Abstract
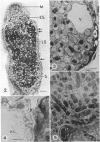
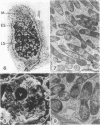
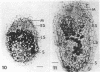
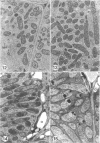
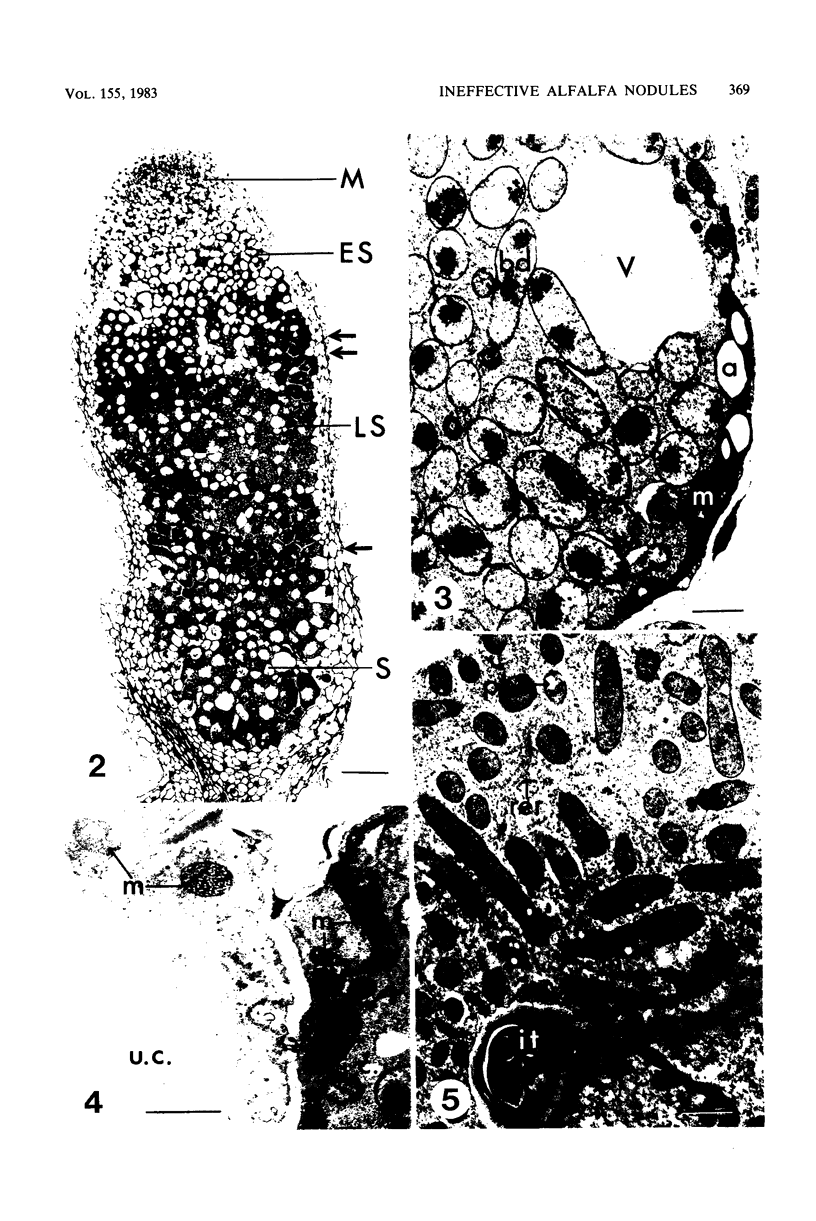
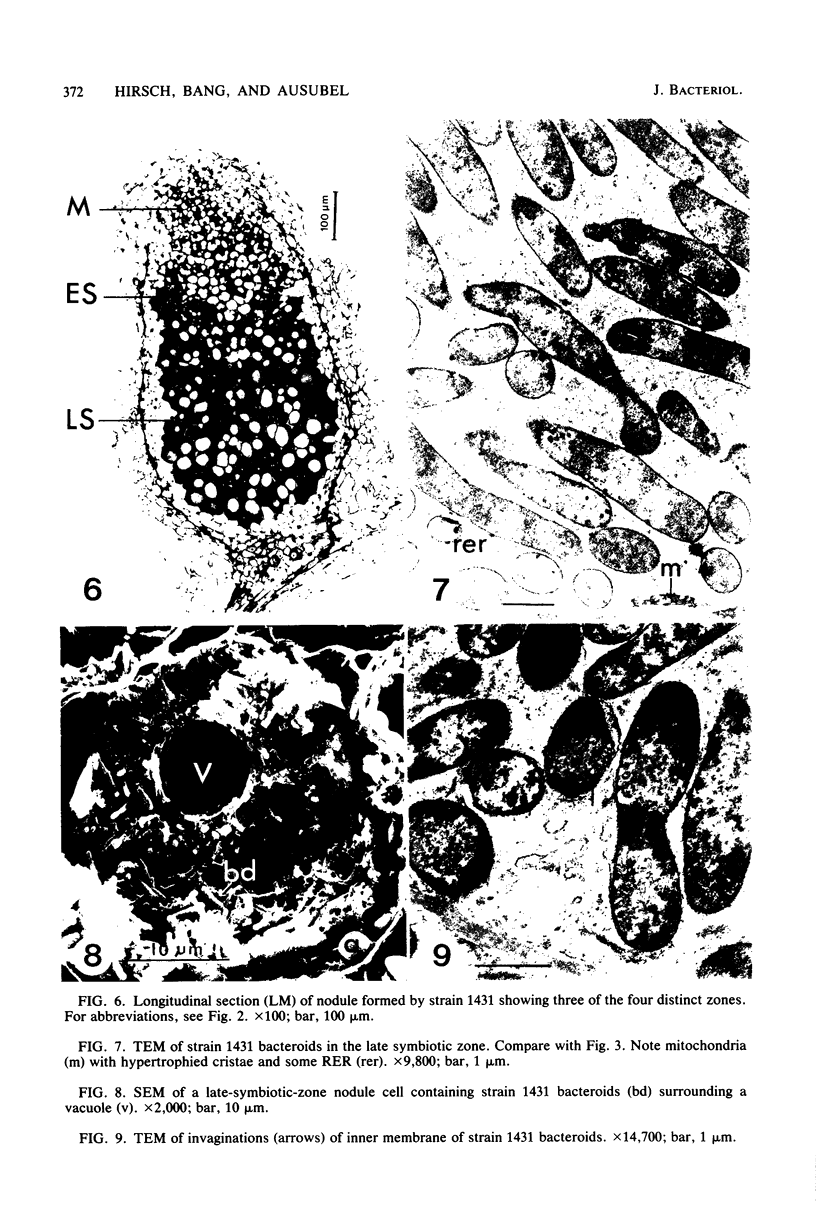
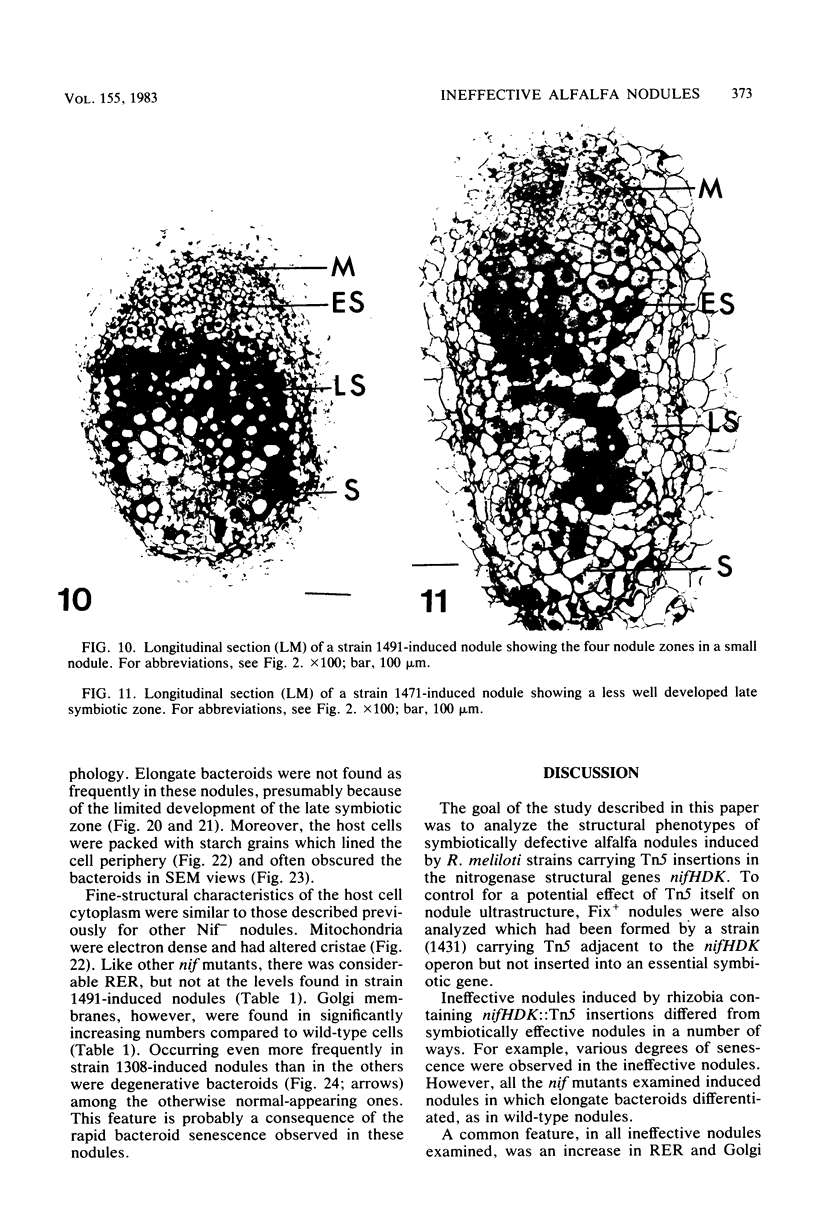
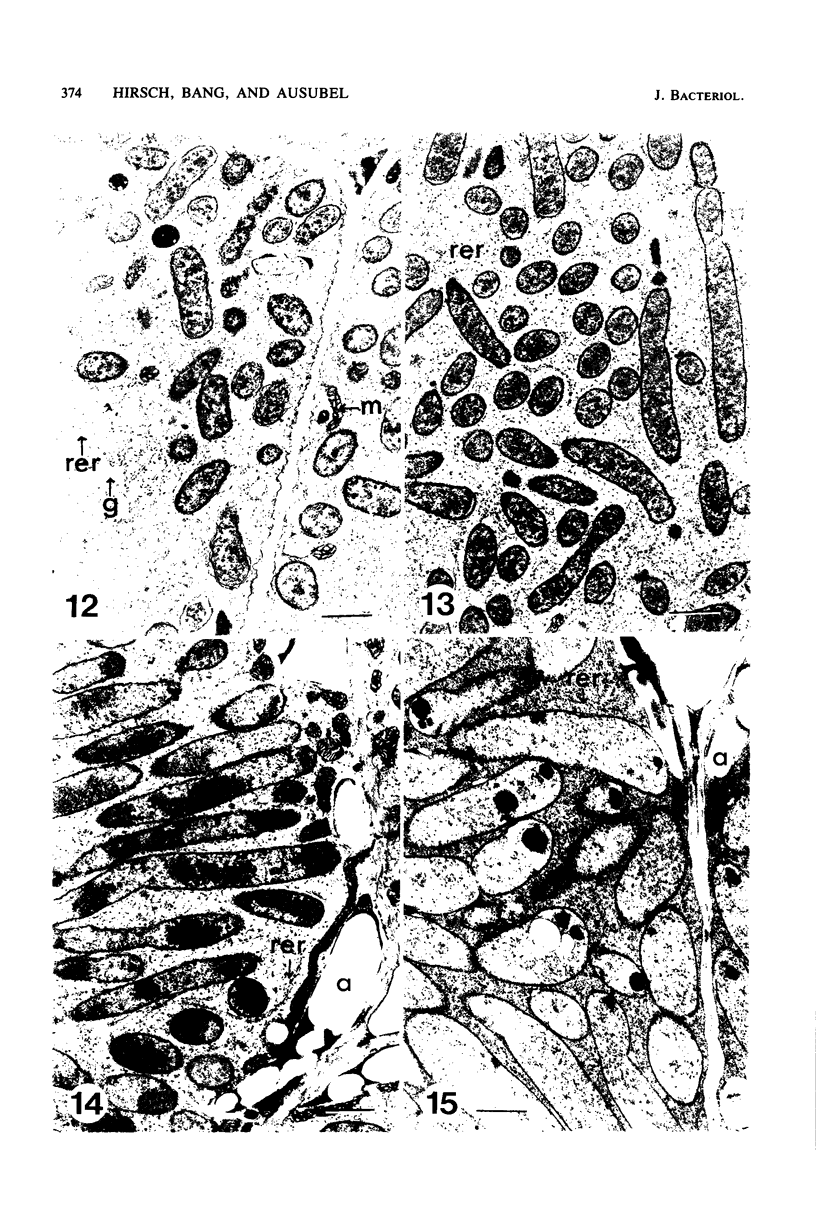
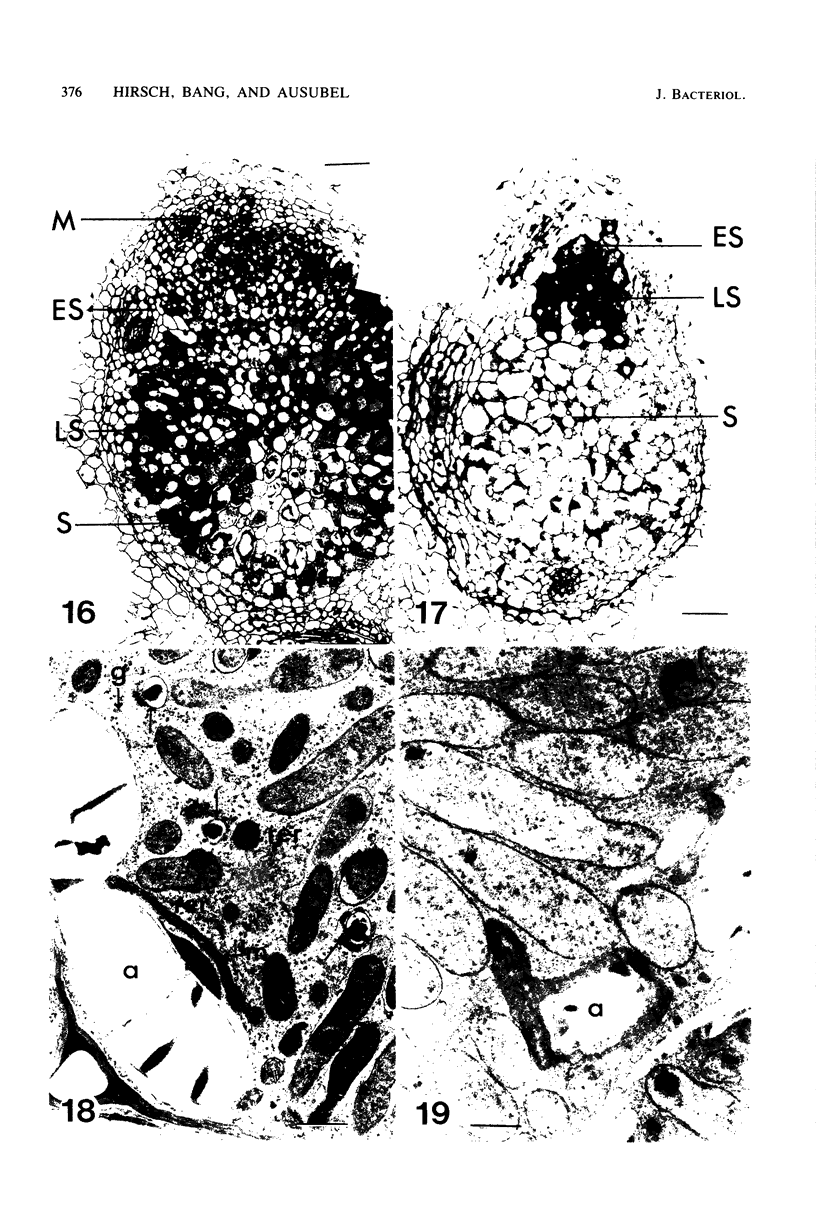
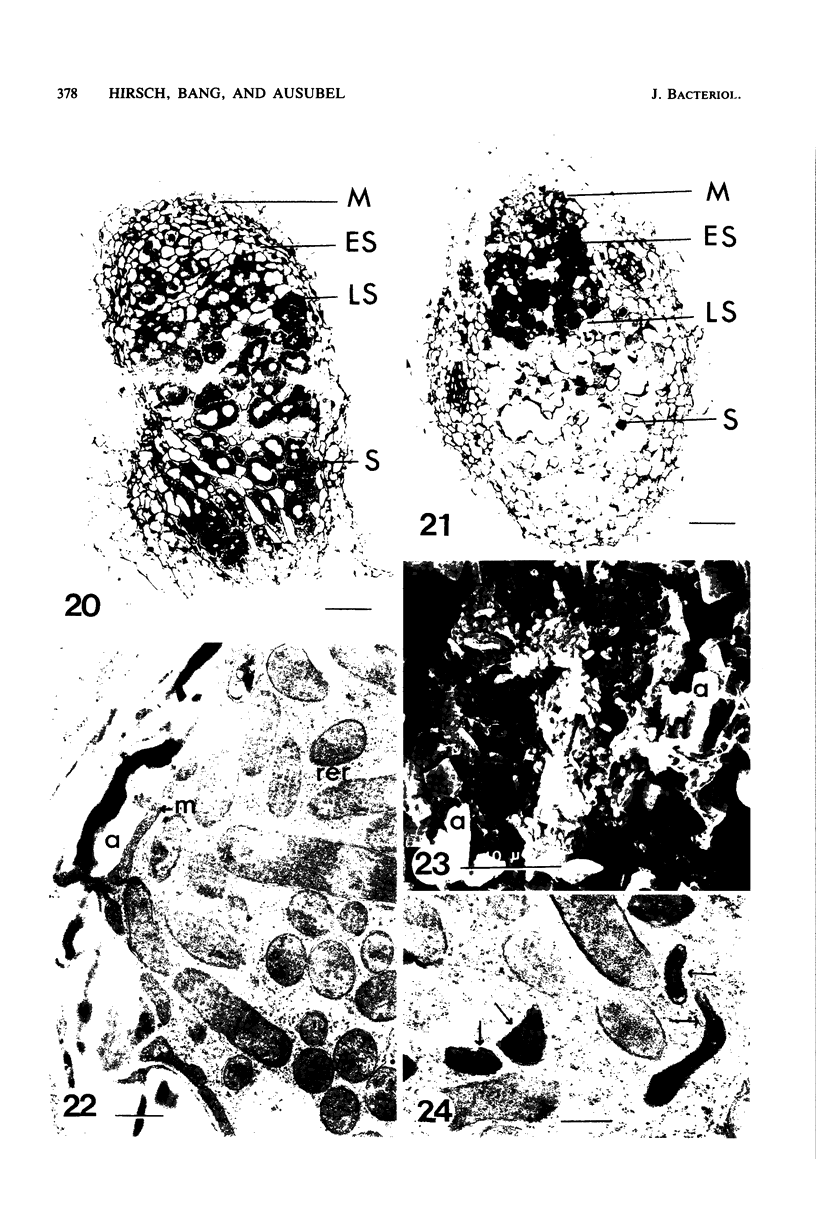
Ineffective alfalfa nodules formed by Rhizobium meliloti nif::Tn5 mutants were examined by light and electron microscopy. R. meliloti nifH::Tn5 mutants formed nodules that were similar in structure to wild-type nodules except that nifH- bacteroids accumulated a compact, electron-dense body. In contrast to nodules induced by wild type and nifH mutants, nifDK- R. meliloti mutants induced nodules which contained numerous starch grains and prematurely senescent