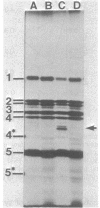
Abstract
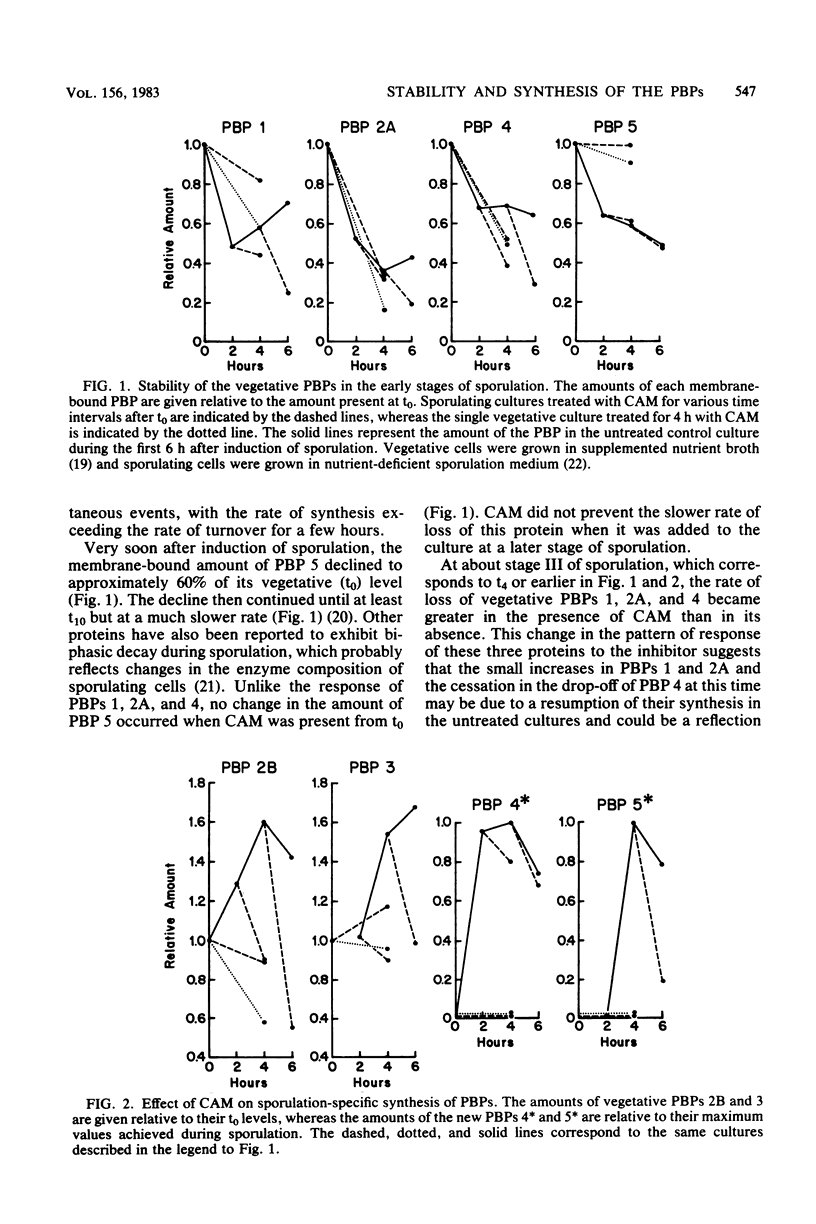
The penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) of Bacillus subtilis were examined after incubation of vegetative and sporulating cultures with chloramphenicol, an inhibitor of protein synthesis. The results indicate that the sporulation-specific increases in vegetative PBPs 2B and 3 and the appearance of two new PBPs, 4* and 5*, depend on concurrent protein synthesis, which is most likely to be de novo synthesis of the PBPs rather than synthesis of an activator or processing enzyme. It was also learned that in vivo the PBPs differ in their individual stabilities, which helps to explain some of the quantitative changes that occur in the PBP profile during sporulation. All the membrane-bound PBPs, except possibly PBP 1, were found to be stable in the presence of crude extracts of sporulating cells that contained proteolytic activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Interaction of penicillin with the bacterial cell: penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin-sensitive enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):291–335. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.291-335.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E. Altered membrane proteins in a minicell-producing mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):305–307. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.305-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan C. E., Strominger J. L. Altered penicillin-binding components in penicillin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER P. D. Site of action of radiopenicillin. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Mar;20(1):28–48. doi: 10.1128/br.20.1.28-48.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancer B. N., Mandelstam J. Production and possible function of serine protease during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):406–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.406-410.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J. H., Carlton B. C. Effects of mutational loss of specific intracellular proteases on the sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):612–617. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.612-617.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins A. D., Slepecky R. A. Antibiotic inhibition of the septation stage in sporulation of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1513–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1513-1515.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson H. F., Kay D., Mandelstam J. Temporal dissociation of late events in Bacillus subtilis sporulation from expression of genes that determine them. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):793–805. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.793-805.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjan P., Keryer E., Szulmajster J. Characterization of a thermosensitive sporulation mutant of Bacillus subtilis affected in the structural gene of an intracellular protease. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):353–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13194.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleppe G., Strominger J. L. Studies of the high molecular weight penicillin-binding proteins of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4856–4862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J., Rogolsky M., Hanh V. T. Binding of radioactive benzylpenicillin to sporulating Bacillus cultures: chemistry and fluctuations in specific binding capacity. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.662-667.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R., Brabson J. S., Switzer R. L. Immunochemical studies of the inactivation of aspartate transcarbamylase by stationary phase Bacillus subtilis cells. Evidence for selective, energy-dependent degradation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5585–5593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reysset G., Millet J. Characterization of an intracellular protease in B. subtillus during sporulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C., Silverman P., Haverback B. J. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Aug;21(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P. Sporulation and the production of antibiotics, exoenzymes, and exotonins. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Mar;33(1):48–71. doi: 10.1128/br.33.1.48-71.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowell M. O., Buchanan C. E. Changes in penicillin-binding proteins during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1331–1337. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1331-1337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germaination. VII. Protein turnover during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4600–4605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Ellar D. J. Alteration in the penicillin-binding profile of Bacillus megaterium during sporulation. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):640–643. doi: 10.1038/300640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINTER V. Spores of microorganisms. Penicillin-induced destruction of sporulating cells of Bacillus cereus. Experientia. 1962 Sep 15;18:409–410. doi: 10.1007/BF02151489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waindle L. M., Switzer R. L. Inactivation of aspartic transcarbamylase in sporulating Bacillus subtilis: demonstration of a requirement for metabolic energy. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):517–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.517-527.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Lindgren D. M., Strominger J. L. High-molecular-weight penicillin-binding proteins from membranes of bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):950–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.950-955.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Limited proteolysis of the penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase purified from Bacillus subtilis membranes. Active water-soluble fragments generated by cleavage of a COOH-terminal membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):2059–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Sequence of active site peptides from the penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. Mechanism of penicillin action and sequence homology to beta-lactamases. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3964–3976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Amanuma H., O'Brien T. A., Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin is an active-site inhibitor for four genera of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1150–1153. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1150-1153.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Waxman D. J., Rasmussen J. R., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of penicillin action: penicillin and substrate bind covalently to the same active site serine in two bacterial D-alanine carboxypeptidases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2730–2734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]