Abstract
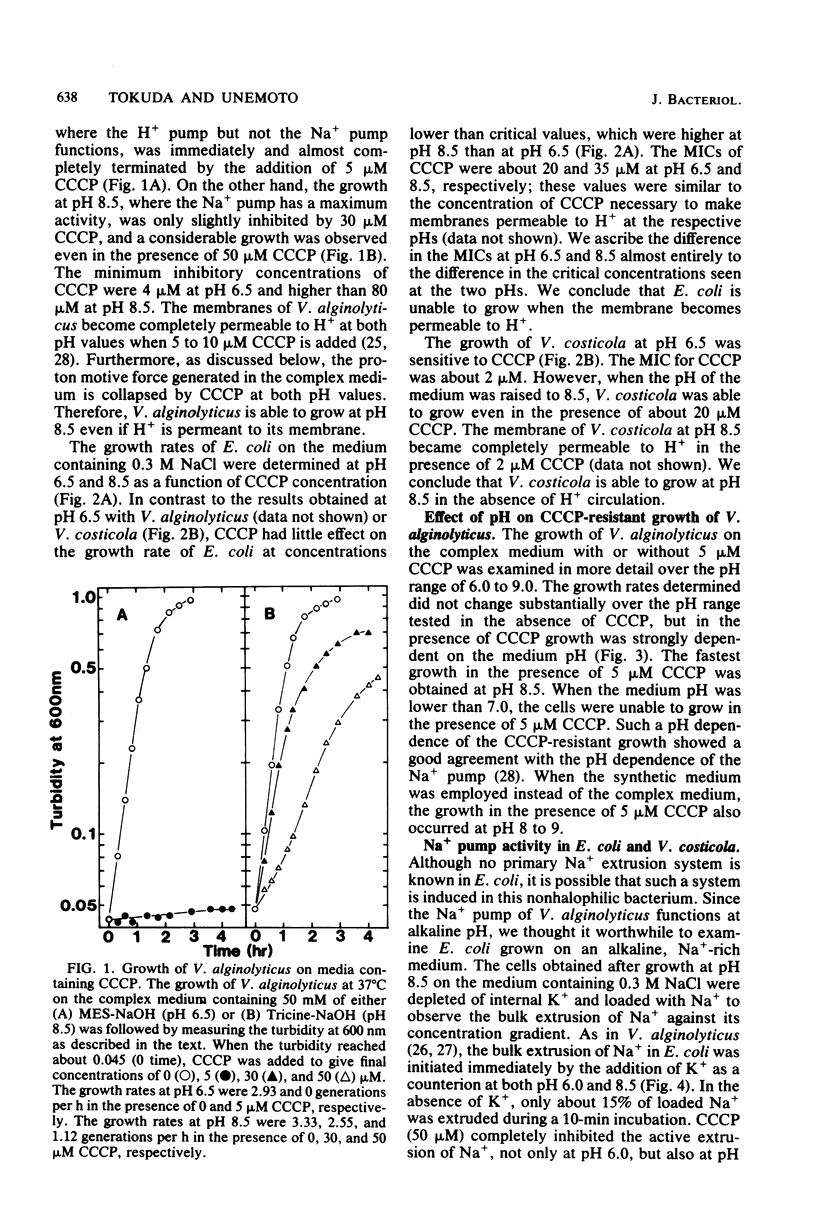
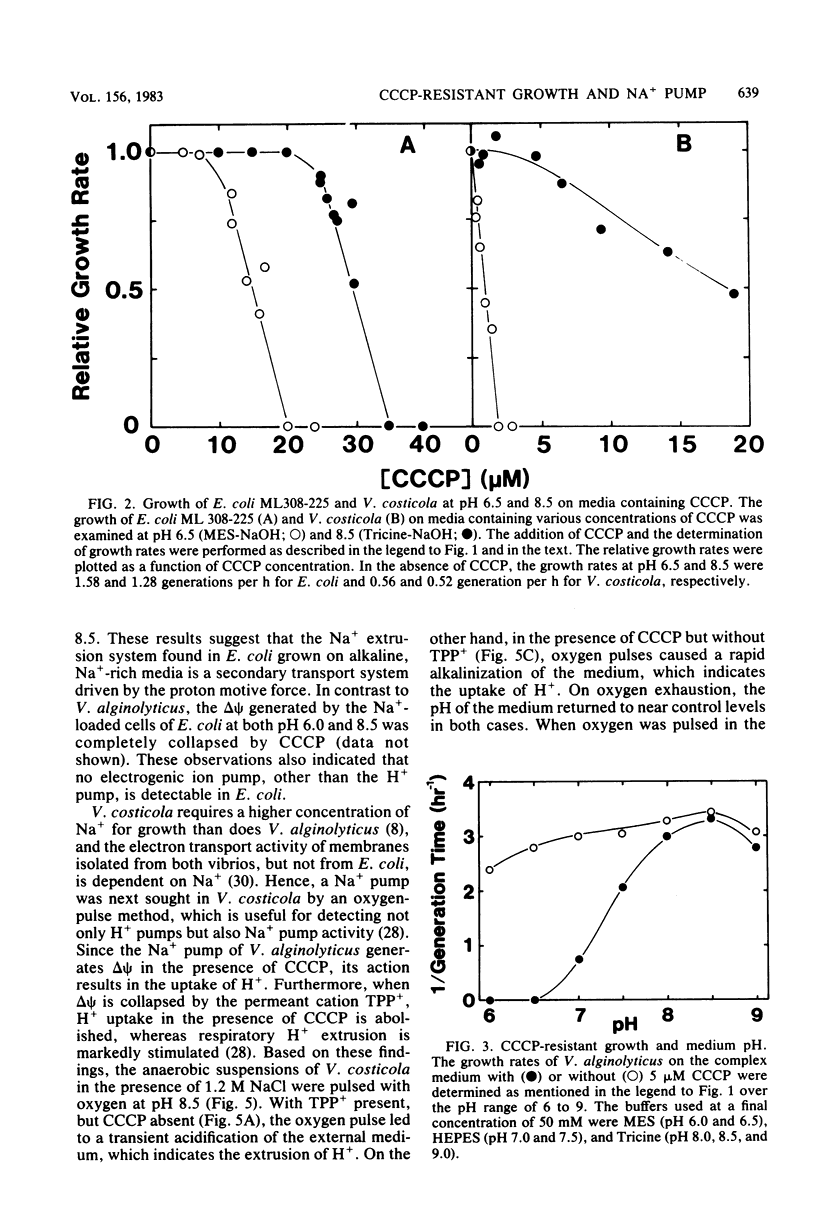
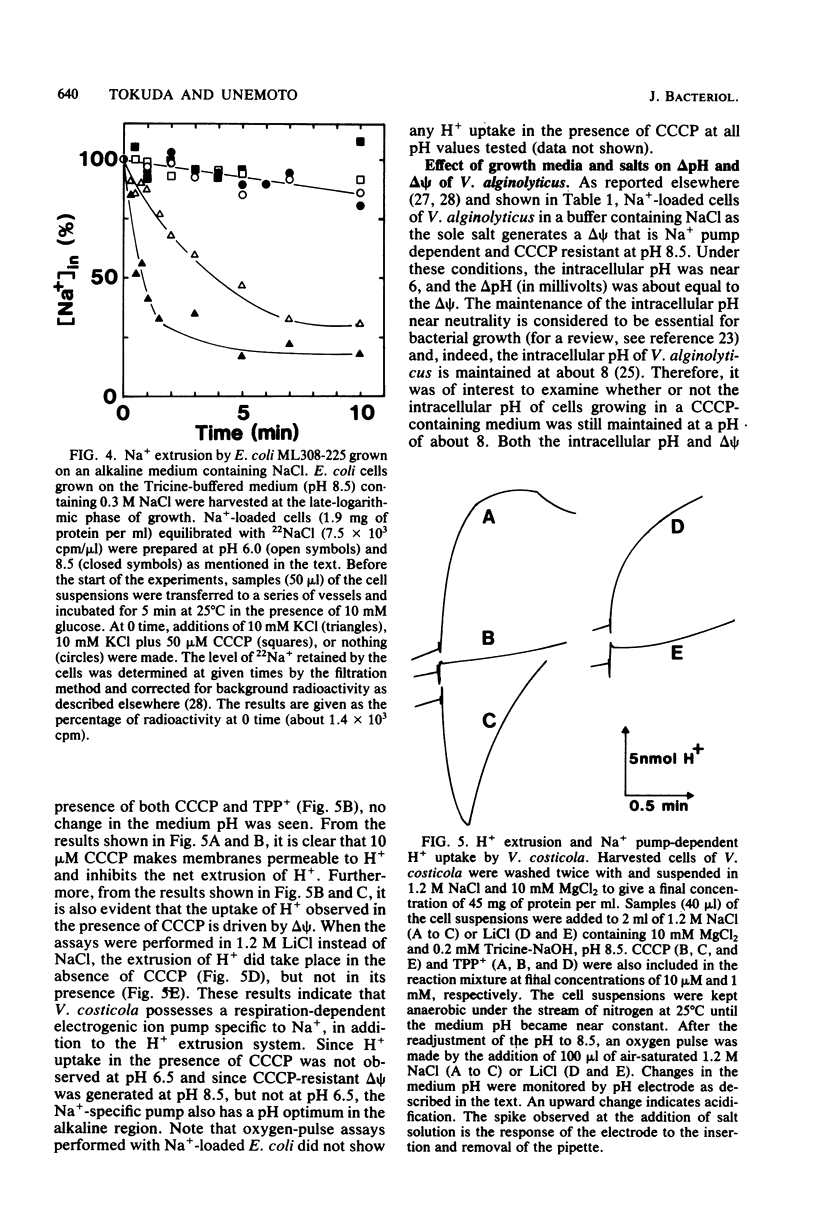
The growth of Vibrio alginolyticus and V. costicola, which possess respiration-dependent Na+ pumps, was highly resistant to the proton conductor carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP), in alkaline growth media, even though the membrane was rendered permeable to H+. The pH dependence of CCCP-resistant growth was similar to that of the Na+ pump. In contrast, Escherichia coli ML308-225 showed neither Na+ pump activity nor CCCP-resistant growth, even when grown in alkaline, Na+-rich media. These results suggest that certain bacteria possess the Na+ pump and are thus able to grow under the conditions where H+ circulation across the membrane does not take place. Moreover, V. alginolyticus growing in the presence of CCCP maintains normal levels of internal K+, Na+, and H+. The Na+ pump, therefore, makes the growth of these organisms resistant to CCCP by maintaining the intracellular cation environments.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bengis-Garber C., Kushner D. J. Role of membrane-bound 5'-nucleotidase in nucleotide uptake by the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.808-815.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Lang D. R. Membrane bioenergetic parameters in uncoupler-resistant mutants of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6738–6743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Lang D. R. Mutants of Bacillus megaterium resistant to uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5936–5938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P. A new sodium-transport system energized by the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):234–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80446-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P. Reconstitution of sodium transport from purified oxaloacetate decarboxylase and phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11974–11976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimroth