambar I., Galron R. A novel subtype of endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):20551–20554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spokes R. A., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Studies with endothelin-3 and endothelin-1 on rat blood pressure and isolated tissues: evidence for multiple endothelin receptor subtypes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S191–S192. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner M. J., Cannon T. R., Mundin J. W., White D. G., Watts I. S. Endothelin ETA and ETB receptors mediate vascular smooth muscle contraction. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):858–860. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Mitchell J. A., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 release EDRF from isolated perfused arterial vessels of the rat and rabbit. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S85–S102. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Murad F. Interactions of endothelins and EDRF in bovine native endothelial cells: selective effects of endothelin-3. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 2):H1600–H1605. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.5.H1600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. L., Jr, Jones K. L., Pettibone D. J., Lis E. V., Clineschmidt B. V. Sarafotoxin S6c: an agonist which distinguishes between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 15;175(2):556–561. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


