Abstract
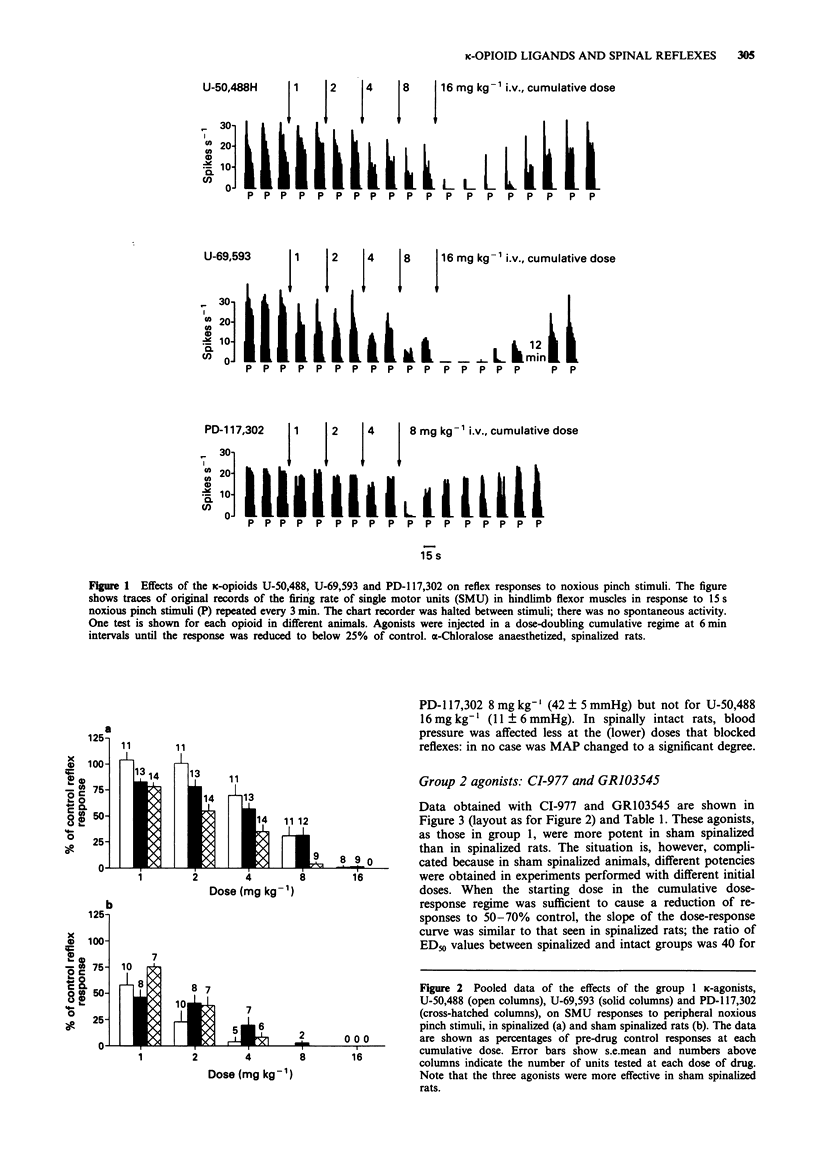
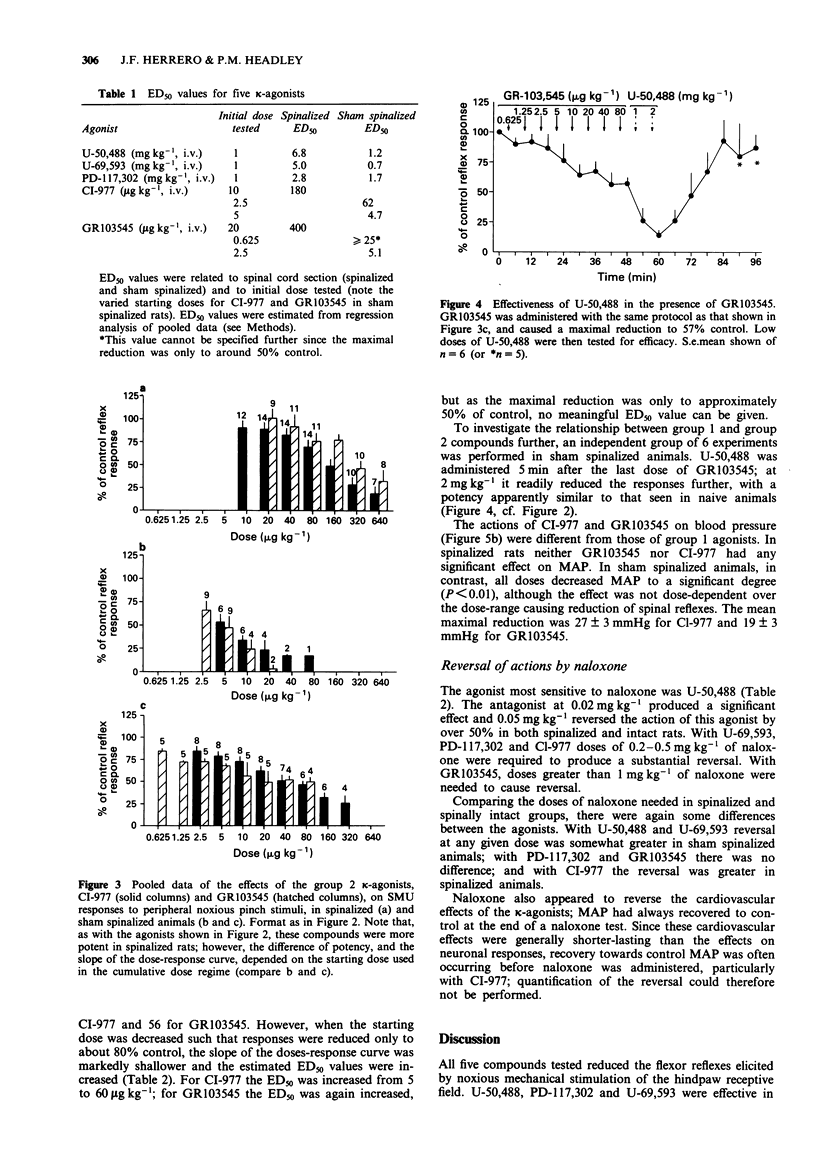
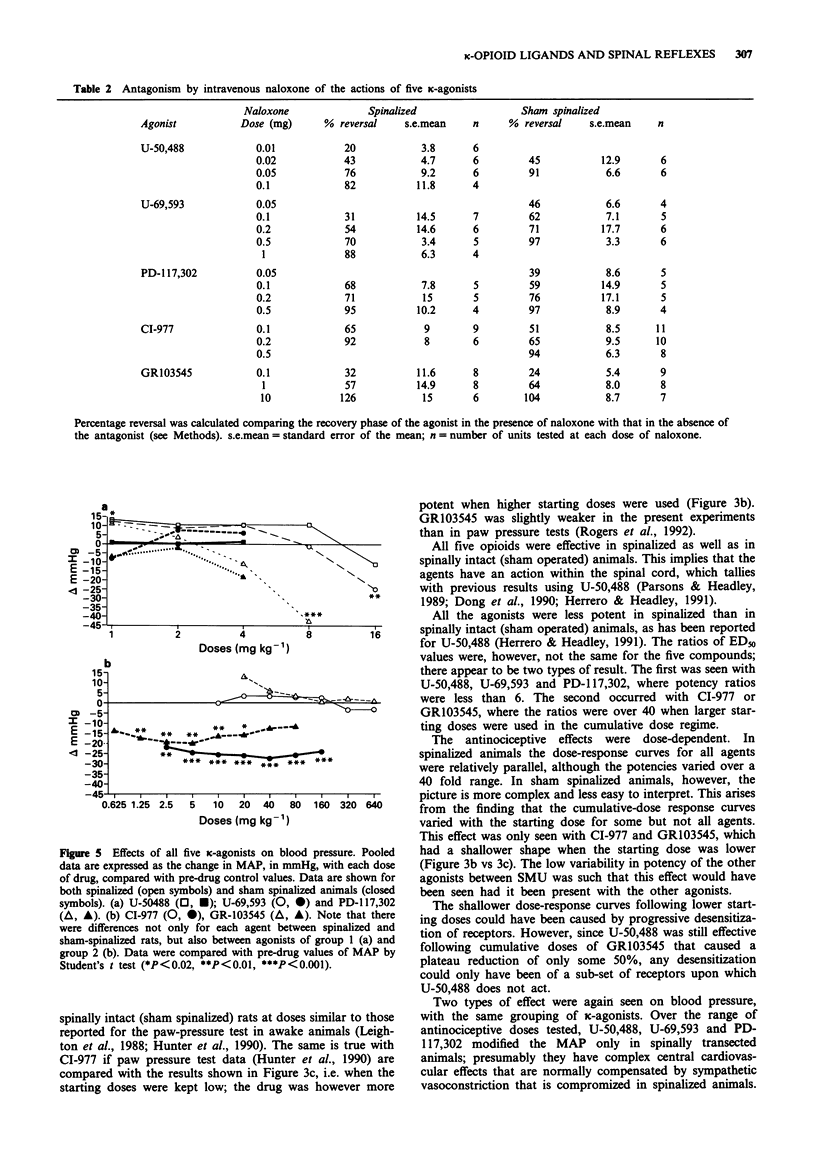
1. The evidence for kappa-receptor heterogeneity is equivocal. We have now investigated this question by comparing the effects of five putatively selective kappa-agonists. The parameters examined were: the relative potencies in depressing hindlimb flexor muscle reflexes to noxious pinch stimuli in both spinalized and sham-spinalized rats; the reversibility of these effects by naloxone; and the effects on blood pressure. 2. Two types of drug effect was discriminated. One drug group, represented by U-50,488, U-69,593 and PD-117,302, had a potency ratio between sham and spinalized rats approximately 10 fold lower than the other group, which comprised GR103545 and CI-977. 3. Under sham-spinalized conditions, CI-977 and GR103545 at high doses caused only sub-maximal reductions of spinal reflexes. U-50,488 was still active when superimposed on these high doses of GR103545. 4. Naloxone reversed all effects, but different doses were required between compounds, with GR103545 taking some 20 times higher doses of naloxone to cause reversal than did U-50,488. 5. The effects on mean arterial pressure were opposite between groups. 6. The results imply that more than one type of naloxone-sensitive non-mu opioid receptor must be involved in mediating these complex actions of ligands that have been claimed to be selective for kappa-receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attali B., Gouardères C., Mazarguil H., Audigier Y., Cros J. Evidence for multiple "Kappa" binding sites by use of opioid peptides in the guinea-pig lumbo-sacral spinal cord. Neuropeptides. 1982 Oct;3(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(82)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Attali B., Mazarguil H., Cros J. Characterization of [3H]-etorphine binding in guinea-pig striatum after blockade of mu and delta sites. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1287–1290. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanas E., Bourhim N., Giraud P., Boudouresque F., Cantau P., Oliver C. Interaction of opiates with opioid binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla: II. Interaction with kappa sites. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):688–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. R., Birchmore B., Sharif N. A., Hunter J. C., Hill R. G., Hughes J. PD117302: a selective agonist for the kappa-opioid receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):618–626. