Abstract
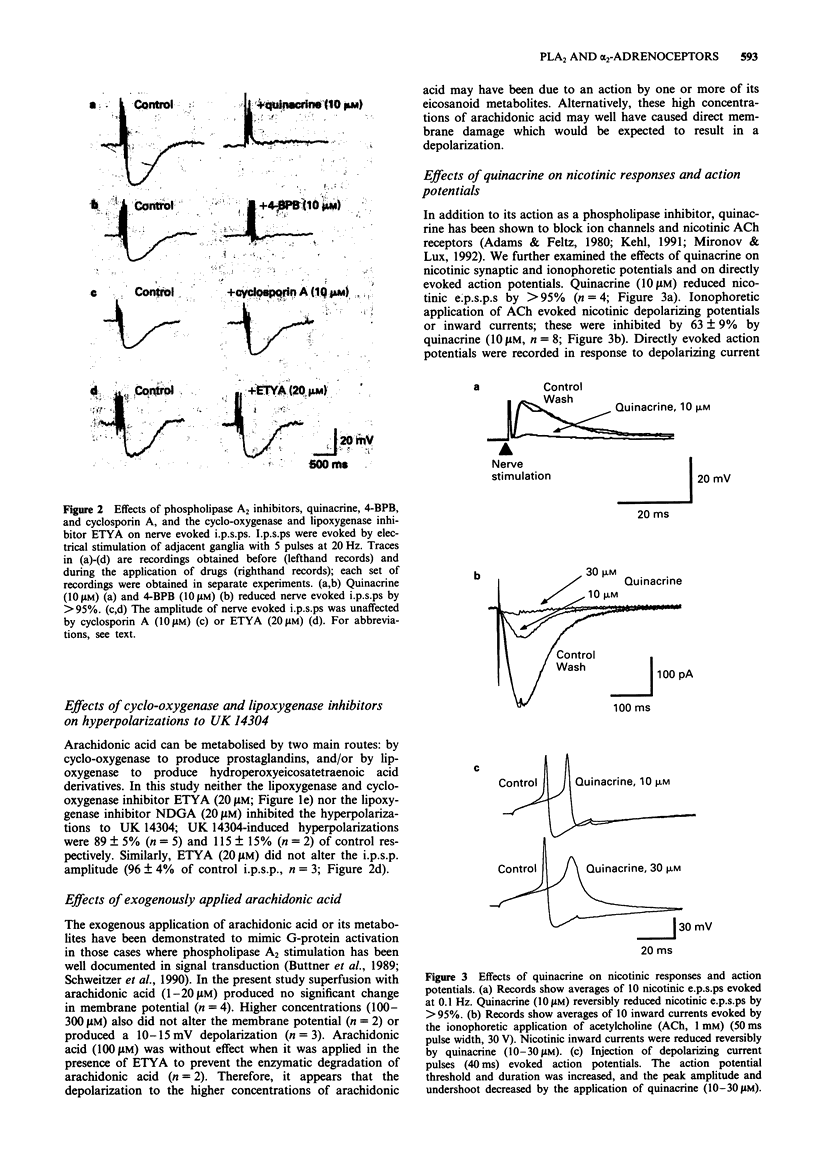
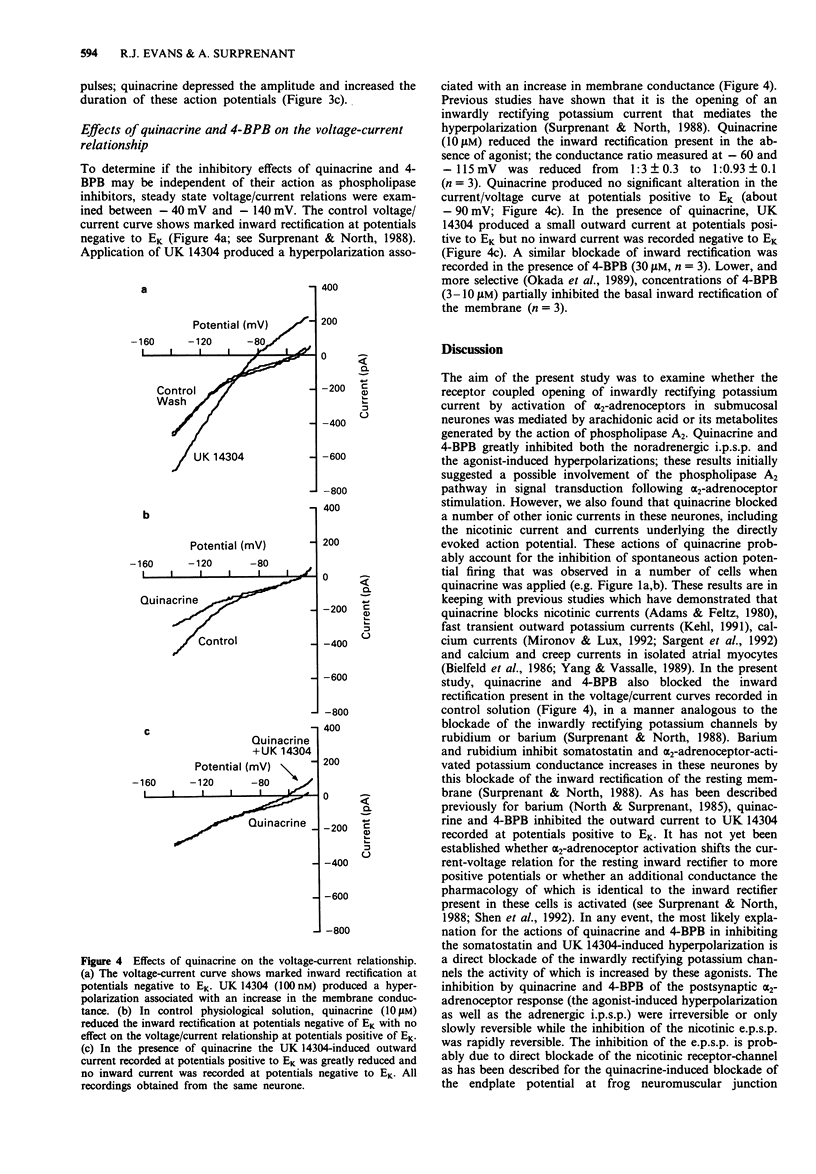
1. Noradrenaline hyperpolarizes guinea-pig submucosal neurones by opening inwardly rectifying potassium channels. Intracellular recordings were made from submucosal neurones and the possible involvement of the phospholipase A2 pathway in this response was examined. 2. The non-specific phospholipase A2 inhibitors, quinacrine (10 microM) and 4-bromophenacyl bromide (4-BPB, 10 microM) inhibited nerve-evoked inhibitory synaptic potentials (i.p.s.ps) and hyperpolarizations to somatostatin and UK 14304. Quinacrine and 4-BPB also blocked the inward rectification present in current-voltage curves in the absence of somatostatin or UK 14304. 3. The more selective phospholipase A2 inhibitor, cyclosporin A (10 microM) and the lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA, 20 microM) and nordihydroguairetic acid (NDGA, 20 microM) did not alter i.p.s.ps or hyperpolarizations to UK 14304. 4. Exogenously applied arachidonic acid (1-300 microM) did not mimic the i.p.s.p. or the hyperpolarization to UK 14304. 5. We conclude that arachidonic acid or its eicosanoid metabolites produced by phospholipase A2 stimulation are unlikely to be involved in the receptor G-protein coupled activation of potassium currents in submucosal neurones. The inhibition of the noradrenaline-induced hyperpolarization by quinacrine and 4-BPB is most likely due primarily to blockade of the basal inwardly rectifying potassium conductance present in these neurones.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Feltz A. Quinacrine (mepacrine) action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1980 Sep;306:261–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J., Burch R. M., Jelsema C. L. Receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase A2 via GTP-binding proteins: arachidonic acid and its metabolites as second messengers. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Mar;11(3):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeld D. R., Hadley R. W., Vassilev P. M., Hume J. R. Membrane electrical properties of vesicular Na-Ca exchange inhibitors in single atrial myocytes. Circ Res. 1986 Oct;59(4):381–389. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell G. J., Flower R. J. Inhibition of phospholipase. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jul;39(3):260–264. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein J. C., Costa M., Furness J. B. Intrinsic and extrinsic inhibitory synaptic inputs to submucous neurones of the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:371–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttner N., Siegelbaum S. A., Volterra A. Direct modulation of Aplysia S-K+ channels by a 12-lipoxygenase metabolite of arachidonic acid. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):553–555. doi: 10.1038/342553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan T. P., Lewis G. P. Mechanism of cyclosporin A-induced inhibition of prostacyclin synthesis by macrophages. Prostaglandins. 1985 Nov;30(5):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(85)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R., Sherbourne C. D., Goldyne M. E., Levine J. D. Noradrenaline-induced prostaglandin production by sympathetic postganglionic neurons is mediated by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1145–1150. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Holman M. E., Spence I. Two types of neurones in the myenteric plexus of duodenum in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(2):303–326. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. B., Halenda S. P., Bylund D. B. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptor stimulation of phospholipase A2 and of adenylate cyclase in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells is mediated by different mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;39(2):239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehl S. J. Quinidine-induced inhibition of the fast transient outward K+ current in rat melanotrophs. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul;103(3):1807–1813. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi Y., Ito H., Sugimoto T., Shimizu T., Miki I., Ui M. Arachidonic acid metabolites as intracellular modulators of the G protein-gated cardiac K+ channel. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):555–557. doi: 10.1038/337555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., Nishi S., North R. A., Surprenant A. A non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic slow inhibitory post-synaptic potential in neurones of the guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:357–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara S., North R. A., Surprenant A. Somatostatin increases an inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:335–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B., Sarantis M., Traynelis S. F., Attwell D. Potentiation of NMDA receptor currents by arachidonic acid. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):722–725. doi: 10.1038/355722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mironov S. L., Lux H. D. The selective action of quinacrine on high-threshold calcium channels in rat hippocampal cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):751–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi S., North R. A. Intracellular recording from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):471–491. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa Y., Kano T., Taniguchi S., Miyachi Y., Sakane T. Effect of cyclosporin A on the membrane-associated events in human leukocytes with special reference to the similarity with dexamethasone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 Mar 15;35(6):947–951. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Surprenant A. Inhibitory synaptic potentials resulting from alpha 2-adrenoceptor activation in guinea-pig submucous plexus neurones. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:17–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. Twelfth Gaddum memorial lecture. Drug receptors and the inhibition of nerve cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):13–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada D., Yamagishi S., Sugiyama H. Differential effects of phospholipase inhibitors in long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampal mossy fiber synapses and Schaffer/commissural synapses. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90674-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Greengard P. Lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid in neuronal transmembrane signalling. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Sep;11(9):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Volterra A., Dale N., Siegelbaum S. A., Kandel E. R., Schwartz J. H., Belardetti F. Lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid as second messengers for presynaptic inhibition of Aplysia sensory cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 2;328(6125):38–43. doi: 10.1038/328038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premkumar L. S., Gage P. W., Chung S. H. Coupled potassium channels induced by arachidonic acid in cultured neurons. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Oct 22;242(1303):17–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Vesterqvist O., McCullough J. R., Ogletree M. L., Grover G. J. Effect of the phospholipase A2 inhibitors quinacrine and 7,7-dimethyleicosadienoic acid in isolated globally ischemic rat hearts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Sep;262(3):1161–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer P., Madamba S., Siggins G. R. Arachidonic acid metabolites as mediators of somatostatin-induced increase of neuronal M-current. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):464–467. doi: 10.1038/346464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen K. Z., North R. A., Surprenant A. Potassium channels opened by noradrenaline and other transmitters in excised membrane patches of guinea-pig submucosal neurones. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:581–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., North R. A. Mechanism of synaptic inhibition by noradrenaline acting at alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jun 22;234(1274):85–114. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1988.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. Slow excitatory synaptic potentials recorded from neurones of guinea-pig submucous plexus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:343–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volterra A., Siegelbaum S. A. Antagonistic modulation of S-K+ channel activity by cyclic AMP and arachidonic acid metabolites. Role for two G proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;559:219–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb22611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. P., Brown V. J. Studies on the arachidonic acid cascade--I. Inhibition of phospholipase A2 in vitro and in vivo by several novel series of inhibitor compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 1;30(11):1315–1324. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Vassalle M. Quinacrine decreases the slow inward current and force in guinea pig ventricular tissue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 7;170(3):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90547-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Etr M., Marin P., Tence M., Delumeau J. C., Cordier J., Glowinski J., Premont J. 2-Chloroadenosine potentiates the alpha 1-adrenergic activation of phospholipase C through a mechanism involving arachidonic acid and glutamate in striatal astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1992 Apr;12(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-04-01363.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