P. The generation of an electrochemical gradient of sodium ions upon decarboxylation of oxaloacetate by the membrane-bound and Na+-activated oxaloacetate decarboxylase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(2):443–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth M. P., Kushner D. J. Nutrition and distribution of salt response in populations of moderately halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):253–261. doi: 10.1139/m70-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Blumenfeld H., Krulwich T. A. ATP synthesis by an uncoupler-resistant mutant of Bacillus megaterium. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8416–8421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guffanti A. A., Fuchs R. T., Krulwich T. A. Oxidative phosphorylation by isolated membrane vesicles from Bacillus megaterium and its uncoupler-resistant mutant derivative. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):35–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Van Brunt J. Circulation of H+ and K+ across the plasma membrane is not obligatory for bacterial growth. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):372–373. doi: 10.1126/science.69317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Harold F. M. ATP-driven sodium pump in Streptococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2798–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Ohnishi Y. Isolation of Escherichia coli mutants which are resistant to an inhibitor of H+-ATPase, tributyltin and also to uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80623-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Ohnishi Y., Itoh S., Nishimura M. Carbonyl cyanide-m-chlorophenyl hydrazone-resistant Escherichia coli mutant that exhibits a temperature-sensitive unc phenotype. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):310–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.310-315.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J. Colicins and other bacteriocins with established modes of action. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:125–144. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecky A. L., Copeland D. P., Lusk J. E. Viability of Escherichia coli treated with colicin K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4631–4634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Performance and conservation of osmotic work by proton-coupled solute porter systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):63–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01516051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H. Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus mutants defective in the respiration-coupled Na+ pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91601-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Nakamura T., Unemoto T. Potassium ion is required for the generation of pH-dependent membrane potential and delta pH by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4198–4203. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Sugasawa M., Unemoto T. Roles of Na+ and K+ in alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport by the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):788–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. A respiration-dependent primary sodium extrusion system functioning at alkaline pH in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Unemoto T. Characterization of the respiration-dependent Na+ pump in the marine bacterium Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10007–10014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Hayashi M., Hayashi M. Na+-dependent activation of NADH oxidase in membrane fractions from halophilic Vibrio alginolyticus and V. costicolus. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1389–1395. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unemoto T., Hayashi M. Regulation of internal solute concentrations of marine Vibrio alginolyticus in response to external NaCl concentration. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Aug;25(8):922–926. doi: 10.1139/m79-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