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. A., Liu L., Price M., Hersh B., Edelson M., Pasternak G. W. Kappa opiate receptor multiplicity: evidence for two U50,488-sensitive kappa 1 subtypes and a novel kappa 3 subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Nov;251(2):461–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. W., Parsons C. G., Headley P. M. Effects of intravenous mu and kappa opioid receptor agonists on sensory responses of convergent neurones in the dorsal horn of spinalized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1230–1236. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartell N. A., Headley P. M. Preparative surgery enhances the direct spinal actions of three injectable anaesthetics in the anaesthetized rat. Pain. 1991 Jul;46(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90036-W. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartell N. A., Headley P. M. Spinal effects of four injectable anaesthetics on nociceptive reflexes in rats: a comparison of electrophysiological and behavioural measurements. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):563–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Birch P. J., Hayward N. J., Sheehan M. J., Rogers H., Tyers M. B., Judd D. B., Scopes D. I., Naylor A. A series of novel, highly potent and selective agonists for the kappa-opioid receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec;101(4):944–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero J. F., Headley P. M. The effects of sham and full spinalization on the systemic potency of mu- and kappa-opioids on spinal nociceptive reflexes in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):166–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. C., Leighton G. E., Meecham K. G., Boyle S. J., Horwell D. C., Rees D. C., Hughes J. CI-977, a novel and selective agonist for the kappa-opioid receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):183–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Kim H. S., Wood P. L. Effects of kappa opiate agonists on neurochemical and neuroendocrine indices: evidence for kappa receptor subtypes. Life Sci. 1986 Aug 18;39(7):637–644. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Mickelson M. M., McCall J. M., Von Voigtlander P. F. [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton G. E., Rodriguez R. E., Hill R. G., Hughes J. kappa-Opioid agonists produce antinociception after i.v. and i.c.v. but not intrathecal administration in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morre M., Bachy A., Gout B., Boigegrain R., Arnone M., Roncucci R. Kappa binding sites in guinea-pig brain membranes: evidence for a dynorphin-resistant subtype. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90472-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. G., Headley P. M. Spinal antinociceptive actions of mu- and kappa-opioids: the importance of stimulus intensity in determining 'selectivity' between reflexes to different modalities of noxious stimulus. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):523–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. G., West D. C., Headley P. M. Spinal antinociceptive actions and naloxone reversibility of intravenous mu- and kappa-opioids in spinalized rats: potency mismatch with values reported for spinal administration. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):533–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S., Lipkowski A. W., Takemori A. E. Binaltorphimine and nor-binaltorphimine, potent and selective kappa-opioid receptor antagonists. Life Sci. 1987 Mar 30;40(13):1287–1292. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90585-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H., Birch P. J., Harrison S. M., Palmer E., Manchee G. R., Judd D. B., Naylor A., Scopes D. I., Hayes A. G. GR94839, a kappa-opioid agonist with limited access to the central nervous system, has antinociceptive activity. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):783–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman R. B., Bykov V., de Costa B. R., Jacobson A. E., Rice K. C., Brady L. S. Interaction of endogenous opioid peptides and other drugs with four kappa opioid binding sites in guinea pig brain. Peptides. 1990 Mar-Apr;11(2):311–331. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90088-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traynor J. Subtypes of the kappa-opioid receptor: fact or fiction? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):52–53. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. S., Rodriguez F. D., Traynor J. R. Characterisation of kappa-opioid binding sites in rat and guinea-pig spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Oct;28(10):1041–1046. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


