Abstract
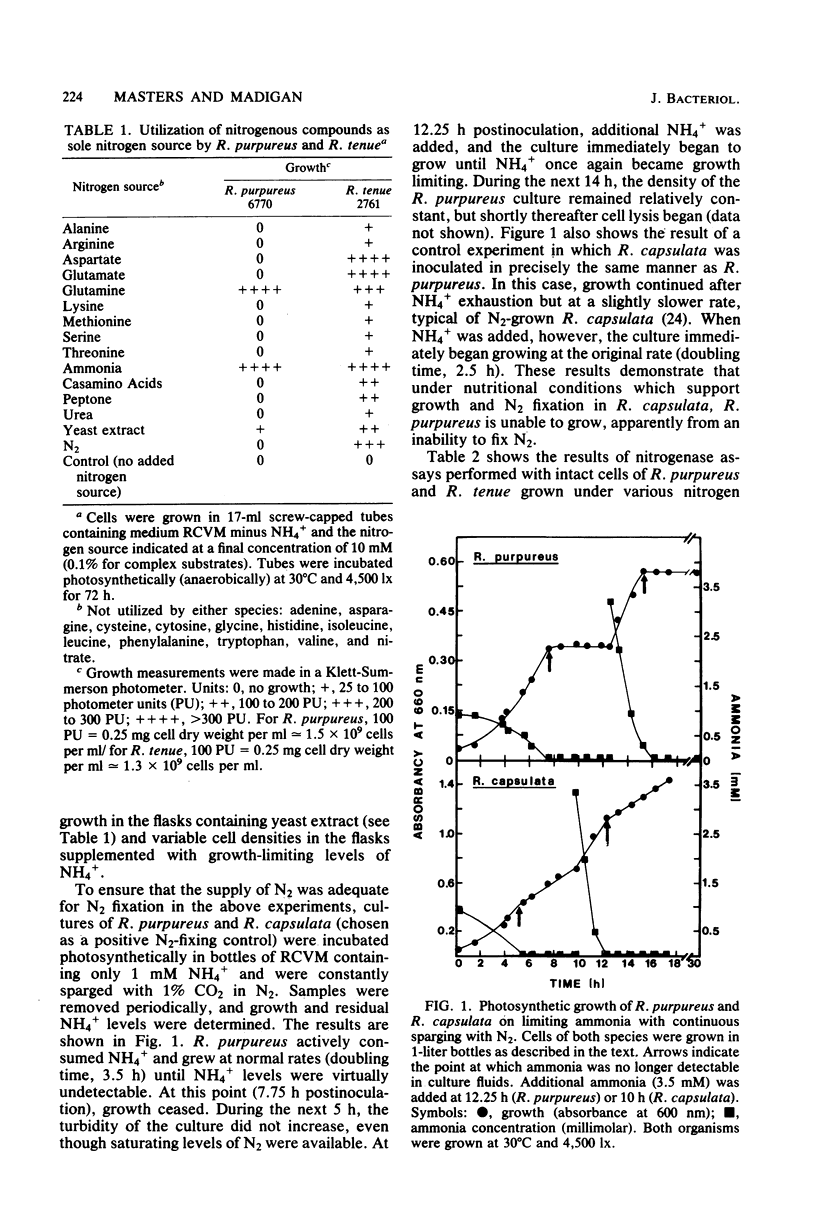
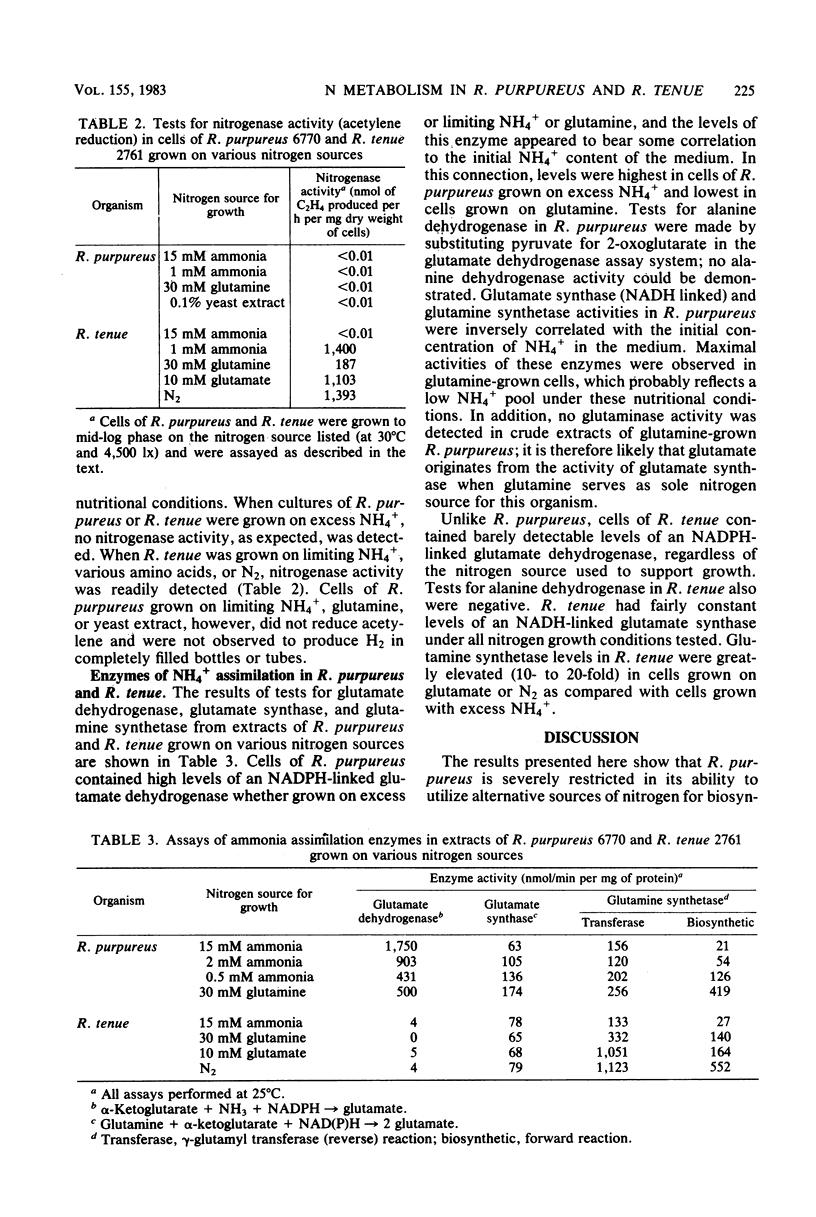
Studies of the nitrogen nutrition and pathways of ammonia assimilation in Rhodocyclus purpureus and Rhodospirillum tenue have shown that these two seemingly related bacteria differ considerably in aspects of their nitrogen metabolism. When grown photoheterotrophically with malate as carbon source, R. purpureus utilized only NH4+ or glutamine as sole nitrogen sources and was unable to fix N2. By contrast, R. tenue was found to utilize a variety of amino acids as nitrogen sources and was a good N2 fixer. No nitrogenase activity was detected in cells of R. purpureus grown on limiting ammonia, whereas cells of R. tenue grown under identical conditions reduced acetylene to ethylene at high rates. Regardless of the nitrogen source supporting growth, extracts of cells of R. purpureus contained high levels of glutamate dehydrogenase, whereas R. tenue contained only trace levels of this enzyme. Alanine dehydrogenase activity was absent from both species. We conclude that R. purpureus is incapable of fixing molecular nitrogen and employs the glutamate dehydrogenase pathway as the primary means of assimilating NH4+ under all growth conditions. R. tenue, on the other hand, employs the glutamine synthetase/glutamate synthase pathway for the incorporation of NH4+ supplied exogenously or as the product of N2 fixation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. R., Tata R. Growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants lacking glutamate synthase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):193–197. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.193-197.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Evolution and gene transfer in purple photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):210–212. doi: 10.1038/283210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert R. A., Siefert E., Pfennig N. Nitrogen assimilation in Rhodopseudomonas acidophila. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Oct 4;119(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00407919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Inorganic nitrogen assimilation by the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.683-688.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. T., Gest H. Growth of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata chemoautotrophically in darkness with H2 as the energy source. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):524–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.524-530.