Abstract
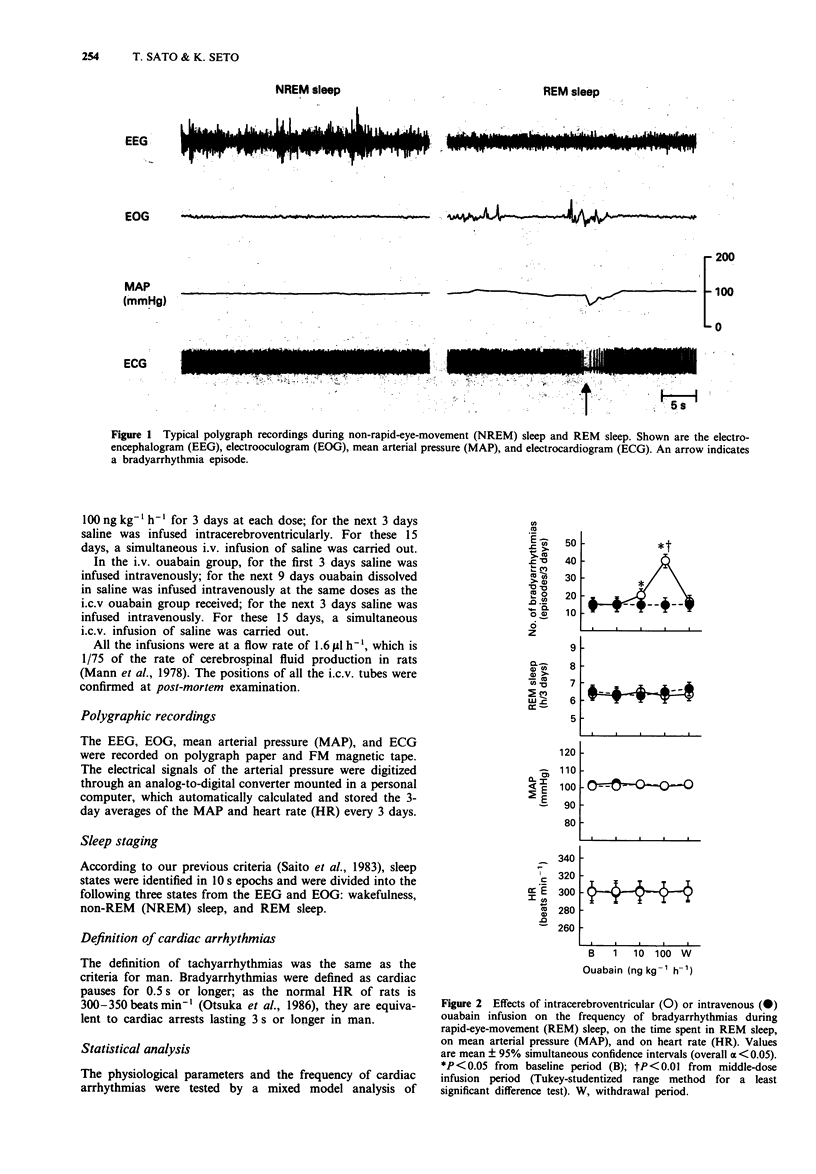
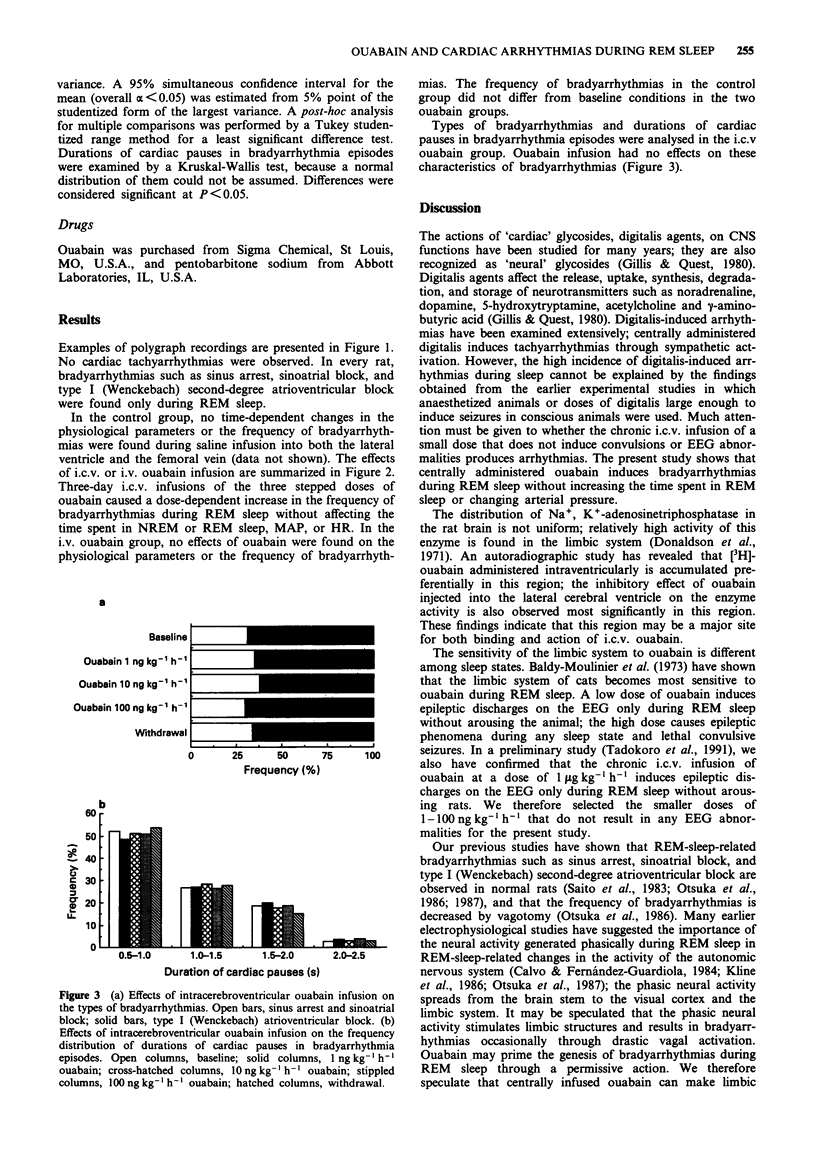
1. The effects of continuous infusions of ouabain on bradyarrhythmias (cardiac pauses for 0.5 s or longer) during sleep were examined in freely moving Wistar-Kyoto rats. 2. In a control group (n = 7), saline was infused into both the lateral ventricle and the femoral vein. In an intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) ouabain group (n = 7), ouabain was infused centrally, such that each rat received three stepped doses of 1, 10, and 100 ng kg-1 h-1 for 3 days at each dose, while saline was infused systemically. In an intravenous (i.v.) ouabain group (n = 7), ouabain was infused systemically at the same doses as the i.c.v. ouabain received, while the simultaneous i.c.v. infusion of saline was carried out. 3. Three-day i.c.v. infusions of the three stepped doses of ouabain caused a dose-dependent increase in the frequency of bradyarrhythmias during rapid-eye movement (REM) sleep without affecting the time spent in REM sleep, arterial pressure, average heart rate, or the frequency of bradyarrhythmias during non-REM sleep. Intravenous ouabain or i.c.v. saline had no effects on the frequency of bradyarrhythmias. 4. Intrinsic CNS activity during REM sleep may be involved in the centrally mediated arrhythmogenic properties of ouabain during sleep.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldy-Moulinier M., Arias L. P., Passouant P. Hippocampal epilepsy produced by ouabain. Studies of cerebral circulation and ionic metabolism. Eur Neurol. 1973;9(6):333–348. doi: 10.1159/000114242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. M., Fernández-Guardiola A. Phasic activity of the basolateral amygdala, cingulate gyrus, and hippocampus during REM sleep in the cat. Sleep. 1984;7(3):202–210. doi: 10.1093/sleep/7.3.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J., St Pierre T., Minnich J., Barbeau A. Seizures in rats associated with divalent cation inhibition of NA + -K + -ATP'ase. Can J Biochem. 