Abstract
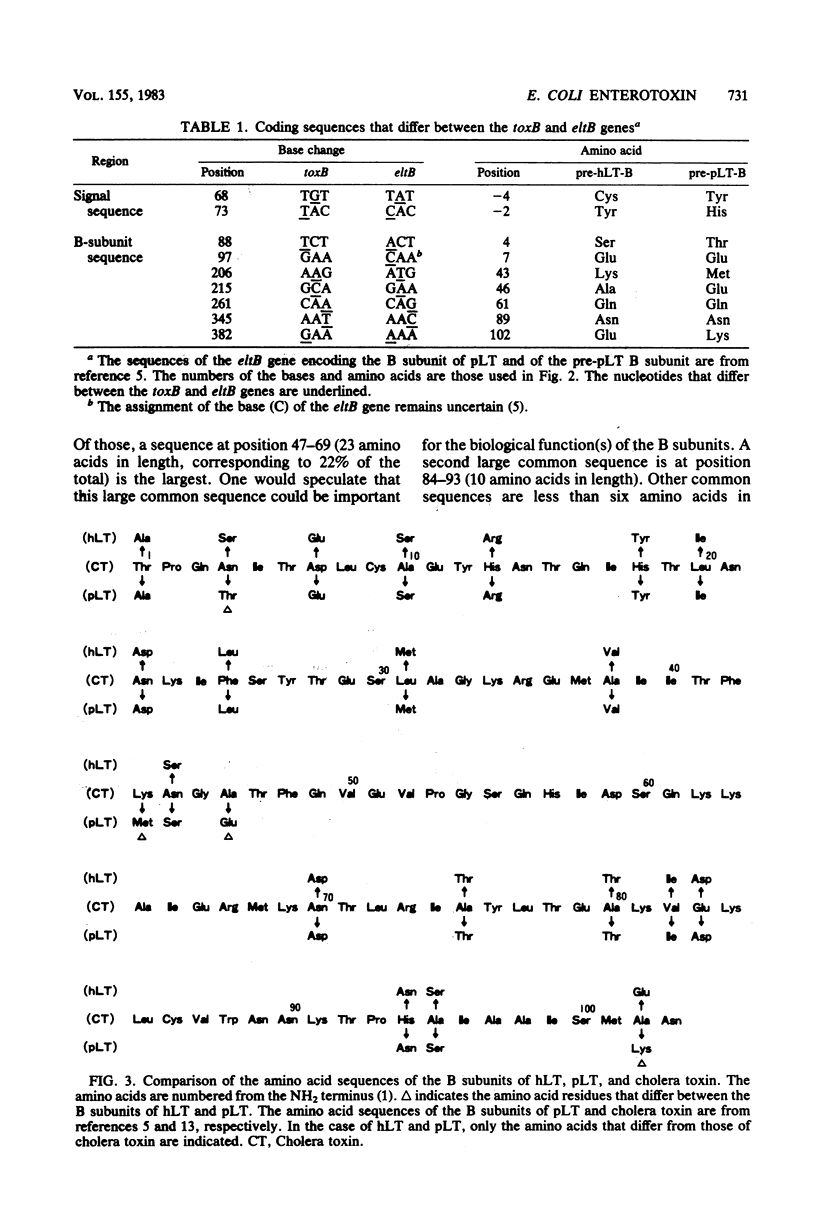
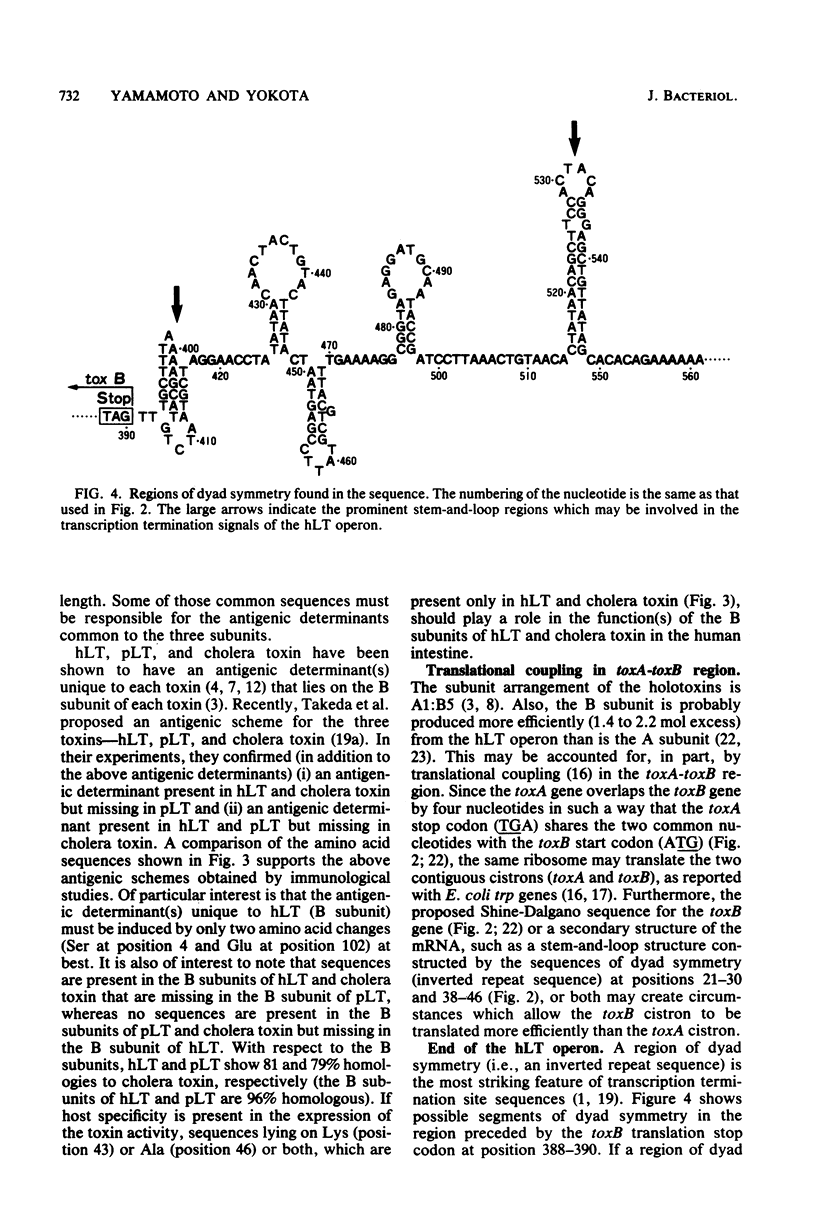
We determined the complete nucleotide sequence of the toxB gene (375 base pairs in length), which encodes the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin produced from Escherichia coli pathogenic for humans (hLT). The amino acid sequence of the B subunit of hLT was deduced from the nucleotide sequence. Consequently, it has become possible to study the homology between the B subunits of three similar toxins: hLT, LT produced from E. coli pathogenic for piglets (pLT), and cholera toxin (the latter two sequences have been reported by others). The three B subunits are all 103 amino acids in length. A comparison of the toxB gene and the eltB gene, which encodes the B subunit of pLT, showed a 98% homology at the nucleotide level and a 95% homology at the amino acid (of a precursor) level, indicating the possibility that the two genes share a common ancestor. With respect to the B-subunit sequences, the homologies between hLT and pLT, between hLT and cholera toxin, and between pLT and cholera toxin were 96, 81, and 79%, respectively. Several large common sequences are conserved by the three peptides. In contrast, no sequences are present in both pLT and cholera toxin but missing in hLT.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Flint D. C., Klipstein F. A. Immunological and physicochemical characterization of heat-labile enterotoxins isolated from two strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):806–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.806-809.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Yancey R. J., Finkelstein R. A. Properties of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxin from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.91-97.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosky A., Markel D. E., Peterson J. W., Fitch W. M. Primary structure of cholera toxin beta-chain: a glycoprotein hormone analog? Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.831277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Garrison S., Fishman P. H., Richardson S. H. Gangliosides sensitize unresponsive fibroblasts to Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):381–384. doi: 10.1172/JCI109472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Yanofsky C. Translational coupling during expression of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T., Yanofsky C. An intercistronic region and ribosome-binding site in bacterial messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards K. L., Douglas S. D. Pathophysiological effects of Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and their exotoxins on eucaryotic cells. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Sep;42(3):592–613. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.3.592-613.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Sima H., Tsuji T., Miwatani T. Analysis of antigenic determinants in cholera enterotoxin and heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.50-53.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji T., Taga S., Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Molecular heterogeneity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):444–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.444-448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Ryoji M., Kaji A., Yokota T., Takano T. Sequence analysis of the heat-labile enterotoxin subunit B gene originating in human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):506–509. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.506-509.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Tamura T., Yokota T., Takano T. Overlapping genes in the heat-labile enterotoxin operon originating from Escherichia coli human strain. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):356–359. doi: 10.1007/BF00332701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin genes are flanked by repeated deoxyribonucleic acid sequences. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.850-860.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T., Kaji A. Molecular organization of heat-labile enterotoxin genes originating in Escherichia coli of human origin and construction of heat-labile toxoid-producing strains. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):983–987. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.983-987.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Plasmids of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli H10407: evidence for two heat-stable enterotoxin genes and a conjugal transfer system. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1352–1360. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1352-1360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Release of heat-labile enterotoxin subunits by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1482–1484. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1482-1484.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


