Abstract
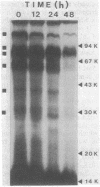
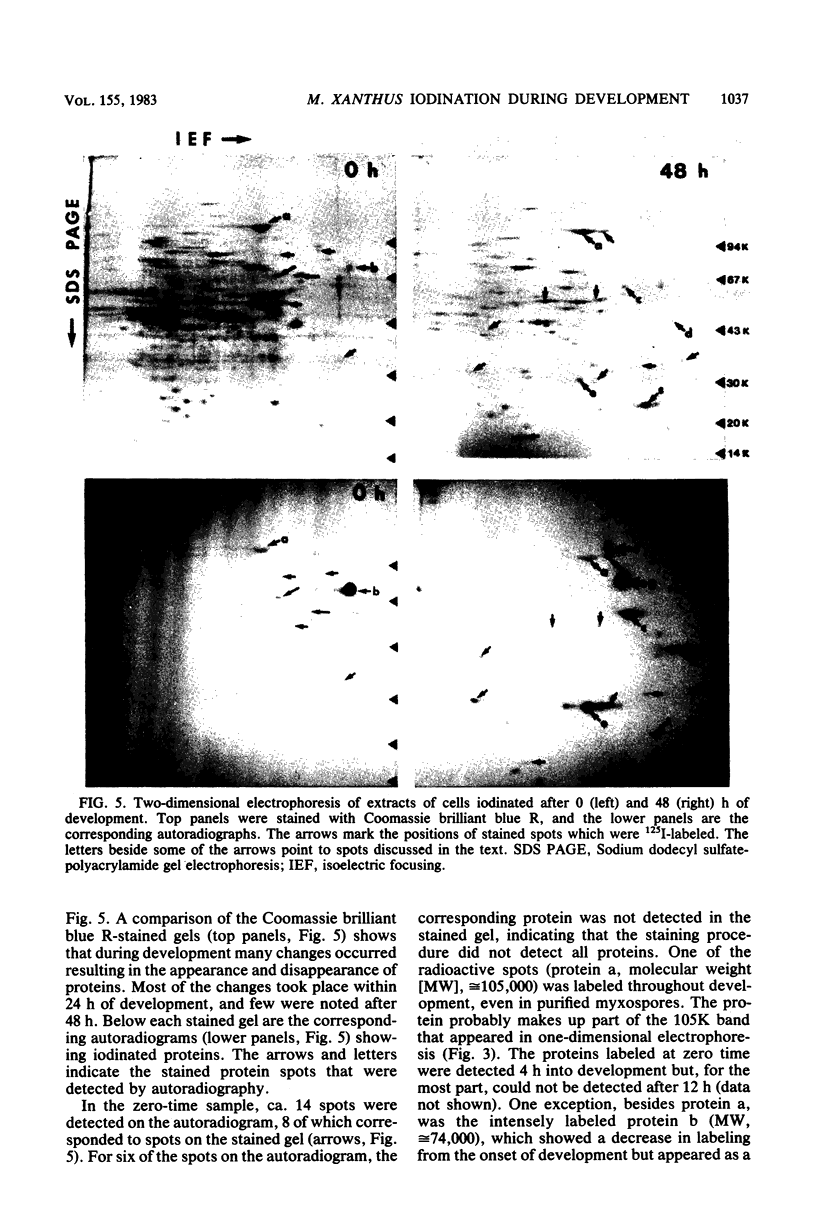
Intact cells of Myxococcus xanthus were iodinated with [125I]lactoperoxidase to permit examination of the surface components accessible to labeling during cell development. Vegetative cells, starved on a defined solid medium, aggregated, formed fruiting bodies, and produced myxospores. Cells collected at different stages were iodinated, and their proteins were analyzed by one- and two-dimensional electrophoresis and autoradiography. One-dimensional electrophoresis revealed six iodinated bands in vegetative cell extracts. During development, 10 radioactive bands were detected, 4 of which migrated to the same positions as those of vegetative cells. Only six bands were detected in purified, labeled myxospores. Of these, one band possessed mobility similar to that of labeled vegetative cell proteins, whereas the other bands possessed mobility similar to that detected in developing cells. Analysis of two-dimensional gels indicated that at least 14 proteins were iodinated in vegetative cells, one of which was intensely labeled (protein b). Another of the proteins (protein a) was labeled throughout development. During development, about 30 proteins were iodinated and the prominently labeled ones were designated c, d, e, f, and g. The latter two (proteins f and g) were not detected in purified, iodinated myxospores. The data indicated a pronounced change in surface structure during development; some of the change may be involved in cellular interaction during aggregation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewick M. A., Lo T. C. Localization of the dicarboxylate binding protein in the cell envelope of Escherichia coli K12. Can J Biochem. 1980 Oct;58(10):885–897. doi: 10.1139/o80-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. R. Cell surface proteins of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jun 30;94(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90522-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Purification and characterization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin, a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12581–12588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M., Zusman D. R. Myxobacterial hemagglutinin: a development-specific lectin of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5505–5509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnosspelius G. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease from Myxococcus virescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.17-25.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckels J. E. The surface properties of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: topographical distribution of the outer membrane protein antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Oct;108(2):213–219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-108-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Biosynthesis and self-assembly of protein S, a development-specific protein of Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Inouye S., Zusman D. R. Gene expression during development of Myxococcus xanthus: pattern of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus I. R., Berg H. C. Gliding motility of Cytophaga sp. strain U67. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):384–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.384-398.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Cumsky M. G., Zusman D. R. Localization of myxobacterial hemagglutinin in the periplasmic space and on the cell surface of Myxococcus xanthus during developmental aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12589–12595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Dworkin M. Separation and properties of the cytoplasmic and outer membranes of vegetative cells of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):914–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.914-927.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Dworkin M. Synthesis of several membrane proteins during developmental aggregation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):29–39. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.29-39.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S. Z., Dworkin M. Comparative biology of prokaryotic resting cells. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:153–224. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S., Dworkin M. Bacteriolytic enzymes produced by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):236–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.236-245.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Developmentally induced autolysis during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.798-802.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]