1971 Nov;49(11):1217–1224. doi: 10.1139/o71-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis R. A., Quest J. A. The role of the nervous system in the cardiovascular effects of digitalis. Pharmacol Rev. 1979 Mar;31(1):19–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline L. R., Hendricks J. C., Davies R. O., Pack A. I. Control of activity of the diaphragm in rapid-eye-movement sleep. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Oct;61(4):1293–1300. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.4.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann J. D., Butler A. B., Rosenthal J. E., Maffeo C. J., Johnson R. N., Bass N. H. Regulation of intracranial pressure in rat, dog, and man. Ann Neurol. 1978 Feb;3(2):156–165. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Ikari M., Ichimaru Y., Saito H., Kawakami T., Otsuka K., Kaba H., Seto K. Experimental study on the relationship between cardiac arrhythmias and sleep states by ambulatory ECG-EEC monitoring. Clin Cardiol. 1986 Jul;9(7):305–313. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960090702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K. [Studies of digitalis-induced arrhythmias by recordings of twenty-four hour continuous electrocardiograms (author's transl)]. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 1980 Dec;71(12):631–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Otsuka K., Sato T., Yoshimatsu K., Kaba H., Seto K., Ichimaru Y., Sato Y., Yanaga T. Arrhythmogenic properties of paradoxical sleep. Am Heart J. 1983 May;105(5):875–877. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(83)90265-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somberg J. C., Smith T. W. Localization of the neurally mediated arrhythmogenic properties of digitalis. Science. 1979 Apr 20;204(4390):321–323. doi: 10.1126/science.219481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


