Abstract
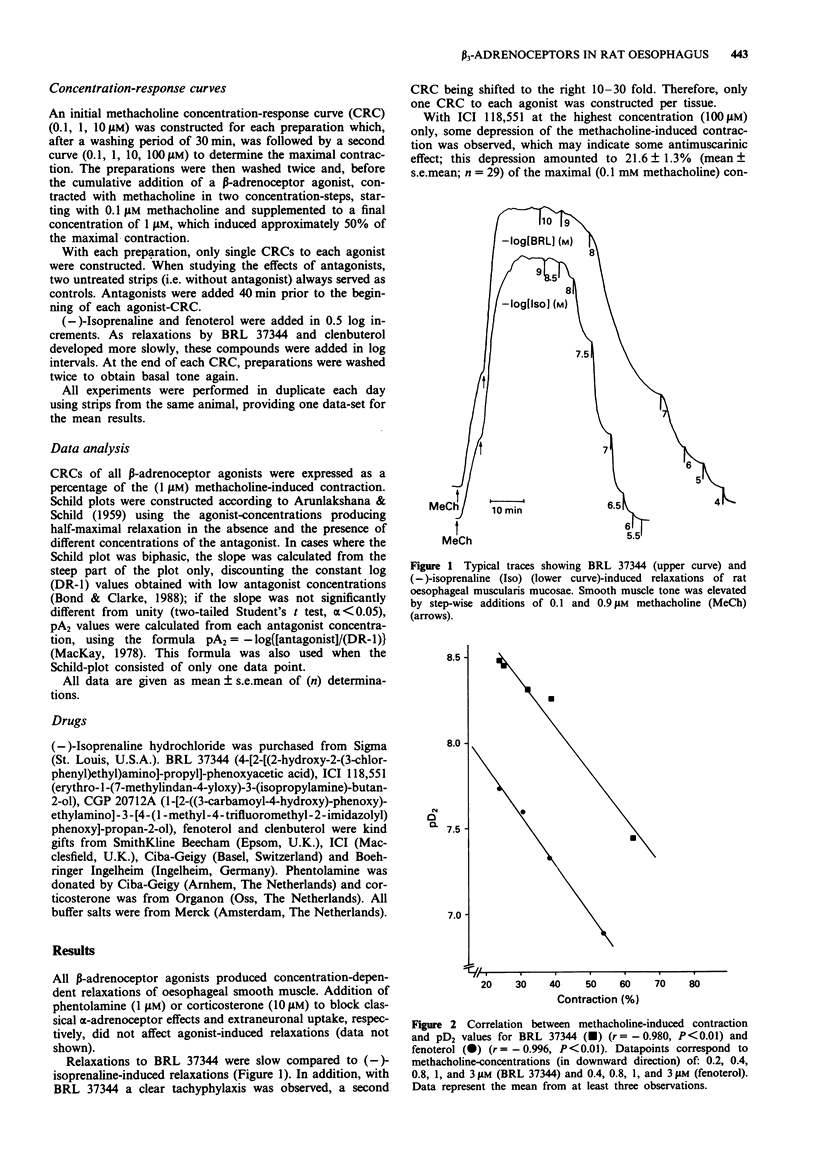
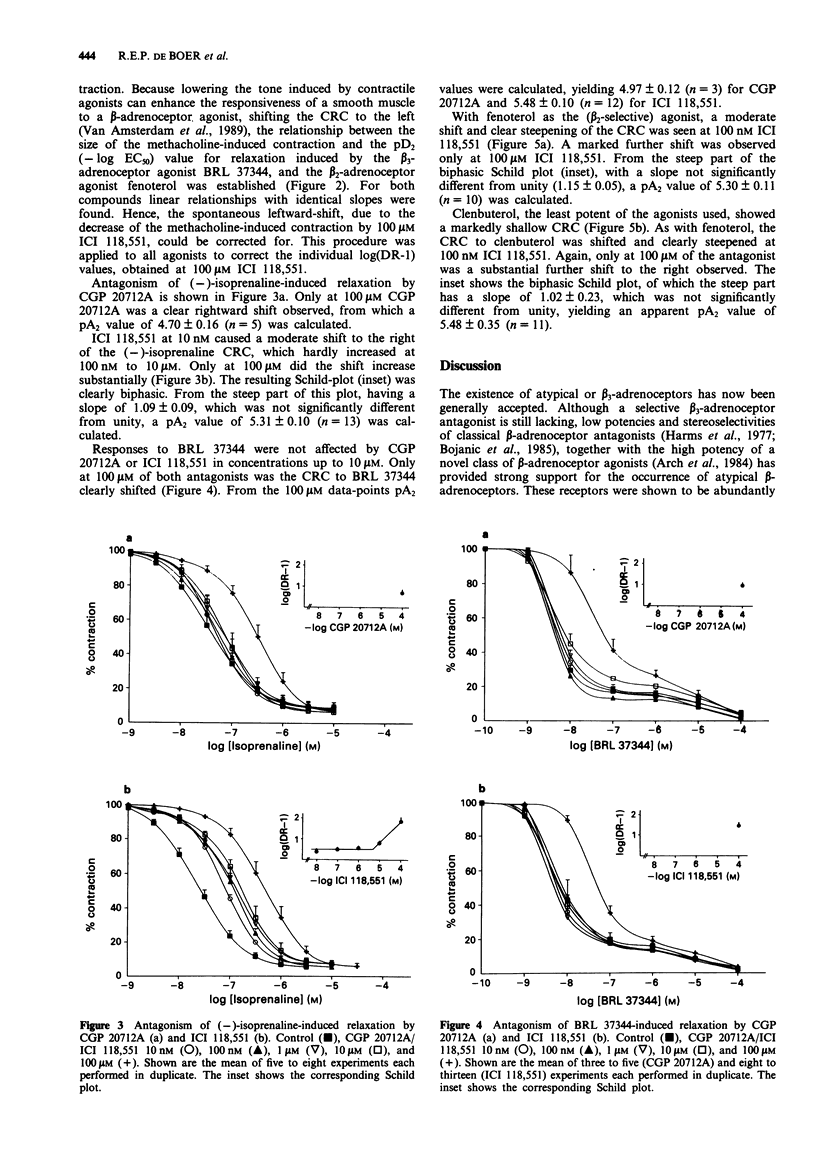
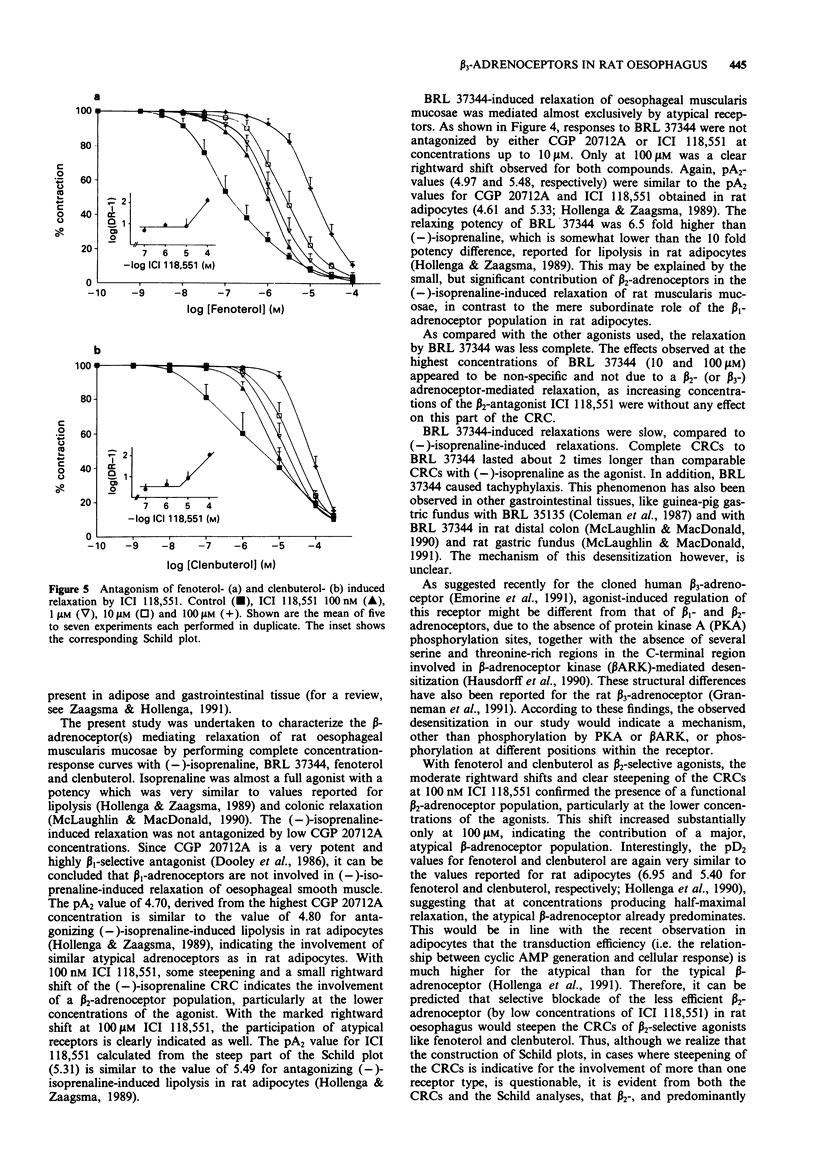
1. beta-Adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation of rat oesophageal smooth muscle was investigated by studying the effects of beta 1- and beta 2-selective antagonists on the relaxation induced by (-)-isoprenaline, the beta 2-selective agonists fenoterol and clenbuterol and the beta 3-agonist, BRL 37344. 2. The highly beta 1-selective antagonist CGP 20721A did not antagonize (-)-isoprenaline- or BRL 37344-induced relaxations in concentrations up to 10 microM. Only at 100 microM of CGP 20712A were clear rightward shifts of the agonist concentration-response curves (CRCs) observed, with pA2 values of 4.70 and 4.97 against (-)-isoprenaline and BRL 37344, respectively. 3. ICI 118,551, a potent and selective beta 2-antagonist, at 100 nM caused moderate rightward shifts of the CRCs of (-)-isoprenaline, fenoterol and clenbuterol; with fenoterol and clenbuterol, this was accompanied by a clear steepening of the curve. Only at the highest concentration (100 microM ICI 118,551) did the shifts to the right further increase substantially. Resulting Schild-plots were clearly biphasic. BRL 37344-induced relaxations were only antagonized at 100 microM ICI 118,551, yielding a pA2 value of 5.48. 4. These results clearly demonstrate that the BRL 37344-induced relaxation of rat oesophageal muscularis mucosae is mediated solely through beta 3-adrenoceptors, whereas (-)-isoprenaline-, fenoterol- and clenbuterol-induced relaxations were shown to involve both beta 2- and, predominantly, beta 3-adrenoceptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bojanic D., Jansen J. D., Nahorski S. R., Zaagsma J. Atypical characteristics of the beta-adrenoceptor mediating cyclic AMP generation and lipolysis in the rat adipocyte. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;84(1):131–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckner C. K., Christopherson R. C. Adrenergic receptors of rat esophageal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 May;189(2):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Leighton B., Wilson S., Thurlby P. L., Arch J. R. An investigation of the beta-adrenoceptor that mediates metabolic responses to the novel agonist BRL28410 in rat soleus muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croci T., Cecchi R., Tarantino A., Aureggi G., Bianchetti A., Boigegrain R., Manara L. Inhibition of rat colon motility by stimulation of atypical beta-adrenoceptors with new gut-specific agents. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1988 Feb;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(88)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. J., Bittiger H., Reymann N. C. CGP 20712 A: a useful tool for quantitating beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Feve B., Pairault J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg D. A. Structural basis for functional diversity of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenergic receptors. 1991 Mar 15-Apr 1Biochem Pharmacol. 41(6-7):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90188-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Zaagsma J., de Vente J. Differentiation of beta-adrenoceptors in right atrium, diaphragm and adipose tissue of the rat, using stereoisomers of propranolol, alprenolol, nifenalol and practolol. Life Sci. 1977 Jul 1;21(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Brouwer F., Zaagsma J. Relationship between lipolysis and cyclic AMP generation mediated by atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):577–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Haas M., Deinum J. T., Zaagsma J. Discrepancies in lipolytic activities induced by beta-adrenoceptor agonists in human and rat adipocytes. Horm Metab Res. 1990 Jan;22(1):17–21. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1004839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenga C., Zaagsma J. Direct evidence for the atypical nature of functional beta-adrenoceptors in rat adipocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1420–1424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay D. How should values of pA2 and affinity constants for pharmacological competitive antagonists be estimated? J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 May;30(5):312–313. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Characterization of catecholamine-mediated relaxations in rat isolated gastric fundus: evidence for an atypical beta-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1351–1356. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09792.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Evidence for the existence of 'atypical' beta-adrenoceptors (beta 3-adrenoceptors) mediating relaxation in the rat distal colon in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Amsterdam R. G., Meurs H., Brouwer F., Postema J. B., Timmermans A., Zaagsma J. Role of phosphoinositide metabolism in functional antagonism of airway smooth muscle contraction by beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber S. E., Stock M. J. Evidence for an atypical, or beta 3-adrenoceptor in ferret tracheal epithelium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):857–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaagsma J., Nahorski S. R. Is the adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor a prototype for the recently cloned atypical 'beta 3-adrenoceptor'? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):3–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet A., Rademaker B., Bast A. A beta adrenoceptor with atypical characteristics is involved in the relaxation of the rat small intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):218–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