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. T., Wall J. D., Gest H. Dark anaerobic dinitrogen fixation by a photosynthetic microorganism. Science. 1979 Jun 29;204(4400):1429–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.204.4400.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W., Brown C. M. 'Glutamine(amide):2-oxoglutarate amino transferase oxido-reductase (NADP); an enzyme involved in the synthesis of glutamate by some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):187–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Kelley B. C., Vignais P. M. Nitrogen fixation and hydrogen metabolism in photosynthetic bacteria. Biochimie. 1978;60(3):245–260. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80821-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Rhodospirillum tenue sp. n., a new species of the purple nonsulfur bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Aug;99(2):619–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.2.619-620.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt K. Carotenoids of purple nonsulfur bacteria. Composition and biosynthesis of the carotenoids of some strains of Rhodopseudomonas acidophila, Rhodospirillum tenue, and Rhodocyclus purpureus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;77(3):231–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siefert E., Irgens R. L., Pfennig N. Phototrophic purple and green bacteria in a sewage treatment plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.38-44.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S. L., Deleo A. B., Magasanik B. Regulation of enzyme formation in Klebsiella aerogenes by episomal glutamine synthetase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.184-192.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall J. D., Johansson B. C., Gest H. A pleiotropic mutant of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata defective in nitrogen metabolism. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Dec 15;115(3):259–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00446450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gibson J., Fox G. E. Do genealogical patterns in purple photosynthetic bacteria reflect interspecific gene transfer? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):212–214. doi: 10.1038/283212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer W. E. On ultrastructures in Rhodopseudomonas gelatinosa and Rhodospirillum tenue. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(2):241–242. doi: 10.1007/BF02219141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