bacteroids. In addition, meristematic activity in nifDK- nodules ceased significantly earlier than in nifH- nodules. All mutant nodules exhibited elevated levels of rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi membranes compared to wild-type nodule cells. These elevated levels may reflect either a response to nitrogen starvation in the ineffective nodules or an abnormal synthesis and export of nodule-specific proteins during later developmental stages.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger S., Verma D. P. Induction and expression of nodule-specific host genes in effective and ineffective root nodules of soybean. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1300–1306. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett B., Goodman R. N., Novacky A. Ultrastructure of soybean nodules. II: deterioration of the symbiosis in ineffective nodules. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jul;23(7):873–883. doi: 10.1139/m77-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derenzini M., Viron A., Puvion-Dutilleul F. The Feulgen-like osmium-ammine reaction as a tool to investigate chromatin structure in thin sections. J Ultrastruct Res. 1982 Aug;80(2):133–147. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Long S. R., Bang M., Haskins N., Ausubel F. M. Structural studies of alfalfa roots infected with nodulation mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.411-419.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN D. C., GRINYER I., COULTER W. H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF INFECTION THREADS AND BACTERIA IN YOUNG ROOT NODULES OF MEDICAGO SATIVA. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:125–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.125-137.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Identification of "nodule-specific" host proteins (nodoulins) involved in the development of rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie C. R., Jordan D. C. Ultrastructure of root nodules formed by ineffective strains of Rhizobium meliloti. Can J Microbiol. 1974 May;20(5):755–758. doi: 10.1139/m74-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Ineffective and non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.763-769.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Bloch C. B., Brill W. J. Developmental fate of Rhizobium meliloti bacteroids in alfalfa nodules. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1480–1490. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1480-1490.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J. J., Yang A. F. Light and electron microscopic studies of nodule structure of alfalfa. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):36–43. doi: 10.1139/m81-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. G., Lyttleton P., Bullivant S., Grayston G. F. Membranes in lupin root nodules. I. The role of Golgi bodies in the biogenesis of infection threads and peribacteroid membranes. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:129–149. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Ausubel F. M. A general method for site-directed mutagenesis in prokaryotes. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):85–88. doi: 10.1038/289085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Directed transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and complementation analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Shelley S. A., Balis J. U. Ultrastructural stereologic analysis of fetal rabbit type II alveolar epithelial cells following maternal pilocarpine treatment or fasting. Anat Rec. 1982 Jan;202(1):23–31. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092020105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Ball S., Guérin C., Wanamaker L. Leghemoglobin biosynthesis in soybean root nodules. Characterization of the nascent and released peptides and the relative rate of synthesis of the major leghemoglobins. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):476–483. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma D. P., Haugland R., Brisson N., Legocki R. P., Lacroix L. Regulation of the expression of leghaemoglobin genes in effective and ineffective root nodules of soybean. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 26;653(1):98–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]