Abstract
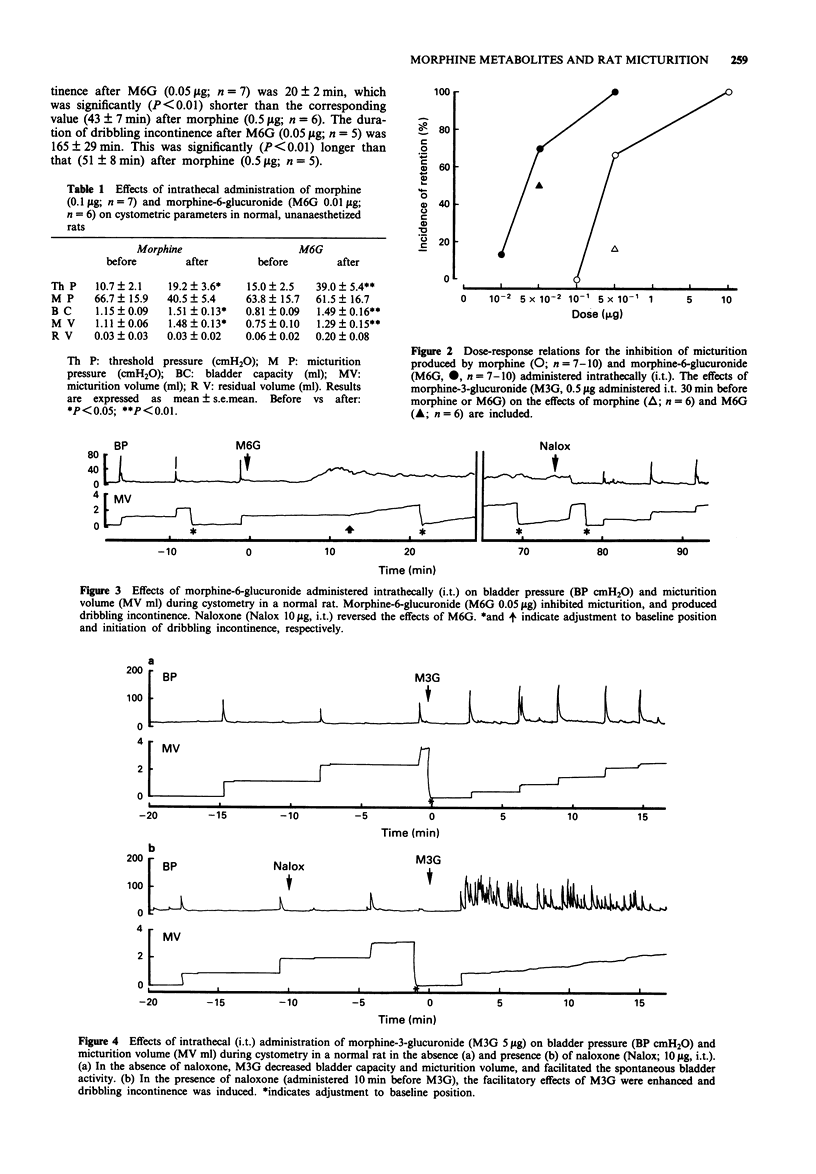
1. By means of continuous cystometry in normal, unanaesthetized rats, the effects on micturition of intrathecally (i.t.) administered morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) and morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G), the two main metabolites of morphine, were studied and compared with those of i.t. morphine. 2. Both M6G (0.01, 0.1, and 0.5 microgram) and M3G (5 micrograms) were found to have significant effects on micturition. Like morphine (0.1, 0.5, and 10 micrograms), M6G was able to inhibit the micturition reflex, and produce urinary retention and dribbling incontinence in a dose-dependent manner. The potency of M6G for inhibiting micturition was approximately 10 times higher than that of morphine, and the duration of its effect was longer. All effects of M6G could be reversed by naloxone. 3. M3G (5 micrograms) facilitated the micturition reflex, resulting in decreases in bladder capacity and micturition volume, and an increase in spontaneous contractile activity. Pretreatment with naloxone (10 micrograms), which by itself had no effect on micturition, enhanced the facilitatory effects of M3G. In addition, M3G tended to counteract the inhibitory effects of both morphine and M6G on micturition. M3G (5 micrograms) also produced an excitatory behavioural syndrome. 4. It is concluded that in rats, i.t. M3G has excitatory effects on micturition and behaviour, probably not mediated via opioid receptors. I.t M6G has a potent inhibitory effect on micturition mediated by stimulation of opioid receptors. It may have effects on somatosensory afferent input in lower doses than those required for effects on micturition.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott F. V., Palmour R. M. Morphine-6-glucuronide: analgesic effects and receptor binding profile in rats. Life Sci. 1988;43(21):1685–1695. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggren A., Rubenson A., Sillén U. Involvement of opioid mechanisms in peripheral motor control of detrusor muscle. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992 Sep;71(3 Pt 1):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1992.tb00541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerner U. The metabolism of morphine and heroin in man. Drug Metab Rev. 1975;4(1):39–73. doi: 10.3109/03602537508993748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromage P. R., Camporesi E. M., Durant P. A., Nielsen C. H. Nonrespiratory side effects of epidural morphine. Anesth Analg. 1982 Jun;61(6):490–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen C. B., Jørgensen L. N. Morphine-6-glucuronide has high affinity for the opioid receptor. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987 Jan;60(1):75–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1987.tb01724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Metsch R. Inhibition of urinary bladder contractions by a spinal action of morphine and other opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Nov;231(2):254–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Metsch R. Morphine and the centrally-mediated inhibition of urinary bladder motility in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 9;297(1):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90559-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Metsch R. Opioid receptor subtypes involved in the central inhibition of urinary bladder motility. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 3;104(1-2):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Nunan L. Supraspinal and spinal mechanisms in morphine-induced inhibition of reflex urinary bladder contractions in the rat. Neuroscience. 1987 Jul;22(1):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Nunan L., Wire W. Central delta-opioid receptor interactions and the inhibition of reflex urinary bladder contractions in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;85(3):717–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb10569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durant P. A., Yaksh T. L. Drug effects on urinary bladder tone during spinal morphine-induced inhibition of the micturition reflex in unanesthetized rats. Anesthesiology. 