Abstract
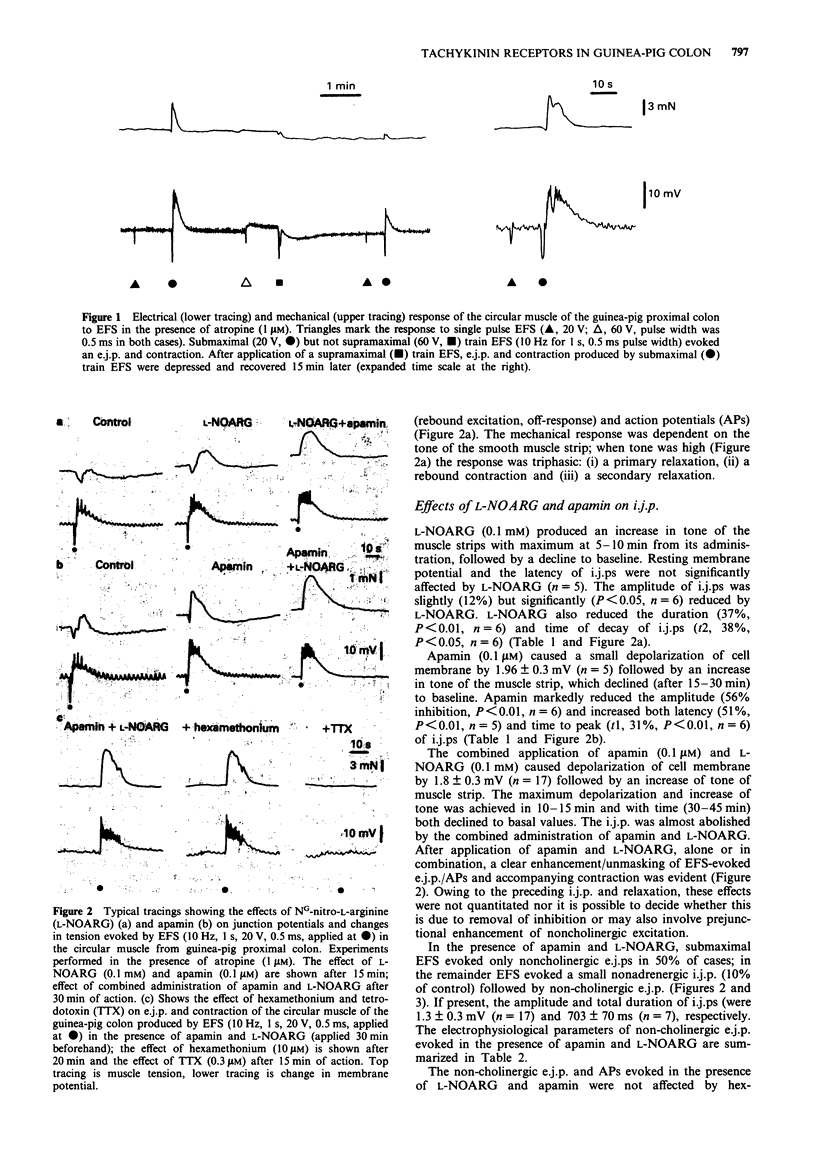
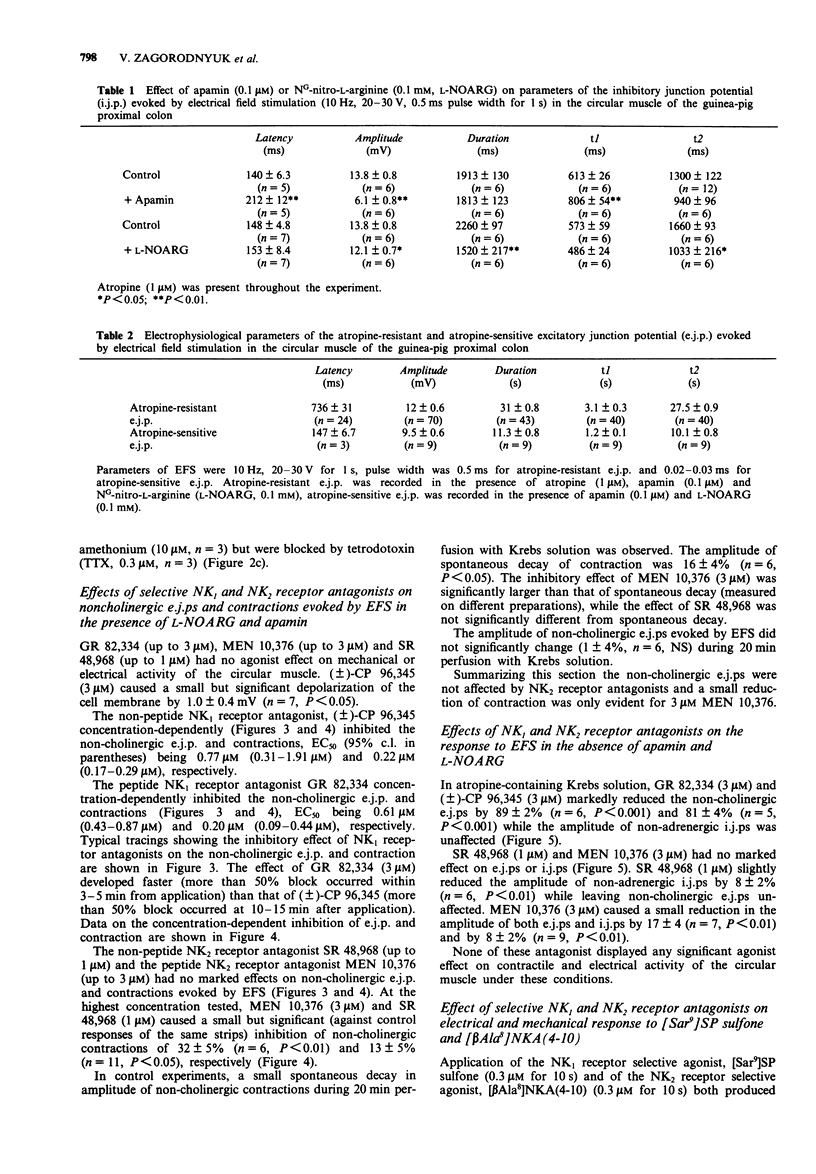
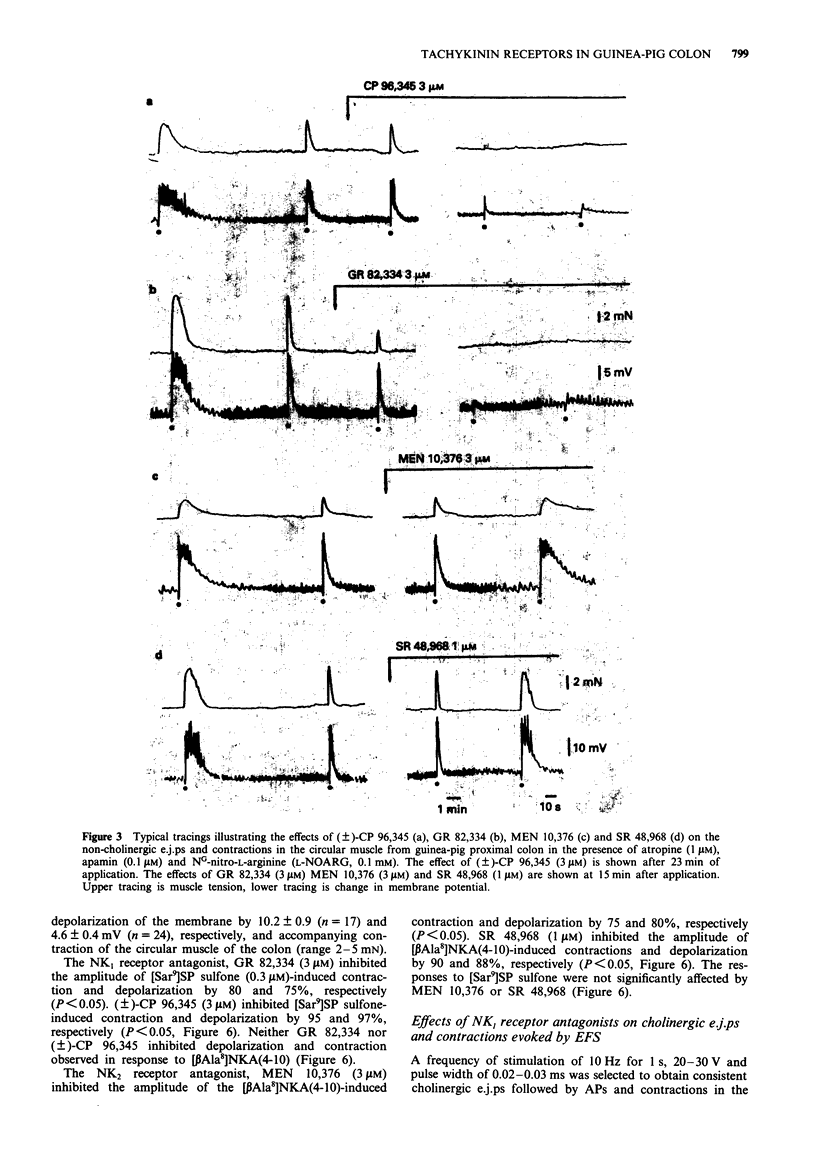
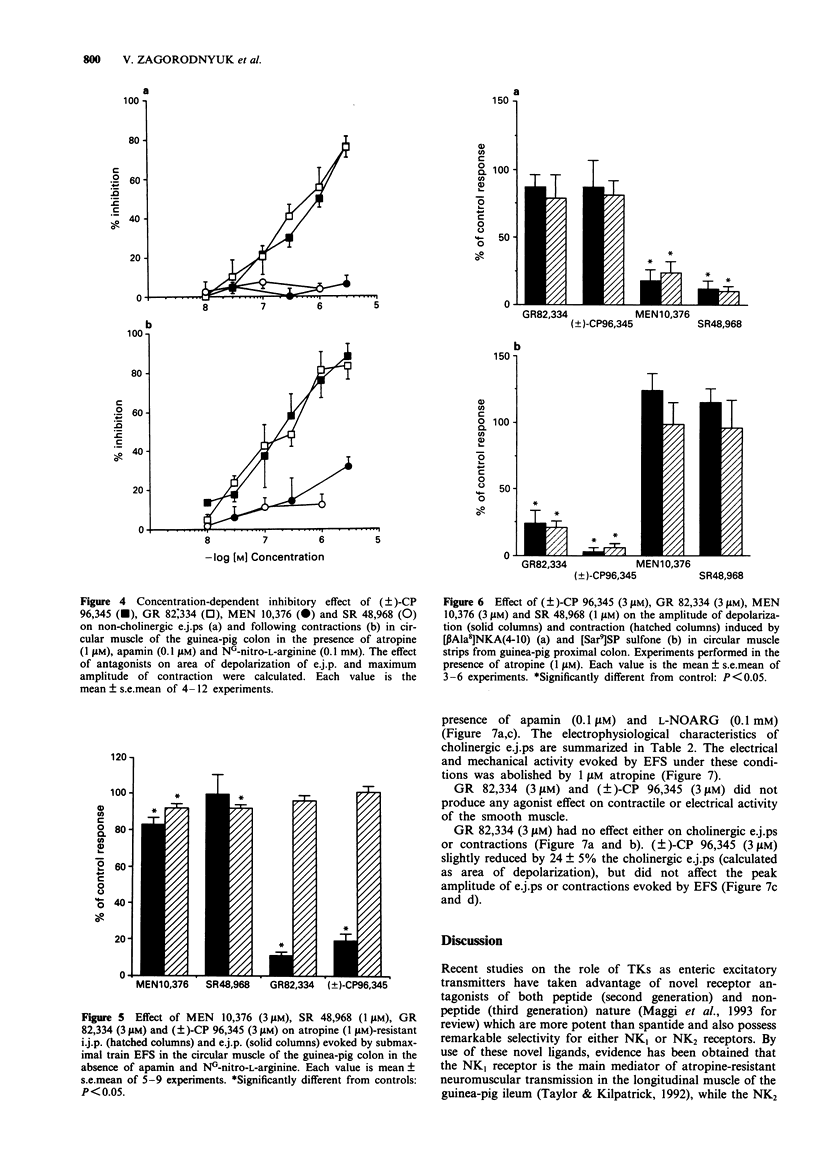
1. The effect of tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptor antagonists on noncholinergic excitatory junction potentials (e.j.ps) evoked by electric field stimulation (EFS) in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig proximal colon was investigated by means of a sucrose-gap technique. 2. In the presence of 1 microM atropine, submaximal EFS (10 Hz, 20-30 V, 0.5 ms pulse width, 1 s train duration) evoked an inhibitory junction potential (i.j.p.) followed by e.j.p. with superimposed action potentials (APs) and contraction. Addition of either NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG, 0.1 mM) or apamin (0.1 microM) inhibited the evoked i.j.p. and the combined administration of the two agents almost abolished it. In the presence of both L-NOARG and apamin, an atropine-resistant e.j.p. was the only electrical response evoked by EFS in 50% of cases and a small i.j.p. (10% of original amplitude) followed by e.j.p. was evident in the remainder. 3. In the presence of L-NOARG and apamin, the tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists, (+/-)-CP 96,345 and GR 82,334 (10 nM-3 microM) concentration-dependently inhibited the atropine-resistant e.j.p. and accompanying contraction evoked by EFS. EC50 values were: 0.77 microM (e.j.p. inhibition) and 0.22 microM (inhibition of contraction) for (+/-)-CP 96,345; 0.61 microM (e.j.p. inhibition) and 0.20 microM (inhibition of contraction) for GR 82,334. The tachykinin NK2 receptor antagonists, MEN 10,376 (up to 3 microM) and SR 48,968 (up to 1 microM) had no effect on the atropine-resistant e.j.p. MEN 10,376 (3 microM) but not SR 48,968 produced a slight inhibition of the evoked contraction.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artemenko D. P., Buryi V. A., Vladimirova I. A., Shuba M. F. Modifikatsiia metoda odinarnogo sakharoznogo mostika. Fiziol Zh. 1982 May;28(3):374–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartho L., Santicioli P., Patacchini R., Maggi C. A. Tachykininergic transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum: evidence for the involvement of NK2 receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):805–810. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Holzer P., Donnerer J., Lembeck F. Evidence for the involvement of substance P in the atropine-resistant peristalsis of the guinea-pig ileum. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Sep 20;32(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Holzer P. Search for a physiological role of substance P in gastrointestinal motility. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V., Kuriyama H. The nature of non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic transmission in longitudinal and circular muscles of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:375–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Shatzer S. A. Agonist and antagonist binding to tachykinin peptide NK-2 receptors. Life Sci. 1988;42(26):2701–2708. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Non-cholinergic excitatory and inhibitory junction potentials in the circular smooth muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:153–164. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Non-cholinergic fast and slow post-stimulus depolarization in the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1983 Jul;340:47–56. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Humphreys C. M. Apamin distinguishes two types of relaxation mediated by enteric nerves in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;332(1):79–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00633202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Pullin C. O., Bornstein J. Substance P enteric neurons mediate non-cholinergic transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig intestine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):446–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00692914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crist J. R., He X. D., Goyal R. K. The nature of noncholinergic membrane potential responses to transmural stimulation in guinea pig ileum. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1006–1015. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90276-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Regoli D. Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci. 1987 Nov 16;41(20):2269–2278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Barthó L., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Intestinal peristalsis associated with release of immunoreactive substance P. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):913–918. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R., Costa M., Furness J. B. Evidence for the release of endogenous substance P from intestinal nerves. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00507103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Schluet W., Maggi C. A. Ascending enteric reflex contraction: roles of acetylcholine and tachykinins in relation to distension and propagation of excitation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jan;264(1):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H. A modified single sucrose gap. Junction potentials and electrotonic potentials in gastrointestinal smooth muscles. J Pharmacol Methods. 1987 Nov;18(3):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(87)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Ballati L., Lecci A., Manzini S., Patacchini R., Renzetti A. R., Rovero P., Quartara L., Giachetti A. In vivo evidence for tachykininergic transmission using a new NK-2 receptor-selective antagonist, MEN 10,376. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):1172–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Theodorsson E., Barbanti G., Turini D., Giachetti A. Tachykinin antagonists inhibit nerve-mediated contractions in the circular muscle of the human ileum. Involvement of neurokinin-2 receptors. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jan;102(1):88–96. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91787-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giachetti A., Meli A. Tachykinin receptors in the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):996–1000. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14195.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Giachetti A. Tachykinin receptors and tachykinin receptor antagonists. J Auton Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;13(1):23–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1993.tb00396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Maggi C. A., Meli A. Pharmacological evidence that at least two different non-adrenergic non-cholinergic inhibitory systems are present in the rat small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 16;123(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90664-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niel J. P., Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. Effect of substance P on non-cholinergic fast and slow post-stimulus depolarization in the guinea-pig ileum. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Dec;9(4):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Structure-activity studies of neurokinin A. Neuropeptides. 1989 May-Jun;13(4):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. W., McLean S., Heym J. The substance P receptor antagonist CP-96,345 interacts with Ca2+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 4;219(3):491–492. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90498-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuba M. F., Vladimirova I. A. Effect of apamin on the electrical responses of smooth muscle to adenosine 5'-triphosphate and to non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve stimulation. Neuroscience. 1980;5(5):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth C. W., Murphy R., Furness J. B., Pompolo S. Comparison of the presence and actions of substance P and neurokinin A in guinea-pig taenia coli. Neuropeptides. 1991 May;19(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(91)90070-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternini C., Anderson K., Frantz G., Krause J. E., Brecha N. Expression of substance P/neurokinin A-encoding preprotachykinin messenger ribonucleic acids in the rat enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology. 1989 Aug;97(2):348–356. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Kilpatrick G. J. Characterization of histamine-H3 receptors controlling non-adrenergic non-cholinergic contractions of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):667–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson E., Smedfors B., Hellström P., Söder O., Aly A., Musat A., Panja A. B., Johansson C. Aspects on the role of tachykinins and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in control of secretion, motility and blood flow in the gut. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;298:233–240. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-0744-8_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Too H. P., Cordova J. L., Maggio J. E. A novel radioimmunoassay for neuromedin K. I. Absence of neuromedin K-like immunoreactivity in guinea pig ileum and urinary bladder. II. Heterogeneity of tachykinins in guinea pig tissues. Regul Pept. 1989 Sep-Oct;26(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(89)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vladimirova I. A., Shuba M. F. Sinapticheskie protsessy v gladkikh myshtsakh. Neirofiziologiia. 1984;16(3):307–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