1988 Mar;68(3):325–334. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198803000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frances B., Gout R., Monsarrat B., Cros J., Zajac J. M. Further evidence that morphine-6 beta-glucuronide is a more potent opioid agonist than morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jul;262(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francés B., Gout R., Campistron G., Panconi E., Cros J. Morphine-6-glucuronide is more mu-selective and potent in analgesic tests than morphine. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1990;328:477–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Q. L., Hedner J., Björkman R., Hedner T. Morphine-3-glucuronide may functionally antagonize morphine-6-glucuronide induced antinociception and ventilatory depression in the rat. Pain. 1992 Feb;48(2):249–255. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90065-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Q. L., Hedner T., Hedner J., Björkman R., Nordberg G. Antinociceptive and ventilatory effects of the morphine metabolites: morphine-6-glucuronide and morphine-3-glucuronide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 25;193(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90199-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann W., Jurna I., Nell T., Theres C. The dependence of the anti-nociceptive effect of morphine and other analgesic agents on spinal motor activity after central monoamine depletion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;24(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisamitsu T., de Groat W. C. The inhibitory effect of opioid peptides and morphine applied intrathecally and intracerebroventricularly on the micturition reflex in the cat. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 23;298(1):51–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren M., Hedner J., Mellstrand T., Nordberg G., Hedner T. Characterization of the antinociceptive effects of some adenosine analogues in the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;334(3):290–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00508784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucks D., Thompson P. I., McLoughlin L., Joel S. P., Patel N., Grossman A., Rees L. H., Slevin M. L. Explanation at the opioid receptor level for differing toxicity of morphine and morphine 6-glucuronide. Br J Cancer. 1992 Jan;65(1):122–126. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igawa Y., Persson K., Andersson K. E., Uvelius B., Mattiasson A. Facilitatory effect of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on spinal and peripheral micturition reflex pathways in conscious rats with and without detrusor instability. J Urol. 1993 Apr;149(4):884–889. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labella F. S., Pinsky C., Havlicek V. Morphine derivatives with diminished opiate receptor potency show enhanced central excitatory activity. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling G. S., Spiegel K., Lockhart S. H., Pasternak G. W. Separation of opioid analgesia from respiratory depression: evidence for different receptor mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren A., Sjögren C., Uvelius B., Mattiasson A., Andersson K. E., Andersson P. O. Cystometrical evaluation of bladder instability in rats with infravesical outflow obstruction. J Urol. 1987 Jun;137(6):1291–1294. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)44485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne R., Thompson P., Joel S., Trew D., Patel N., Slevin M. The analgesic activity of morphine-6-glucuronide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;34(2):130–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Bodnar R. J., Clark J. A., Inturrisi C. E. Morphine-6-glucuronide, a potent mu agonist. Life Sci. 1987 Dec 28;41(26):2845–2849. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90431-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Standifer K. M., Inturrisi C. E., Pasternak G. W. Pharmacological characterization of morphine-6 beta-glucuronide, a very potent morphine metabolite. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelligrino D. A., Riegler F. X., Albrecht R. F. Ventilatory effects of fourth cerebroventricular infusions of morphine-6- or morphine-3-glucuronide in the awake dog. Anesthesiology. 1989 Dec;71(6):936–940. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198912000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porreca F., Mosberg H. I., Omnaas J. R., Burks T. F., Cowan A. Supraspinal and spinal potency of selective opioid agonists in the mouse writhing test. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):890–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulain P., Ribon A. M., Hanks G. W., Hoskin P. J., Aherne G. W., Chapman D. J. CSF concentrations of morphine-6-glucuronide after oral administration of morphine. Pain. 1990 Apr;41(1):115–116. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)91116-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawal N., Möllefors K., Axelsson K., Lingårdh G., Widman B. An experimental study of urodynamic effects of epidural morphine and of naloxone reversal. Anesth Analg. 1983 Jul;62(7):641–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Deadwyler S. A. Morphine excitation: effects on field potentials recorded in the in vitro hippocampal slice. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jun;19(6):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmauss C., Yaksh T. L. In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R. J., Nunan L., Porreca F. Mu antagonist properties of kappa agonists in a model of rat urinary bladder motility in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon R. J., Nunan L., Porreca F. U50,488H differentially antagonizes the bladder effects of mu agonists at spinal sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 9;146(2-3):229–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura K., Kamata O., Ueki S., Ida S., Oguri K. Analgesic effect of morphine glucuronides. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1971 Sep;105(1):45–52. doi: 10.1620/tjem.105.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. T., Watt J. A., Cramond T. Morphine-3-glucuronide--a potent antagonist of morphine analgesia. Life Sci. 1990;47(6):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soulard C., Pascaud X., Roman F. J., Grouhel A., Junien J. L. Pharmacological evaluation of JO 1870: relation to the potential treatment of urinary bladder incontinence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1152–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenseth R., Sellevold O., Breivik H. Epidural morphine for postoperative pain: experience with 1085 patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1985 Jan;29(1):148–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1985.tb02176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. F., McQuay H. J., Bailey D., Dickenson A. H. The spinal antinociceptive actions of morphine metabolites morphine-6-glucuronide and normorphine in the rat. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 20;482(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Säwe J., Svensson J. O., Rane A. Morphine metabolism in cancer patients on increasing oral doses--no evidence for autoinduction or dose-dependence. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;16(1):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf C. J. Intrathecal high dose morphine produces hyperalgesia in the rat. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 30;209(2):491–495. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Harty G. J., Onofrio B. M. High dose of spinal morphine produce a nonopiate receptor-mediated hyperesthesia: clinical and theoretic implications. Anesthesiology. 1986 May;64(5):590–597. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198605000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Harty G. J. Pharmacology of the allodynia in rats evoked by high dose intrathecal morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura H., Ida S., Oguri K., Tsukamoto H. Biochemical basis for analgesic activity of morphine-6-glucuronide. I. Penetration of morphine-6-glucuronide in the brain of rats. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jun 15;22(12):1423–1430. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


